Continue statement is used with the loops to skip a few lines of code below it.
Let us make it simple with the below example.
Say we have a for loop that prints all the letters of a String (i.e. CAT).
<html>
<body>
<script language = "javascript" type = "text/javascript">
for (x of "CAT") {
document.write(x, ", ")
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
Now, let's say, we don't want the letter A to be printed. We just want to document.write C and T as output.
Let us rewrite the program using continue statement.
<html>
<body>
<script language = "javascript" type = "text/javascript">
for (x of "CAT") {
if (x == 'A') {
continue
}
document.write(x, ", ")
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
Now, if you see the output, the space A is omitted from the output. Printing only C and T.
Let us see it in detail :
So, we have a for loop that Iterates through the letters CAT.
for (x of "CAT")
And the Iteration starts,
In the 1st Iteration, C is taken and stored in the variable x.
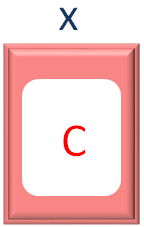
So, in the next line, we check if the value of the variable x is A or not.
if (x == 'A') {
continue
}In this case the value of x is C. So, we do not enter the if block and come to the document.write statement.
document.write(x, ", ")
Printing the value of x.
Then we start the second Iteration of for loop.
In the 2nd Iteration, A is taken and stored in the variable x.

So, in the next line, we check if the value of the variable x is A or not.
if (x == A) {
continue
}In this case the value of x is A. So, we enter the if block and come to the continue statement.
continue
And what the continue statement does is, ends the current Iteration of the for loop and starts the next Iteration.

And the value of x i.e. A is not printed..
And the 3rd Iteration starts.
Similarly, in the 1st Iteration, T is taken and stored in the variable x.
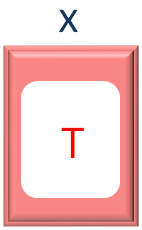
Same way, in the next line, we check if the value of the variable x is A or not.
if (x == 'A') {
continue
}In this case the value of x is T. So, we do not enter the if block and come to the document.write statement.
document.write(x, ", ")
Printing the value of x.
With this we end the execution of for loop.
Next, let us see another example of continue using the while loop.
Say you have a while loop that is used to document.write the numbers from 1 to 4.
<html>
<body>
<script language = "javascript" type = "text/javascript">
var x = 1
while (x <= 4) {
document.write(x, ", ")
x++
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
But let us say, you do not want to print the value 3.
i.e. You just want to document.write the numbers 1, 2 and 4.
And we can achieve it using continue statement.
Let us modify the above program using the continue statement.
<html>
<body>
<script language = "javascript" type = "text/javascript">
var x = 1
while (x <= 4) {
if (x == 3) {
x++
continue
}
document.write(x, ", ")
x++
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
And all we have done is placed an if condition, right before the document.write statement, checking if the value of x is equal to 3.
if (x == 3) {
x++
continue
}And the continue statement helps to skip the below lines of the while loop.
document.write(x, ", ") x++
Just remember if the value of x is equal to 3. Only then continue statement executes skipping the document.write statement and the increment statement (i.e. x = x + 1).

And the value 3 is not printed.