Date and Time is one of the important topic in any programming language. In Ruby, there are three classes named Time, Date and DateTime to work with Date and Time.
Let us start with the Time class that provides both Time and Date.
x = Time.now() puts x
Now, if we dissect the output,
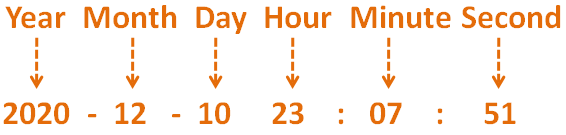
So, with the below statement,
x = Time.now()
We get a Time object, x that has Year, Month, Day, Hour, Minute, Second.
So, you got the date in clubbed format. Now, what if you want everything separately.
Well! Ruby provides that way as well.
x = Time.now()
year = x.year
month = x.month
day = x.day
hour = x.hour
minute = x.min
second = x.sec
puts "The full format is #{x}"
puts "The year is #{year}"
puts "The month is #{month}"
puts "The day is #{day}"
puts "The hour is #{hour}"
puts "The minute is #{minute}"
puts "The second is #{second}"
Now, if you look at the above output, we have separated the clubbed formatted date.
To display the year, you need to invoke x.year.
year = x.year
Similar, logic applies for Month, Day, Hour, Minute and Second.
Now, let us see how to work with Date and Time separately.
To work only with Dates. We can only import date.
Let us look at the below example.
require 'date'
date = Date.today()
puts "Today's date is #{date}"
So, in the above example, we have just imported the date.
require 'date'
Next, we have invoked the Method today() of date class to get today's date.
date = Date.today()
And if you see the output.
Today's date is 2020-12-10
Only the date is displayed and not the time.
Next, let us see, how to work with time.
Similarly, to work only with Time. We can only import the time module.
x = Time.new
t = x.strftime("%H:%M:%S")
puts t
So, in the above example, we have used the localtime() Method from the time module and got the unformatted time in the variable x.
x = time.localtime()
Then we have used strftime() Method to format the String.
t = time.strftime("%H:%M:%S", x)Where %H stands for Hour,
%M stands for Minute,
And %S stands for Second.
And we get the time in Hour, Minute and Seconds.
20:09:46
strftime() Method itself needs an explanation. Let us look at it next.
To work with Date and Time and to format it properly. There is a Method called strftime().
In Time class it takes one argument and you can format the date and time in the way you want to.
Let us look at it in the below example.
x = Time.new
t = x.strftime("%d-%B-%Y")
puts t
As we have seen earlier, with the below statement.
x = Time.new
We get a Time object, x that has Year, Month, Day, Hour, Minute, Second and Microsecond.
Then we have used the strftime() Method to display the date in a proper format.
t = x.strftime("%d-%B-%Y")Where the formats,
%d is to display the day.
%B is to display the Month
%Y is to display the Year.
And we get the date in the below format,
10-January-2021
Now let us see all the formats available for strftime() Method.
| Directive | Meaning | Represented as |
|---|---|---|
| %y | Short Version for Year | 21 |
| %Y | Full Version for Year | 2021 |
| %H | Hour | 00-23 |
| %I | Hour | 00-12 |
| %p | AM/PM | AM/PM |
| %M | Minute | 00-59 |
| %j | Day number in a year | 001-366 |
| %U | Week number in a year. Sunday is the first day of week. | 00-53 |
| %W | Week number of year. Monday is the first day of week. | 00-53 |
| %c | Date and Time | Sun Jan 10 20:38:00 2021 |
| %x | Date | 01/10/21 |
| %X | Time | 20:38:00 |
| %S | Second | 00-59 |
| %f | Microsecond | 000000-999999 |
| %z | UTC offset | +0100 |
| %a | Short form of Weekday | Sun |
| %A | Full form of Weekday | Sunday |
| %w | Weekday in number | 0-6, 0 is Sunday |
| %d | Day of month | 01-31 |
| %b | Name of the Month in Short | Jan |
| %B | Name of the Month in Full | January |
| %m | Month in the form of number | 01-12 |
| %Z | Timezone | CST |