A Method in C# is a chunk of Code that is used to conduct a particular task. And that chunk is only executed when it is called.
Say if you want to add two numbers, you can have an add Method that would be dedicated to add the numbers.
Similarly, if you want to divide two numbers, you can have a divide Method that would divide the numbers.
So, instead of placing all the codes in a single place. You can distribute the work among different Methods. So, that your code looks more structured and clean.
Below are the rules to create a Method :
Below is how an add method would look like:
int add(int firstNumber, int secondNumber)
{
int result;
result = firstNumber + secondNumber;
return result;
}And thats how we define a Method.
But it was mentioned in the Method description that a Method only executes only when it is called.
So, how a Method is called?
Let us see in the below example.
public class MyApplication
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
myMethod();
}
static void myMethod()
{
System.Console.WriteLine("This is my first method");
}
}
So, in the above code, there are two parts,
static void myMethod()
{
System.Console.WriteLine("This is my first method");
}myMethod();
So, in the above code we have defined a Method, myMethod(). You can give any name to the Method(In this case we have given the name myMethod()).
static void myMethod()
{
System.Console.WriteLine("This is my first method");
}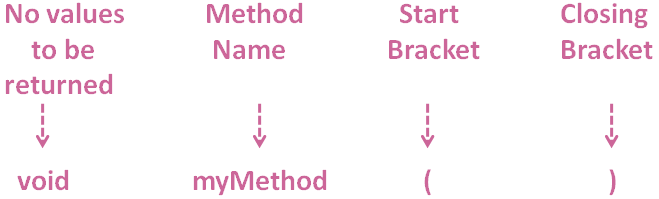
And the work of the Method, myMethod() is, just to print This is my first method.
Now, just remember one thing, the above Method, myMethod() will never execute until it is called.
And thus we have called the Method, myMethod() from Main() method.
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
myMethod();
}And the Method, myMethod() is called,
static void myMethod()
{
System.Console.WriteLine("This is my first method");
}We have placed static in the method definition because it is called from Main() method. And Main() method is static.
public static void Main(string[] args)
For now just remember that if any method is called from a static method. That should also be static.
Now, let us look at another example of adding two numbers and returning the result using a Method.
public class MyApplication
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
int firstNum = 5;
int secondNum = 8;
int addedResult;
addedResult = add(firstNum,secondNum);
System.Console.WriteLine("The added value is : "+addedResult);
}
//Add method starts here.
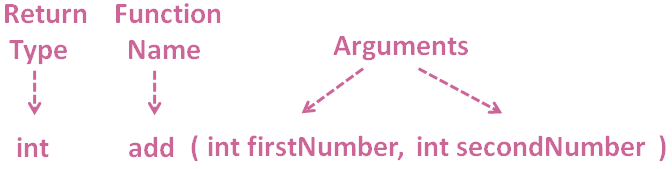
static int add(int firstNumber, int secondNumber)
{
int result;
result = firstNumber + secondNumber;
return result;
}
}
Let us explain the above example with a practical scenario.
Say you are given a task of adding two numbers. And you would follow the below steps to achieve it :
static int add(int firstNumber, int secondNumber)
result = firstNumber + secondNumber;
return result;

So far, we have seen how a Method works. Now, let us see who is the caller?
When the program execution begins,

And we initialise the first variable firstNum with the value 5.
int firstNum = 5;

Then in the next line, we have initialised the second variable secondNum with the value 4.
int secondNum = 8;

Then we call the add(int firstNumber, int secondNumber) Method.
addedResult = add(firstNum,secondNum);
And C# searches for a Method with two arguments.
When it finds the Method, it assigns the value of firstNum to firstNumber and secondNum to secondNumber. And expects a value in return.


And gets into the block of the int add(int firstNumber, int secondNumber) Method.
This is where the numbers are added,
result = firstNumber + secondNumber;
And the result is stored in a variable result.

And in the next line we return the added value(i.e. result).
return result;
And the returned value goes back to the line, where the Method was called.
addedResult = add(firstNum,secondNum);
And the variable value gets the added result(i.e. 13) from the variable result.

And in the next line the added value is printed as output.
System.Console.WriteLine("The added value is : "+addedResult);