Just imagine, you are asked to enter your gmail Id and Password to login to your Gmail account. But, by mistake you have entered a wrong password. And what if, Gmail exits without giving you a second chance to enter the Password? - It is not acceptable.
Same thing applies for any application. We are allowed to make some sort of mistakes, so that we get a second chance to rectify that. Such mistakes in java are called as Exceptions.
So, the Exceptions should be handled/caught at runtime, and also the entire application should not close due to that Exception.
It is same as your Gmail account doesn't close when someone types a wrong password and at the same time Gmail needs to keep a track on how many times the user is entering a wrong Password.
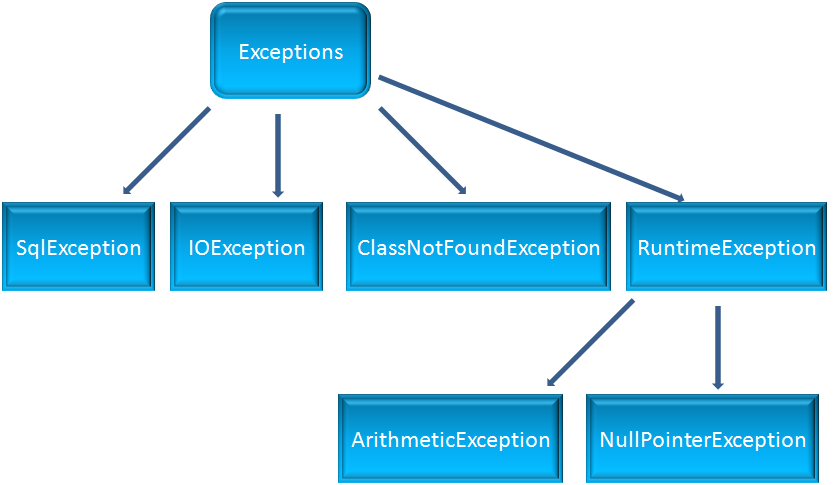
Exceptions in java are classified into two types :
1. Checked Exception
2. UnChecked Exception
There are some Exceptions in java which are bound to be checked/handled at compile time. They are called Checked Exception.
Say, for example if we are using 'Class.forName()' to create an Instance of 'Animal' class.
The above error occurred because there was no try - catch block to catch the Exception.
So, in the above example there is an error in the below line,
With the Error message :
This means, the above line should be inside a 'try' block, so that whenever an Exception happens the catch block should be able to hold that.
Let us modify the 'Main' class to see, how we can fix the error with try - catch block.
So, as stated we have put
inside the try block.
And if any Error occurs will be caught by the 'catch' block.
And, using
We will be able to display the exception.
So, ClassNotFoundException(As seen in the above example), FileNotFoundException, SQLException are a few checked Exceptions which must be handled inside a try - catch block, else will come up with compile time error.
There are some Exceptions that occurs at Runtime. These types of Exceptions are ignored by the Compiler.
A common Unchecked Exception is 'ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException'. Which occurs when you are trying to access a location of an array which doesn't actually exist.
Let us look at the below example :
So, in the above example, we are trying to access the 6th location of the array. Which doesn't actually exist. And thus we are getting the above Exception.
But there is also a line
Which doesn't gets printed. In other words the application got halted with this Exception.
After using the try - catch block. The Exception got caught in the 'try' block and is thrown to the 'catch' block. And the Exception is printed there.
And most importantly the programme execution doesn't stops but continues as usual. And as we can see the below line is printed.
There can be a scenario where a piece of code inside a try block may result in more than one Exception. And that is when we need multiple catch blocks to catch those Exceptions but only one which encounters first.
Let us look at the below example :
So, in the above case it is a Divide by Zero Exception. Which is caught in
Similarly, if there would be any Exception related to Array Index, it would be caught in
Also we have put a general catch block to handle the Exception other than the above,
The Finally block always runs, no matter if the Exception has occurred or not.
So, as we can see in the above example. The finally block executed
No matter if an Exception has occurred or not.
Errors in java are such conditions which cannot be handled. Common errors are a Memory Leak that causes a OutOfMemoryError.