A Fibonacci Series is generated by by adding the previous number of the sequence with the current number to generate the next number in the sequence.
Let us see the first six numbers of the Fibonacci Series.
Let us look at the below example to print first 6 numbers in the Fibonacci Series.
previous = 0
current = 1
print(previous)
print(current)
for i in range(4):
temp = current
current = previous + current
previous = temp
print(current)
So, in the above code, we have initialised the variables 'previous' and 'current' with '0' and '1' as those are the first two elements by default.
And we have printed '0' and '1' initially.
So, we have printed the first two elements of the Fibonacci Series. And to print the rest 4 elements of the Fibonacci Series, we get into the 'for' loop.
for i in range(4):
temp = current
current = previous + current
previous = temp
print(current)
Let us see the Iterations of the 'for' loop.
In the first Iteration, we have stored the 'current' value (i.e. '1') in a temporary variable 'temp'.

Then we add the 'current' and 'previous' value.
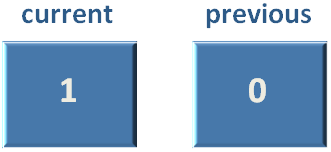
And the new value of 'current' becomes '1 + 0 = 1',

Then in the next line, we take the value of 'temp' and put in 'previous'.

And the print statement inside the loop prints the value of 'current'(i.e. The next value of the sequence, '1').
Then starts the second Iteration.
Similarly, in the second Iteration, we have stored the 'current' value (i.e. '1' again) in the temporary variable 'temp'.

Then we add the 'current' and 'previous' value.

And the new value of 'current' becomes '1 + 1 = 2',

Then in the next line, we take the value of 'temp' and put in 'previous'.

And the print statement inside the loop prints the value of 'current'(i.e. The next value of the sequence, '2').
Similarly, in the third Iteration, we have stored the 'current' value (i.e. '2') in the temporary variable 'temp'.

Then we add the 'current' and 'previous' value.

And the new value of 'current' becomes '1 + 2 = 3',

Then in the next line, we take the value of 'temp' and put in 'previous'.

And the print statement inside the loop prints the value of 'current'(i.e. The next value of the sequence, '3').
Similarly, in the fourth Iteration, we have stored the 'current' value (i.e. '3') in the temporary variable 'temp'.

Then we add the 'current' and 'previous' value.

And the new value of 'current' becomes '3 + 2 = 5',

Then in the next line, we take the value of 'temp' and put in 'previous'.

And the print statement inside the loop prints the value of 'current'(i.e. The next value of the sequence, '5').
And we are done printing all the six values in the Fibonacci Sequence.