As we have seen the implementations of a List are :
Let us see the ArrayList implementation,
The Collections.sort() Method is used to sort a List in Ascending order.
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
public class MyApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List x = new ArrayList<>();
x.add("Mohan");
x.add("Kriti");
x.add("Salim");
Collections.sort(x);
for (String data : x) {
System.out.println(data);
}
}
}
So, in the above code we have created a List,
Listx = new ArrayList<>();
And initialised three names to the variable x,
x.add("Mohan");
x.add("Kriti");
x.add("Salim");Below is how the values are positioned in the List,
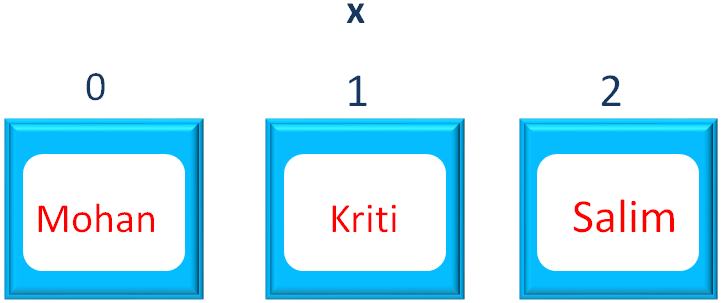
Then we have used the Collections.sort() method to sort the List x in ascending order.
Collections.sort(x);
And the List x gets sorted with Kriti as the first value, Mohan second and Salim as the third.
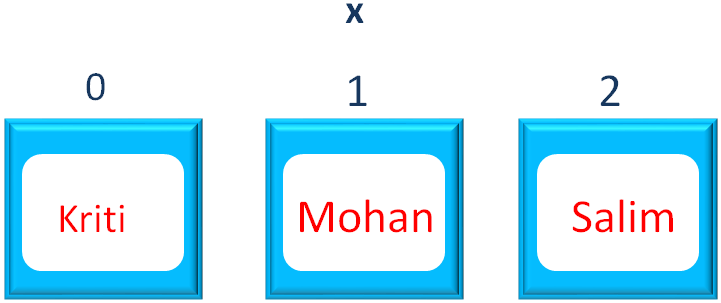
And we get the below output.
Even here the Collections.sort() Method is used to sort a List with numbers in Increasing Order.
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
public class MyApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List x = new ArrayList<>();
x.add(5);
x.add(3);
x.add(2);
x.add(4);
Collections.sort(x);
for (Integer data : x) {
System.out.println(data);
}
}
}
So, in the above code we have created a List and initialised to the variable x.
Listx = new ArrayList<>(); x.add(5); x.add(3); x.add(2); x.add(4);
Below is how the values are positioned in the List,
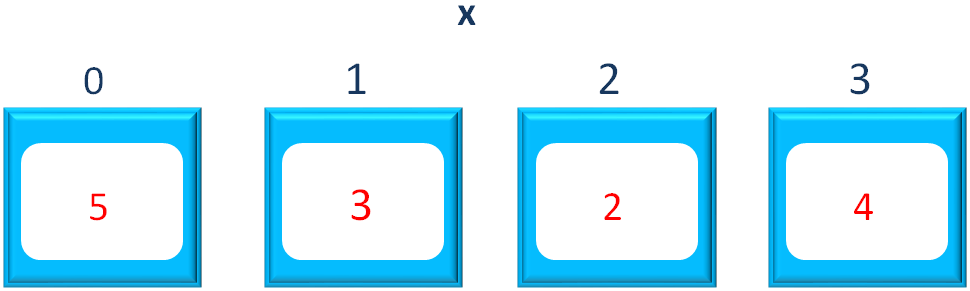
Then we have used the Collections.sort() method to sort the List x in increasing order.
Collections.sort(x);
And the numbers in the List x gets sorted.
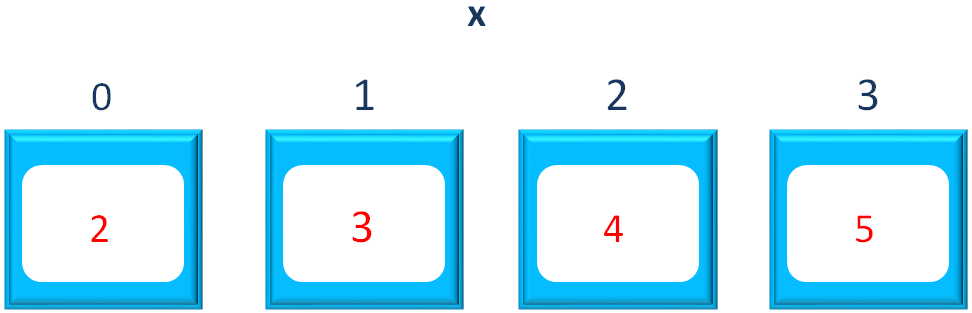
And we get the below output.