public class MyApplication
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String x = "Hello";
char y = x.charAt(1);
System.out.println(y);
}
}
So, we have a String Hello,
String x = "Hello";
And we have assigned Hello to a variable x.

Let us elaborate more, on how the String Hello is stored in the variable x.

So, just for the sake of understanding, you can assume the variable x is divided into 5 parts to store Hello.
Now, if you check from the front, the count starts from 0 and ends with 4.
So, if we look at the next line in the code,
char y = x.charAt(1);
We are trying to access the 2nd location,
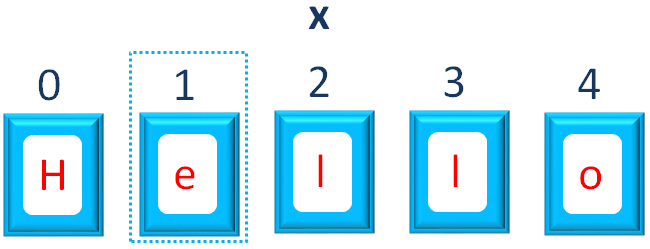
So, x.charAt(1) is referring to the 2nd location where e is stored.
char y = x.charAt(1);
And we have assigned e to the variable y.

Now, if you look at the print statement,
System.out.println(y)
The value of y is printed as output.