A 'Lambda' or 'Anonymous Function' is a small one liner function that can just have only one expression.
Let us write the 'Function' that adds two numbers and returns the result.
def add(first_number, second_number):
result = first_number + second_number
return result
Now, let us write, exactly same 'Lambda' or 'Anonymous Function' for the above 'add' Function.
And we are done.

Let us see the below example with to add two numbers using 'Lambda' or 'Anonymous Function'.
add = lambda first_number, second_number : first_number + second_number
first_num = 5
second_num = 4
value = add(first_num, second_num)
print("The added result is ",value)
So, in the above code the execution of the program starts from the second line. As 'add' is a 'Function'(i.e. A Lambda)

So, we have the variables, 'first_num' and 'second_num' for addition of two numbers.

And in the next line, we call the 'Lambda' or 'Anonymous Function'.
The 'Lambda' or 'Anonymous Function' call is just like any other Function call. And the 'Lambda' Function call is made.
And the 'Lambda' or 'Anonymous Function' is executed, adding two numbers and returning the added result.
We have explained the details of 'Lambda' or 'Anonymous Function'.
And the added result is printed.
A 'Lambda' Function can be used in,
At First let us see, how a 'Lambda' Function can be used in a Function Argument.
x = [(4, 'Cal'), (3, 'Ali'), (2, 'Daniel'), (1, 'Bose')] x.sort(key=lambda x: x[1]) print(x)
So, in the above example, we have used 'Lambda' in the argument of 'sort( )' Function.
So, we have created a List with four tuples inside it.

Then we have used the 'sort( )' Function to sort the List.
And put the 'Lambda' Function as a value to the 'key' (i.e. 'key=lambda x: x[1]'), such that the sorting happens with the second element of the Tuple (i.e. 'Cal', 'Ali', 'Daniel' and 'Bose') inside the List.

And the print statement,
Prints the sorted List.
To understand the use of 'Lambda' Function in return statement. Let us try to corelate with another example.
Let us, say, we have a first Function, whose return statement calls another Function.
Let us make it a little simpler with the below example.
def second_fun(p, q):
return p*q
def first_fun(n):
return second_fun(5, n)
i = first_fun(2)
print(i)
So, in the above example we have two Functions,
So, at first, we have called the first Function 'def first_fun(n):' passing the value '2' as argument.
And the execution of the Function 'def first_fun(n):' begins,
def first_fun(n):
return second_fun(5, n)
Now, the value of 'n' is '2' as '2' is passed as an argument.

Then in the 'return' statement, we have done something different,
We have called the second Function 'def second_fun(p, q):' from the return statement.
So, the value won't be returned. And will be waiting until the execution of second Function 'def second_fun(p, q):' is over.

And the control goes to the second Function 'def second_fun(p, q):' and its execution starts.
def second_fun(p, q):
return p*q
And the first argument (i.e. 5) and the value of 'n' (i.e. '2') is passed to the second Function as argument.

And the value of 'p' and 'q' is ''

Then in the next line, we 'return' values of 'p' and 'q', multiplying them(i.e. 'p*q').
So the returned value of the second Function, 'def second_fun(p, q):' is 'return p*q' i.e. '10'.
Now, the control comes to the return statement of the First Function, 'def first_fun(n):' that was unfinished.

And substitute the value of 'second_fun(x, n)' with '10'(Since that is the return value of the second Function).

And the returned value of the the First Function, 'def first_fun(n):' is '2'.
Which gets assigned to 'i'. And the print statement.
Prints the value of 'i'.
Now, let us rewrite the same example using 'Lambda' Function.
def first_fun(n):
return lambda p : p * n
i = first_fun(2)
print(i(5))
So, in the above example, we have replaced the entire second Function,
def second_fun(p, q):
return p*q
With the Lambda Function in the return statement,
Now, if we see the above example,

The call to the first Function 'def first_fun(n):' is made,
And the first Function 'def first_fun(n):' gets executed,
def first_fun(n):
return lambda p : p * n
And in the return statement, 'Lambda' Function does a lot in a single line.

Now, just remember, 'i' is a function that represents Lambda Function.
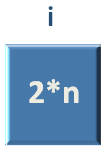
Next, we make a call to the 'Lambda' Function using 'i' passing the value of 'n' in the argument of 'i'.
And the value of 'n' is substituted with '5', i(5) = 2*5 = 10.

And the print statement,
Prints '10' as output,