Let us say, we have a Map that contains,
As Key and Value pair.
Now, let us say, we want to insert a new entry,
Where Rose is the Key and Is a Flower is its corresponding Value.
Let us see in the below example.
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
int main() {
map<string, string> x =
{
{ "Five", "Is a Number" },
{ "John", "Is a Name" },
{ "C++", "Is a Language"}
};
x["Rose"] = "Is a Flower";
for (auto i : x)
{
cout << "The Key is : " << i.first << " and the Value is :" << i.second << endl;
}
return 0;
}
So, in the above code we have created a Map using braces {} and Key and Value pairs.
map<string, string> x =
{
{ "Five", "Is a Number" },
{ "John", "Is a Name" },
{ "C++", "Is a Language"}
};And initialised to the variable x.

Now, we are supposed to add a new entry to the Map. Where the Key would be Rose and the Value Is a Flower.
So, we have used the below way to add it.
x["Rose"] = "Is a Flower";
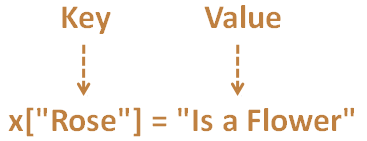
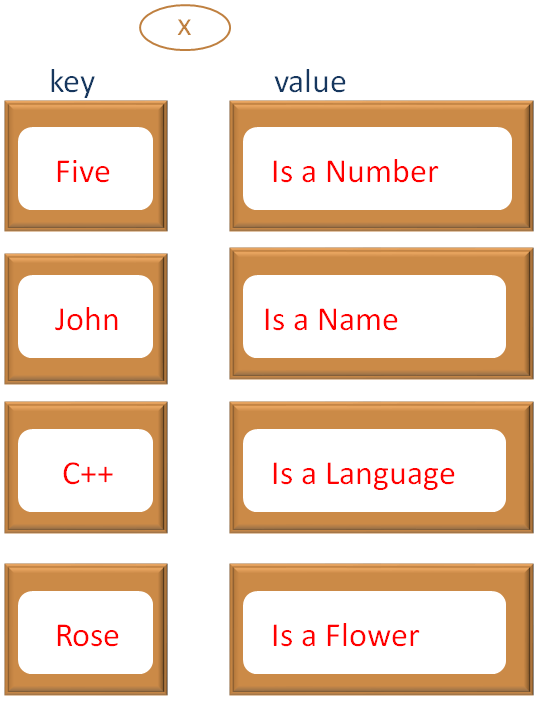
And the entry is added to the Map.
And we get the below output,
The insert() method is also used to insert a new Entry into a Map.
Let us rewrite the above example,
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
int main() {
map<string, string> x =
{
{ "Five", "Is a Number" },
{ "John", "Is a Name" },
{ "C++", "Is a Language"}
};
x.insert({"Rose", "Is a Flower"});
for (auto i : x)
{
cout << "The Key is : " << i.first << " and the Value is :" << i.second << endl;
}
return 0;
}
So, in the above code we have created a Map using braces {} and Key and Value pairs.
map<string, string> x =
{
{ "Five", "Is a Number" },
{ "John", "Is a Name" },
{ "C++", "Is a Language"}
};And initialised to the variable x.
Now, we are supposed to add a new entry to the Map. Where the Key would be Rose and the Value Is a Flower.
So, we have used the insert() method to add it.
x.insert({"Rose", "Is a Flower"});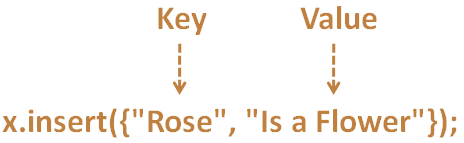
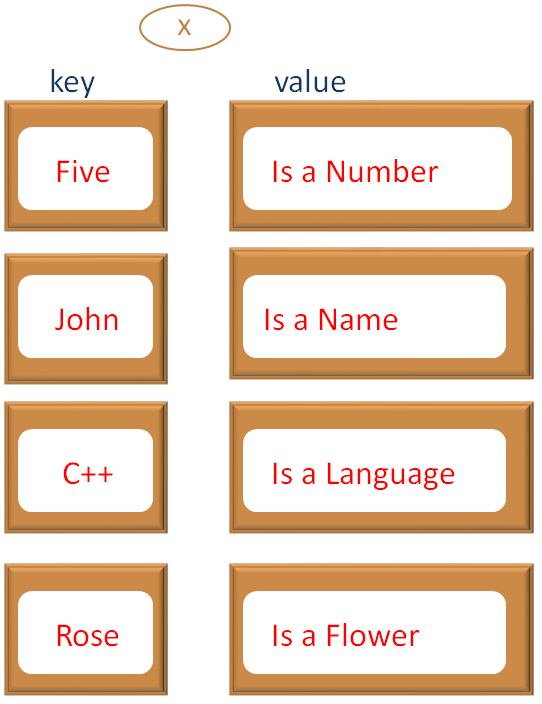
And the entry is added to the Map.
And we get the below output,
Let us say, we have a Map that contains,
As Key and Value pair.
Now, let us say, we want to insert a new entry,
Where John is the Key and Is an English Name is its corresponding Value.
Let us see in the below example.
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
int main() {
map<string, string> x =
{
{ "Five", "Is a Number" },
{ "John", "Is a Name" },
{ "C++", "Is a Language"}
};
x["John"] = "Is an English Name";
for (auto i : x)
{
cout << "The Key is : " << i.first << " and the Value is :" << i.second << endl;
}
return 0;
}
So, for the Key, John the initial value was Is a Name.
map<string, string> x =
{
{ "Five", "Is a Number" },
{ "John", "Is a Name" },
{ "C++", "Is a Language"}
};And we wanted to add a new entry with the Key as John and the Value as Is an English Name.
x["John"] = "Is an English Name";
But if we see the output.
We can see the Key, John is updated with the Value, Is an English Name.
That's because duplicate Keys are not allowed in Map. The corresponding value for that Key will get updated with the new Value.