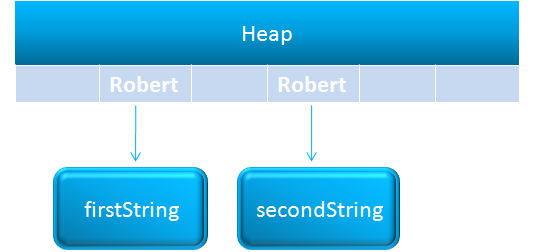
When we create a String data type using the new operator,
String firstString = new String("Robert");A memory space will be created for firstString in so called heap and the value Robert will be stored in it.
Now, if we define another String type variable secondString and assign the same value Robert to it,
String secondString = new String("Robert");Java creates a new memory space for secondString and the value Robert will be assigned to it.