Say, you want to create a Function to add two numbers and want that add Function to be used by every other programmer, who wants to use it.
And this is where a Import comes into picture.
Let us take the below scenario and understand Import statement.
Say we have a Kotlin Function defined in a separate Kotlin file and we want to use that Function in our main application.
Let us explain it with the below example.
fun addition(x: Int, y: Int): Int {
var z: Int = x + y
return z
}
import addition
fun main(){
var a = 10
var b = 11
var c = addition(a, b)
println("The added result is "+ c)
}
So, in the above code, we have created a Function called fun addition(x: Int, y: Int): Int, that takes two values as Arguments(i.e. x and y). And returns the added result z.
fun addition(x: Int, y: Int): Int {
var z: Int = x + y
return z
}Then we have saved it in a file and named it add.kt.
Our next task would be to use the addition() function in add.kt from a different Kotlin file.
For that we come to our actual application and say, named the Kotlin file as main.kt.
And the first thing we do is, import the addition Function using the import keyword. So that we can use it.
import addition
And that's it. The addition Function is ready for use.
The next thing we do is, create two variables a and b, and initialise them with 10 and 11.
var a = 10 var b = 11
Then we try adding them using the addition(x, y) Function, that is defined in the add.kt module.
var c = addition(a, b)
And the addition function gets called from the add.kt module.
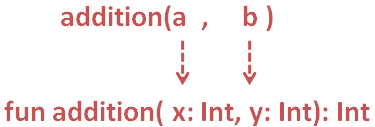
And we get the added result returned and printed.
So, to summarise, creating and invoking a Function is a three step process.
fun addition(x: Int, y: Int): Int {
var z: Int = x + y
return z
}import addition
c = addition(a, b)
So far, we have seen that we have imported Functions. But we can also have variables that can be imported. It can be a Integer or a String, a List, Map or any Collection.
Say for example, we need a Module that will have a List with three names,
names = ["John", "Sean", "Prakash"]
And an add Function that will add two numbers and return the result.
So, we can create a Module in the same way and declare a List along with a Function.
Let us see in the below example.
var names = arrayOf("John", "Sean", "Prakash")
fun addition(x: Int, y: Int): Int {
var z: Int = x + y
return z
}
import addition
import names
fun main(){
var a = 10
var b = 11
var c = addition(a, b)
println("The added result is "+ c)
var name = names[1]
println("The second name in the List is "+name)
}
So, in the above Example, we have created a file named, newaddfunction.kt.
var names = arrayOf("John", "Sean", "Prakash")
fun addition(x: Int, y: Int): Int {
var z: Int = x + y
return z
}And created a List containing three names,
var names = arrayOf("John", "Sean", "Prakash")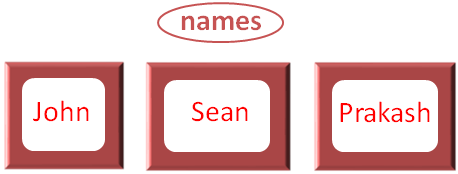
And also the module has a Function fun addition(x: Int, y: Int): Int.
fun addition(x: Int, y: Int): Int {
var z: Int = x + y
return z
}Now, in our main application, we have imported the Array and Function, names and addition.
import addition import names
Then as usual, we have called the addition(...) Function.
var c = addition(a, b)
And since, we have already imported the addition function, the addition() Function works seamlessly.
Next, we have accessed the second name of the Array names.
name = names[1]
And as we can see, the second element in the Array is, Sean. And we got it printed.
The second name in the List is Sean
Even in this case, since, we have already imported the names Array, we were able to access the names array just fine.