An Array in Ruby is a Collection that holds multiple values, of different Data Types. And in an Array the elements are ordered (We will explain it soon), the values are changeable and allows duplicate values.
There are two ways by which you can declare an Array.
x = [5, "John", "Ruby"]
arr = Array.new(10)
Let us see the first way of creating Array, i.e. Using square brackets [].
x = [5, "John", "Ruby"] puts x
So, in the above code we have created a Array using square brackets [].
And put an Integer type value (i.e. 5) and two String type value (i.e. John and Ruby)
x = [5, "John", "Ruby"]
And initialised to the variable x.
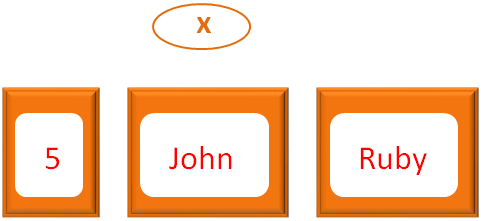
So, we can see that two different data types are assigned to a Array.
In the next line we have printed the Array using the puts statement.
puts x
Now, if we see the output,
x = [5, "John", "Ruby"] for i in x puts i end
Similarly, in the above code we have created a Array using square brackets [].
x = [5, "John", "Ruby"]
And initialised to the variable x.
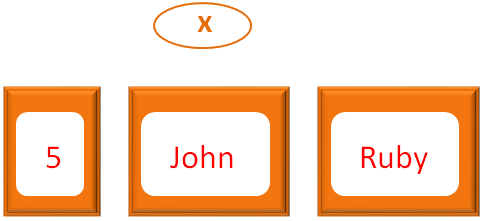
In the next line we have used the for loop to Iterate through the Array.
for i in x puts i end
Now, if we see the iterations of for loop,
for i in x
In the first Iteration the first value of the Array x (i.e. 5) is taken and put into the variable i.

And the print statement, prints the value of i.
Similarly, in the second Iteration the second value of the Array x (i.e. John) is taken and put into the variable i.
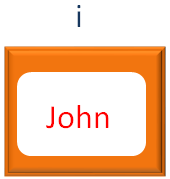
And the print statement, prints the value of i.
Similarly, in the third Iteration the third value of the Array x (i.e. Ruby) is taken and put into the variable i.
And the print statement, prints the value of i.
Now, if you see the final output. You can find that the values of the Array are displayed in the same way they were inserted.
i.e. First 5 is printed, then the name John and finally Ruby is printed.
And if you see the Array,
x = [5, "John", "Ruby"]
It is printed in the same order it was inserted. And this is why a Array is said to be Ordered.
Let us see the second way of creating an Array. i.e. Using the new method.
So far we have seen variables, which is used to store a single value. But what if we need to store 100 values?
We cannot create 100 variables. And to fill this gap Arrays came into picture.
Arrays are used to store multiple values of the same or different type.
Below is the way of declaring an array of size 10:
arr = Array.new(100)
Now, we will be asking Ruby to store numbers 1 to 10 in an array.
arr = Array.new(10)
for i in 0..9
arr[i] = i + 1
end
for i in 0..9
puts "The contents of the array are : #{arr[i]}"
end
So, in the above code, we have declared an Array to hold 10 numbers.
arr = Array.new(10)
And used the for loop to store the numbers 1 to 10 in the Array arr.
for i in 0..9 arr[i] = i + 1 end
So, 10 locations are created in the array and the numbers, 1 to 10 are stored there.

arr[0] = 1 arr[1] = 2 arr[2] = 3 arr[3] = 4 arr[4] = 5 arr[5] = 6 arr[6] = 7 arr[7] = 8 arr[8] = 9 arr[9] = 10
Similarly, we have used the next for loop to print the values of the array, arr.
for i in 0..9
puts "The contents of the array are : #{arr[i]}"
endNext, let us see, how to access the elements of the Array in the next tutorial.