A String is a collection of letters/alphabets. It can be a word or a sentence.
The 'Data Type' for String is 'string'.
When Kotlin finds data inside Double Quotes (""). It creates a String type variable for that value.
fun main() {
var x = "Hello World"
println(x)
}
And that's all! You have a String in place.
Well! There are other ways using which you can create a string.
fun main() {
var x: String = "Hello World"
println(x)
}
So, in the above code, we have declared a variable 'x' of 'String' type.
So that it would not accept any other values other than a String.
Also one more advantage of declaring using a 'String' type is that you can assign the value to the String variable later.
Let us understand with the below code.
fun main() {
var x: String
x = "Hello World"
println(x)
}
Just note that we have not initialised the variable 'x'. We have just declared it.
So that an empty variable 'x' would be created that would only hold a String.

Then in the next line, we have assigned the value 'Hello World' to the variable 'x'.

Well! We have declared a String type variable and assigned it later.
But the below code won't work, if we do not specify a data type.
fun main() {
var x
x = "Hello World"
println(x)
}
So far, we have seen, how to declare a String type variable in one line.
Now, what if, we want a paragraph, separated by lines, to be assigned to a variable.
i.e. Let's say, you want to assign the below paragraph to a variable.
In such cases, you can use three double quotes ("""""").
Declaring a multiline String with three double quotes ("""""") :
fun main() {
var str = """In a huge pond,
there lived many fish.
They were arrogant
And never listened to anyone."""
println(str)
}
fun main() {
var x = "Hello"
var y = x[1]
println(y)
}
So, we have a string 'Hello',
And we have assigned 'Hello' to a variable 'x'.

Let us elaborate more, on how the String 'Hello' is stored in the variable 'x'.
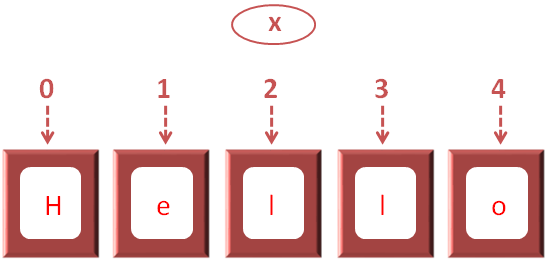
So, just for the sake of understanding, you can assume the variable 'x' is divided into '5' parts to store 'Hello'.
Now, if you check from the front, the count starts from '0' and ends with '4'.
So, if we look at the next line in the code,
We are trying to access the 2nd location,
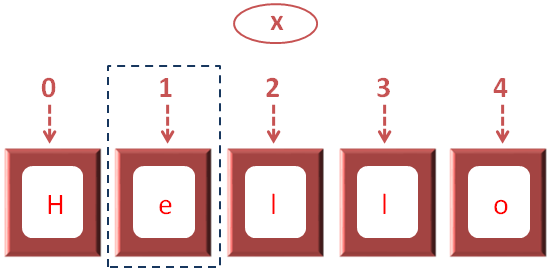
So, 'x[1]' is referring to the 2nd location where 'e' is stored.
And we have assigned 'e' to the variable 'y'.

Now, if you look at the print statement,
The value of 'y' is printed as output.
In the earlier examples, we have seen the '+' sign. And as we know, '+' is used for addition of two numbers.
Well! In Kotlin, '+' can be used to join two Strings as well.
Say, we have two Strings, 'Hello' and 'World'. And we want to join/concatenate them into one String, 'HelloWorld'.
Let us solve it with the below example.
fun main() {
var x = "Hello"
var y = "World"
var z = x + y
println(z)
}
So, we have stored the String 'Hello' in 'x'.
And, stored the String 'World' in 'y'.
And used the '+' operator to join/concatenate 'Hello' and 'World'.
And store the concatenated value in 'z'.

So, '+' is not just used to add two numbers but '+' is also used to join/concatenate two Strings.
But we cannot use the '+' operator to join/concatenate a number and a String.
i.e. The below code will result into an error.
fun main() {
var x = 5
var y = "World"
var z = x + y
println(z)
}
And as said it ended up with an error.
Now, what if, you wish to repeat a string a few number of times.
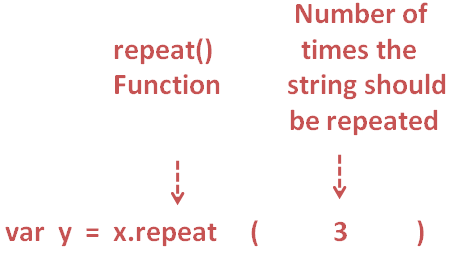
To repeat a String a few number of times, Kotlin provides us with a Function called 'Repeat()' that repeats a string a few number of times.
Let us see the below example.
fun main() {
var x = "Hello"
var y = x.repeat(3)
println(y)
}
So, if you see the output. The statement,
Repeats the String 'Hello' three times.
Next, let us see how to Iterate through the values of a String.
fun main() {
var x = "Hello"
for (i in x) {
println(i)
}
}
So, in each Iteration of 'for loop',
The values are taken from the variable 'x', one by one and put in the variable 'i'.
And values are printed at each Iteration.
Now, let us look at a scenario, where you need to find out, if a particular letter or a chunk of letters is present in the string or not.
Let us check, if the substring 'el' is present in the String 'Hello' or not.
To achieve it, Kotlin provides a function called 'Contains()' that checks if a substring is present in a string or not.
fun main() {
var x = "Hello"
if (x.contains("el")) {
println("The sub-string, el is present in the String, Hello")
} else {
println("The sub-string, el is not present in the String, Hello")
}
}
So, to check if the substring 'el' is present in the String 'Hello', we have used the 'contains()'function with 'if' statement.
Say, you have stored a number in a variable and you want to insert it in the middle of a String.
i.e. Say, you have two numbers '3' and '4' and you have added them and want to display the result in the following way,
Well! We can achieve it using String formatting.
Let us rewrite the above example using the String Template Operator '$'.
fun main() {
var x = 3
var y = 4
var z = x + y
println("The added value of $x and $y is $z")
}
Now, if you look at the output,
The variables of 'x', 'y' and 'z' is replaced with the actual values i.e. '3', '4' and '7'.
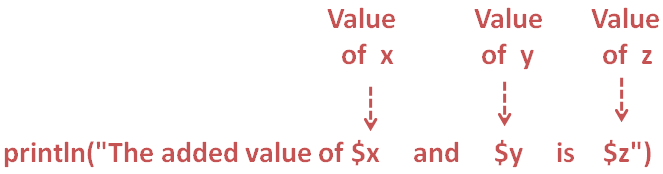
We can also achieve the above using String formatting.
Let us rewrite the above example using the String Formatting Operator '%'.
fun main() {
var x = 3
var y = 4
var z = x + y
var result = "The added value of %d and %d is %d"
println(result.format(x, y, z))
}
Now, if you look at the output,
You can see that '%d' is replaced with the actual values of the variables.
Similarly, we can use other placeholders for all types of data.
Below is the List :
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| d, i, u | Decimal Number |
| x, X | Hexadecimal Number |
| o | Octal Number |
| f, F | Floating Point Number |
| e, E | Exponential Number |
| g, G | Floating point/Exponential |
| c | Single character |
| s, r, a | String |
'length' keyword is used to return the length of a String.
fun main() {
var x = "Hello"
println("The length of the String is : "+x.length)
}
Next, let us look at the Functions provided by Kotlin to handle Strings more effectively.