In simple words it is the Constructor which is helping the object to be created.
There are two types of Constructor :
1. Default Constructor or the no argument Constructor.
2. Constructor with arguments or Parameterized Constructor.
Say we are going to create two Human objects out of the above Human class. i.e. 'John' from America and Wang Chu from China.
We have seen how to create an object of 'Human' class using 'new' keyword with the below statement :
Although 'Human()' looks like a normal java method, but it has the same name as that of the class name(i.e Human). And that is what makes is different from a method and is called as 'Constructor' which is helping the compiler to create a java object.
But the strange fact is 'Human()' is not present inside the above class. Then how is it helping the compiler to create an object?
The answer is, a constructor with no arguments is called as a default constructor. Even if you don't place it in the class, the compiler will automatically place it for you. Just wait a second, I just said a default constructor is a constructor with no arguments. So, that does mean there can be constructors with arguments. Yes, there are and we will have a detail look at it.
Lets modify the 'Human' class with constructors:
So, in the above class we have two contructors. One with no arguments(default constructor), which the compiler inserted by default in the previous 'Human' class.
And the other is the constructor with three arguments.
Lets see whats happens in the above code:

So, in the above image! name, food and language variables of human1 and human2 are not assigned any values. It is because 'human1' and 'human2' are created using the default constructor :
and no values are assigned to it.
Again let us relook at the below Image:
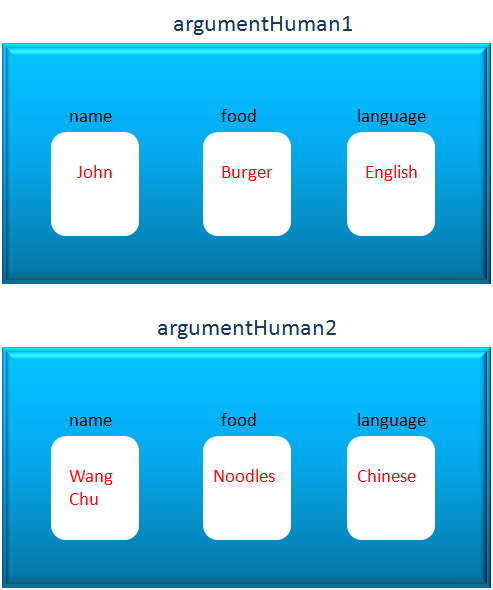
So, in the above image argumentHuman1 and argumentHuman2 contains the values we have put in the constructor with arguments.
Let's have a look at the below code :
As we have already seen argumentHuman1 is the name of the object. And on the right hand side we have 'new' which creates a new object named 'argumentHuman1'.
Now, let's see what 'Human("John","Burger","English")' does, relating with the below code(i.e constructor with arguments).
So, "John" gets assigned to 'nme', "Burger" to 'fd' and "English" to 'lang'

Now, if we see the code inside the Constructor.
The value inside nme (i.e "John") gets assigned to 'this.name', value inside 'fd' (i.e. "Burger") inside 'this.food' and the value inside 'lang' (i.e. "English") inside 'this.language'.
Similarly, 'Burger' is assigned to 'this.food', which is the 'food' property of 'Human' class and 'English' is assigned to 'language' property of 'Human' class.