-
findall( ) Function
We have already seen the findall( ) Function in the earlier examples.
The findall( ) Function is ued to search for a pattern and returns the result as a List.
Say for example, let us take the String,
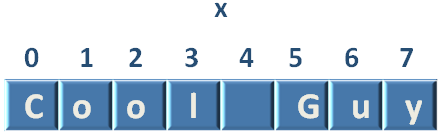
"Cool Guy"
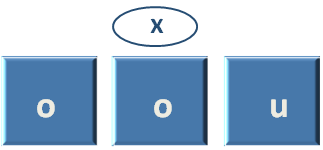
And let us say, you want to check, how many times 'o' and 'u' is there in the string?
In such case '|' Symbol is the option. Just give the option of 'u|o'(i.e. 'u' or 'o').
'u|o'
And no matter, where 'u' or 'o' is. Python finds them.
Let us see in the below example,
Example :
import re
str = "Cool Guy"
x = re.findall("u|o", str)
print("The string is :",x)
if x:
print("Found a match")
else:
print("Did not find a match")
Output :
The string is : ['o', 'o', 'u']
Found a match
So, in the above example, we have checked, how many times 'o' and 'u' is there in the string?
And we have used the 'findall( )' Function to find the results.
x = re.findall("u|o", str)
And Python checks the actual String,
And finds that there is a word, 'Cool' has two 'o's and the word, 'Guy' has one 'u'.
Now, if you see the output,
The string is : ['o', 'o', 'u']
So, the 'findall( )' Function had returned the List 'x' has three items in it. i.e. 'o','o' and 'u'.
-
search( ) Function
search( ) Function returns a Match Object if the pattern is matched. We will see soon,what a Match Object is.
Let us take the above example and understand the 'search( )' Function.
Example :
import re
str = "Cool Guy"
x = re.search("u|o", str)
print("The Match Object is :",x)
if x:
print("Found a match")
else:
print("Did not find a match")
Output :
The Match Object is : <re.Match object; span=(1, 2), match='o'>
Found a match
So, if you see the above output, this is how a Match Object looks like.
<re.Match object; span=(1, 2), match='o'
We will see the Match Object in detail later in this tutorial.
But if we see if it did return the match or not. We can find that there is a 'match' field that returned the character 'o'.
match='o'
But what about the other 'o' and 'U'.
Well! the 'search( )' Function would just search for the first occurrence of the match.And the rest two matches would be discarded.
-
split( ) Function
split( ) Function returns the searched results as a List, splitted by the search pattern.
Let us say, we have the below String,
"Hello Beautiful World"
And we want to split the above String with respect to white space and put the pieces into a list.
i.e. There are two spaces between 'Hello' and 'Beautiful', 'Beautiful' and 'World'.
So what we want is, form a List with 'Hello', 'Beautiful' and 'World'.
Let us see in the below example:
Example :
import re
str = "Hello Beautiful World"
x = re.split("\s", str)
print("The List is :",x)
Output :
The List is : ['Hello', 'Beautiful', 'World']
So, in the above code, we have used the 'split( )' Function to split the String 'Hello Beautiful World' using a white space (i.e. '\s').
x = re.split("\s", str)
Now, if you see the below output, we got a List with 'Hello', 'Beautiful' and 'World'.
The List is : ['Hello', 'Beautiful', 'World']
-
sub( ) Function
The sub( ) Function is used to replace the searched pattern with a given text.
Let us say, we have the below String,
"Hello Beautiful World"
And we want to replace white spaces with ':'.
i.e. The new String should be,
"Hello:Beautiful:World"
Let us see in the below example:
Example :
import re
str = "Hello Beautiful World"
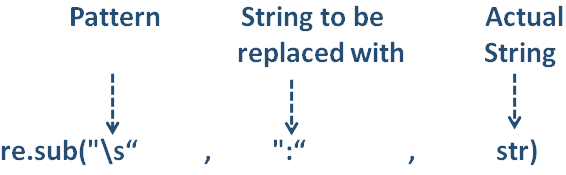
x = re.sub("\s", ":", str)
print("The new String is :",x)
Output :
The new String is : Hello:Beautiful:World
So, in the above code, we have used the 'sub( )' Function to replace white spaces with ':'.
x = re.sub("\s", ":", str)
Now, if you see the below output, we got the new String, where the spaces are replaced by ':'.
The new String is : Hello:Beautiful:World
Now, what if you want to replace just the first space with ':' and leave the second white space as is.
i.e. The new String should be,
"Hello: World"
Let us see in the below example:
Example :
import re
str = "Hello Beautiful World"
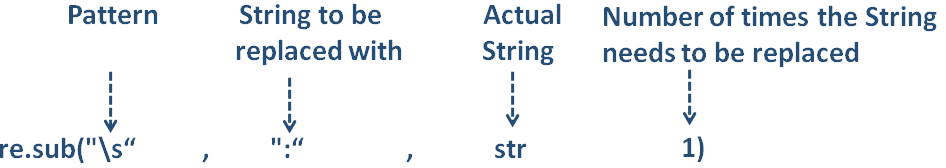
x = re.sub("\s", ":", str, 1)
print("The new String is :",x)
Output :
The new String is : Hello: World
So, in the above code, we have used the 'sub()' Function to replace white spaces with ':'.
x = re.sub("\s", ":", str)
Now, if you see the below output, we got the new String, where the spaces are replaced by ':'.
The new String is : Hello:Beautiful World
-
subn( ) Function
subn( ) Function is exactly similar to sub( ) Function with an added feature. i.e. The subn( ) Function returns a tuple that contains the replaced string and the number of times the replacement is made.
Let us say, we have the below String,
"Hello Beautiful World"
And we want to replace white spaces with ':'.
i.e. The new String should be,
"Hello:Beautiful:World"
Also, we want to check, how many spaces were replaced with ':'
Let us see in the below example:
Example :
import re
str = "Hello Beautiful World"
x = re.sub("\s", ":", str)
print("The new String is :",x)
Output :
The new String is : ('Hello:Beautiful:World', 2)
Now, if you see the below output, we got the new String, where the spaces are replaced by ':'. And since the white spaces were replaced 2 times. We got a tuple with the replaced String and the number of times the white spaces were replaced (i.e. '2')
The new String is : ('Hello:Beautiful:World', 2)