A 'List' is a Collection that holds multiple values, of different Data Types. And in a 'List' the elements are ordered (We will explain it soon) and allows duplicate values.
The declaration of a 'List' 'Data Type' is super easy. You can place multiple values inside the method 'listOf()' or 'mutableListOf()' and Kotlin will understand that it is a 'List'.
Using the 'listOf()' method, we can create an immutable list(i.e. A read only List).
fun main() {
var x = listOf(5, "John", "Kotlin")
println(x)
}
So, in the above code we have created a 'List' using the 'listOf()' method.
And put an Integer type value (i.e. 5) and two String type value (i.e. 'John' and 'Kotlin')
And initialised to the variable 'x'.
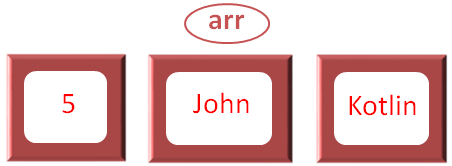
So, we can see that two different data types are assigned to a 'List'.
In the next line we have printed the 'List' using the print statement.
Now, if we see the output,
The values are enclosed inside square brackets '[]'. This means that the values are inside a List.
So, in the above code we have created a List with 2 different Datatype(i.e. String and Integer).
Now, what if we want to restrict the List to accept only a String or an Integer or a Float.
Let's see in the below example.
fun main() {
var x: List<String> = listOf(5, "John", "Kotlin")
println(x)
}
So, what we have done is, created a List with three values, '5', 'John' and 'Kotlin'.
And at the time of initialisation, we have ended up with an error.
This is because we have restricted the List to accept only values of String datatype.

And the values we are trying to use contains an integer value i.e. '5'.
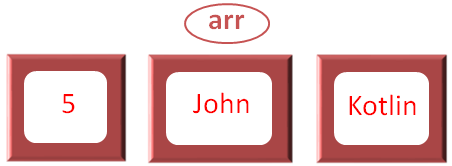
Now, let us try inserting all String values.
fun main() {
var x: List<String> = listOf("Tom", "John", "Kotlin")
println(x)
}
Now, if you look at the output. We got the correct entries printed.
So, the values are enclosed inside square brackets '[]'. This means that the values are inside a List.
Now, what if we don't want the output enclosed in square brackets '[]'.
Let us see that in the below example.
fun main() {
var x = listOf(5, "John", "Kotlin")
for (i in x) {
println(i)
}
}
Similarly, in the above code we have created a 'List' using the 'listOf()' method.
And initialised to the variable 'x'.
In the next line we have used the 'for loop' to Iterate through the 'List'.
for i in x:
print(i)
Now, if we see the iterations of for loop,
for (i in x) {
println(i)
}
In the first Iteration the first value of the 'List' 'x' (i.e. 5) is taken and put into the variable 'i'.

And the print statement, prints the value of 'i'.
Similarly, in the second Iteration the second value of the 'List' 'x' (i.e. 'John') is taken and put into the variable 'i'.

And the print statement, prints the value of 'i'.
Similarly, in the third Iteration the third value of the 'List' 'x' (i.e. 'Kotlin') is taken and put into the variable 'i'.
And the print statement, prints the value of 'i'.
Now, if you see the final output. You can find that the values of the 'List' are displayed in the same way they were inserted.
i.e. First '5' is printed, then the name 'John' and finally 'Kotlin' is printed.
And if you see the List,
It is printed in the same order it was inserted. And this is why a List is said to be 'Ordered'.
Using the 'mutableListOf()' method, we can create a mutable list(i.e. The List values can be changed/replaced).
fun main() {
var x = mutableListOf(5, "John", "Kotlin")
println(x)
}
Next, let us see, how to access the elements of the List in the next tutorial.