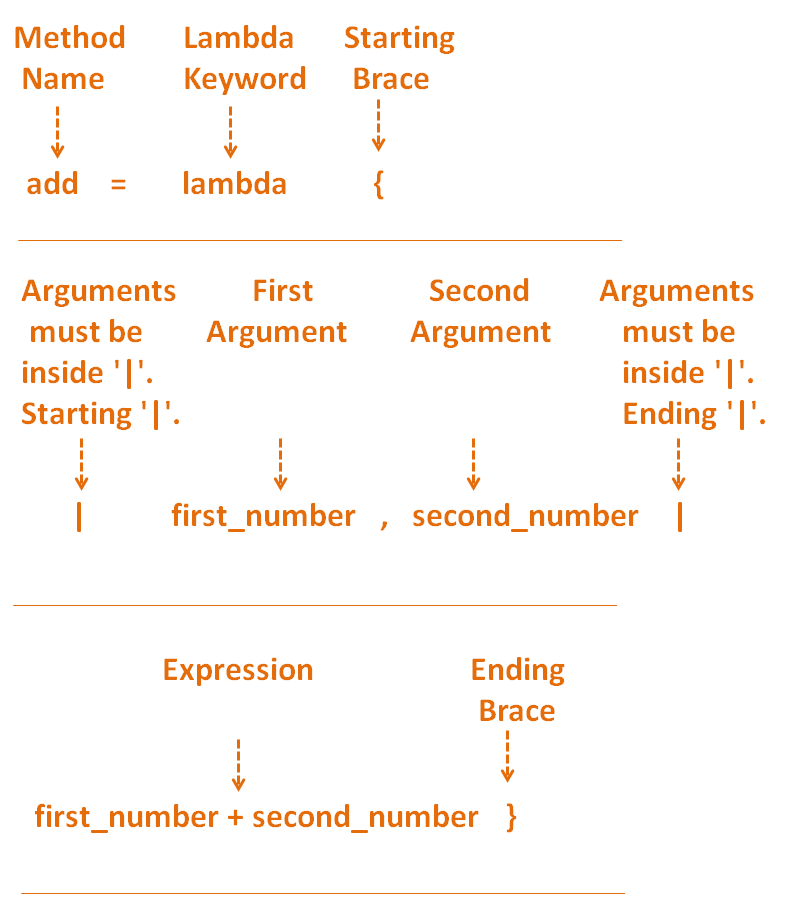
A Lambda or Anonymous Method is a small one liner Method that can just have only one expression.
Let us write the Method that adds two numbers and returns the result.
def add(first_number, second_number): result = first_number + second_number return result
Now, let us write, exactly same Lambda or Anonymous Method for the above add Method.
add = lambda { |first_number, second_number| first_number + second_number}And we are done.
Let us see the below example with to add two numbers using Lambda or Anonymous Method.
add = lambda { |first_number, second_number| first_number + second_number}
first_num = 5
second_num = 4
value = add.(first_num, second_num)
puts "The added result is #{value}"
So, in the above code the execution of the program starts from the second line. As add is a Method(i.e. A Lambda)

So, we have the variables, first_num and second_num for addition of two numbers.
first_num = 5 second_num = 4

And in the next line, we call the Lambda or Anonymous Method. Well! Since Lambda is a special kind of Method, we need to have a separate way to call it.
value = add.(first_num, second_num)
The Lambda or Anonymous Method is called using a dot .. i.e. Between the method name and parameters, there should be a ..

And the method is called,
add = lambda { |first_number, second_number| first_number + second_number}Then the Lambda or Anonymous Method is executed, adding two numbers and returning the added result.
And the added result is printed.
The added result is 9
A Lambda Method can be used in the return statement of a Method.
To understand the use of Lambda Method in return statement. Let us try to corelate with another example.
Let us, say, we have a first Method, whose return statement calls another Method.
Let us make it a little simpler with the below example.
def second_fun(p, q) return p*q end def first_fun(n) return second_fun(5, n) end i = first_fun(2) puts i
So, in the above example we have two Methods,
So, at first, we have called the first Method def first_fun(n) passing the value 2 as argument.
i = first_fun(2)
And the execution of the Method def first_fun(n): begins,
def first_fun(n) return second_fun(5, n) end
Now, the value of n is 2 as 2 is passed as an argument.
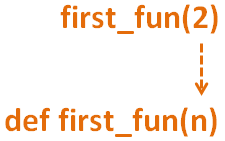
Then in the return statement, we have done something different,
return second_fun(5, n)
We have called the second Method def second_fun(p, q) from the return statement.
So, the value won't be returned. And will be waiting until the execution of second Method def second_fun(p, q) is over.

And the control goes to the second Method def second_fun(p, q) and its execution starts.
def second_fun(p, q) return p*q end
And the first argument (i.e. 5) and the value of n (i.e. 2) is passed to the second Method as argument.
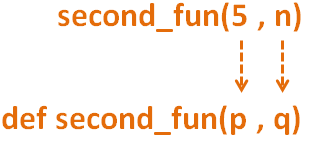
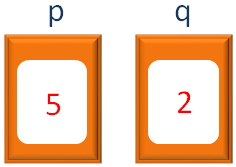
And the value of p and q is 5 and 2.
Then in the next line, we return values of p and q, multiplying them(i.e. p*q).
return p*q
So the returned value of the second Method, def second_fun(p, q) is return p*q i.e. 10.
second_fun(p, q) --- 10
Now, the control comes to the return statement of the First Method, def first_fun(n) that was unfinished.

And substitute the value of second_fun(x, n) with 10(Since that is the return value of the second Method).

And the returned value of the the First Method, def first_fun(n): is 2.
i = first_fun(2)
Which gets assigned to i. And the print statement.
puts i
Prints the value of i.
Now, let us rewrite the same example using Lambda Method.
def first_fun(n)
return lambda { | p | p * n }
end
i = first_fun(2)
puts i.(5)
So, in the above example, we have replaced the entire second Method,
def second_fun(p, q) return p*q end
With the Lambda Method in the return statement,
lambda { | p | p * n }Now, if we see the above example,

The call to the first Method def first_fun(n): is made,
i = first_fun(2)
And the first Method def first_fun(n): gets executed,
def first_fun(n):
return lambda { | p | p * n }And in the return statement, Lambda Method does a lot in a single line.
return lambda { | p | p * n }
p * n
i = first_fun(2)
Now, just remember, i is a Method that represents Lambda Method.

Next, we make a call to the Lambda Method using i passing the value of n in the argument of i.
i.(5)
And the value of n is substituted with 5, i(5) = 2*5 = 10.

And the print statement,
puts i.(5)
Prints 10 as output,