So far we have seen variables, which is used to store a single value. But what if we have to store 100 values?
We cannot just create 100 variables.
And to fill this gap arrays came into picture.
An Array is a Data Structure that holds multiple values, of different Data Type.
The declaration of a Array is super easy.
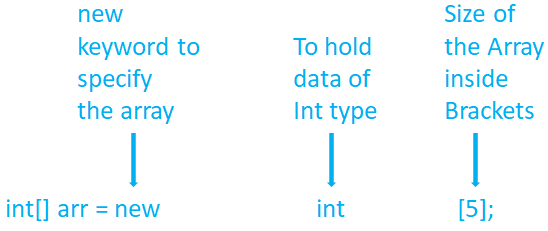
Below is the way of declaring an Int array of size 5:
int[] arr = new int[5];
The syntax is quite simple.
To create an Array, you need to tell Java that the variable arr is going to hold an Array.
int[] arr = new int[5];
So, in the next example, we will be asking Java to store the numbers 1 to 5 in an array.
public class MyApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = new int[5];
for (int i = 0; i <= 4; i++) {
arr[i] = i + 1;
}
for (int i = 0; i <= 4; i++) {
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
}
}
So, in the above code, we have declared an Array arr that is going to store the values from 1 to 5.
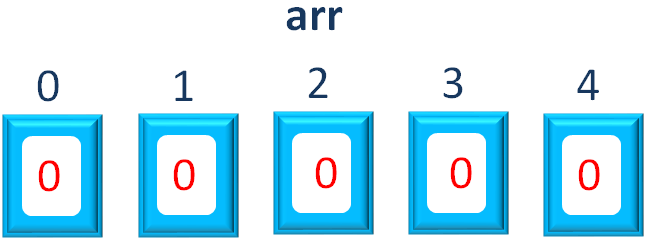
As we have seen above, the first line declares an array, arr that would store 5 numbers.
int[] arr = new int[5];
Now, internally what happens is, 5 empty locations are created with indexes from 0 to 4 and all are initialised with 0.
Then we have used the for loop to insert the numbers from 1 to 5 in each Iteration
for (int i = 0; i <= 4; i++)
{
arr[i] = i + 1;
}So, in the first Iteration of for loop, the value of i is 0.

And we use this i as index to access the first location of the array.
Accessing array elements is quite simple. Just put the index (i.e. i) inside square brackets, [] and you can access that element.
arr[i] = i + 1;
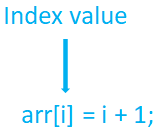
And what happens is, the value from the right hand side (i.e. i+1 or 0+1 or 1) gets assigned to the first array location (i.e. arr[0]).
So, internally the number 1 goes and sits inside arr[0].

Similarly, in the second Iteration of for loop, the value of i becomes 1.

And in the same way, we use this i as index to access the second location of the array.
arr[i] = i + 1;
And as we have seen, the value from the right hand side (i.e. i+1 or 1+1 or 2) gets assigned to the second array location (i.e. arr[1]).
So, internally the number 2 goes and sits inside arr[1].
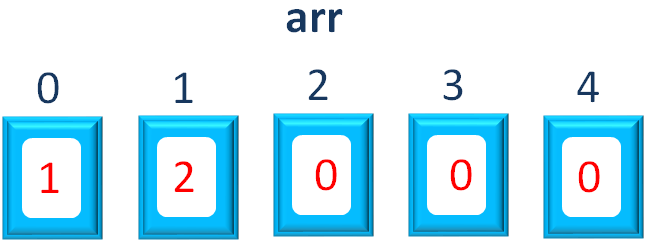
Continuing in the same way, all the numbers are assigned to all the 5 locations in the Array.

Now that we have all the 5 numbers stored in the Array. We can use another for loop to display all the numbers.
for (int i = 0; i <= 4; i++)
{
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}The above for loop picks all the numbers one by one and displays on the screen.
Declaring an Array that is going to hold 5 String/names is quite similar as creating an Array that holds numbers.
Just replace Int with String and the default value to "".
String[] arr = new String[5];
So, in the next example, we will be asking Java to store five names, Mohan, John, Paul, Kriti and Salim in the Array.
public class MyApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] arr = new String[5];
arr[0] = "Mohan";
arr[1] = "John";
arr[2] = "Paul";
arr[3] = "Kriti";
arr[4] = "Salim";
for (int i = 0; i <= 4; i++) {
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
}
}
So, in the above code, we have declared an Array arr that is going to store five names, Mohan, John, Paul, Kriti and Salim
And we have created a String Array that would be holding 5 values of String data types.
String[] arr = new String[5];
Now, internally what happens is, 5 locations are created to hold values of String type with indexes from 0 to 4.
And in the next few lines, we have assigned the names to the respective location, one by one.
arr[0] = "Mohan"; arr[1] = "John"; arr[2] = "Paul"; arr[3] = "Kriti"; arr[4] = "Salim";

Then we have used the for loop to to display the names in each Iteration
for (int i = 0; i <= 4; i++)
{
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}And we get the below output.
In the next tutorial, we will see, how to iterate the elements of the Array in a different way.