As we have seen the implementations of a List are :
Let us see the ArrayList implementation first.
Let us say, we have a List that contains three names, Mohan, Kriti and Salim. And we want to insert a new List with two names Sia and Andrew at the end of the List.
In such case we can use addAll() method.
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class MyApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List x = new ArrayList<>();
x.add("Mohan");
x.add("Kriti");
x.add("Salim");
List y = new ArrayList<>();
y.add("Sia");
y.add("Andrew");
x.addAll(y);
for (String data : x) {
System.out.println(data);
}
}
}
So, in the above code we have created a List,
Listx = new ArrayList<>();
And initialised three names to the variable x,
x.add("Mohan");
x.add("Kriti");
x.add("Salim");Below is how the values are positioned in the List,
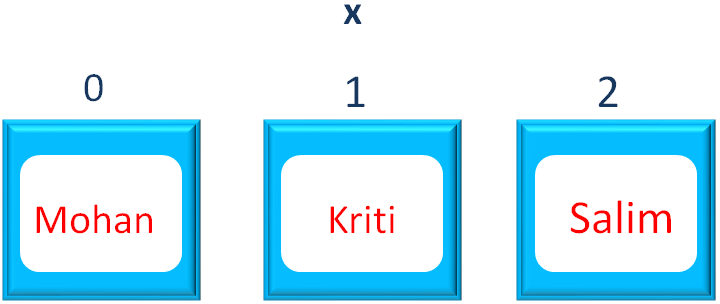
Also we have another List that contains, Sia and Andrew.
Listy = new ArrayList<>(); y.add("Sia"); y.add("Andrew");

Next, we have used the addAll() method to add the new List y that contains Sia and Andrew at the end of the List x.
x.addAll(y);
And the List y is joined with x.
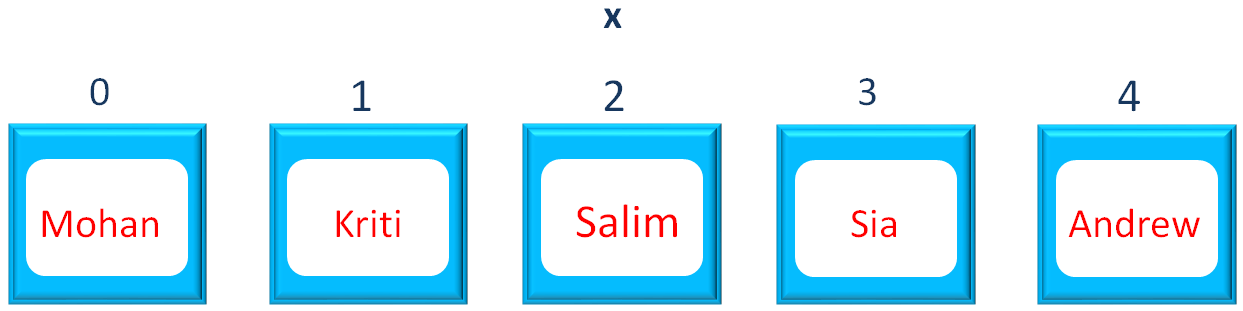
And we get the below output,
Next, let us see the implementation using LinkedList. It is exactly similar to ArrayList.
Let us say, we have a List that contains three names, Mohan, Kriti and Salim. And we want to insert a new List with two names Sia and Andrew at the end of the List.
In such case we can use addAll() method.
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
public class MyApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List x = new LinkedList<>();
x.add("Mohan");
x.add("Kriti");
x.add("Salim");
List y = new LinkedList<>();
y.add("Sia");
y.add("Andrew");
x.addAll(y);
for (String data : x) {
System.out.println(data);
}
}
}