Polymorphism by definition means many forms. Which signifies, an object can exist in different forms.
class Animal
{
public:
void breathe()
{
cout << "Breathes Oxygen." << endl;
}
virtual void sound() = 0; //Undefined so abstract
};
Now, the Cat creator God, Dog creator God e.t.c came into picture.
class Cat : public Animal
{
public:
void sound()
{
cout << "Cats Meao" << endl;
}
void catRelated()
{
cout << "It loves sleeping." << endl;
}
};
And for Dog :
class Dog : public Animal
{
public:
void sound()
{
cout << "Dog Barks" << endl;
}
void dogRelated()
{
cout << "Very obidient." << endl;
}
};
Thus, we have the below hierarchy :

So we have seen how Animal exists in various forms. Since Animal is abstract, we cannot create any object out of it. Also if you think in reality Animal does not exist. But Cat, Dog etc exists and thus we can create Cat or Dog objects.
Now, comes the most vital part. Creating Cat and Dog objects using the Animal reference. Also known as Dynamic Binding. Little tricky but used everywhere.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Animal
{
public:
void breathe()
{
cout << "Breathes Oxygen." << endl;
}
virtual void sound() = 0; //Undefined so abstract
};
class Cat : public Animal
{
public:
void sound()
{
cout << "Cats Meao" << endl;
}
void catRelated()
{
cout << "It loves sleeping." << endl;
}
};
class Dog : public Animal
{
public:
void sound()
{
cout << "Dog Barks" << endl;
}
void dogRelated()
{
cout << "Very obidient." << endl;
}
};
int main() {
Animal *animalCat;
Animal *animalDog;
Cat cat;
Dog dog;
animalCat = &cat;
animalDog = &dog;
animalCat -> sound(); // Calls the sound() behaviour of Cat.
animalDog -> sound(); // Calls the sound() behaviour of Dog.
animalCat -> breathe(); // Calls the breathe() behaviour of Animal.
animalDog -> breathe(); // Calls the breathe() behaviour of Animal.
return 0;
}
In the above code, we have seen something new. The Animal reference variable animalCat is holding a Cat object.
Now, lets dig the below line:
Animal *animalCat;
So, we are using something called as a pointer (i.e. *). A pointer is something that is going to hold an address.
So the *animalCat is a pointer type object that is expecting an address.
Sounds extremely complex ?
Let's simplify.
When we declare,
Animal *animalCat;
A space is allocated for it. Say the memory location is 100(Just suppose),

The *animalCat can only hold an address. But whose address?
Let's see.
Then we are creating a normal Cat object.
Cat cat;
Similarly a space is allocated for cat object. Say, the memory location is 1180.

Now, in the next line, we are taking the address of cat object using the & operator
animalCat = &cat;
And the address of cat gets assigned to animalCat.
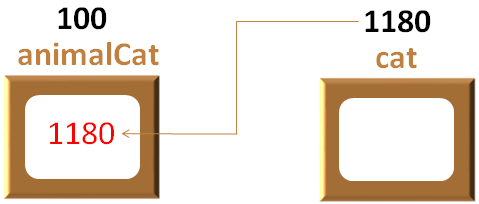
So, indirectly animalCat can access the methods of Cat class but with -> operator.
animalCat -> sound();
And we have called the sound() method of Cat.
Similarly, process is applied for Dog class as well.