Variables in JavaScript are storage location where the data(Be it a number or a Name) is stored.It is like a container where something is stored.
Well! Pyton takes the same step to add two numbers. The only difference is, you have used one notebook to write and add the numbers.
But JavaScript uses different locations to store each number. And they are called as Variables.
Let us see how Variables are used in JavaScript for addition of two numbers.
<html>
<body>
<script language = "javascript" type = "text/javascript">
var x = 5
var y = 6
var z = x + y
document.write("The added value is : ",z)
</script>
</body>
</html>
Now, if you look at the above code, x, y and z are Variables.
And below are the steps involved in addition of the numbers.
var x = 5

var y = 6
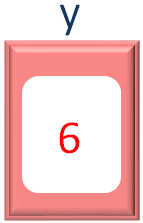
z = x + y
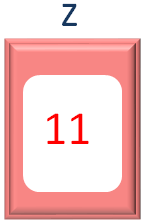
document.write("The added value is : ",z)"The added value is : "
z
"The added value is :",z
The added value is : 11
So far we have seen, how to store a number (i.e. var x = 5) in a Variable.
Now, let us see how to store a String(i.e. It could be a Name or a City) in a Variable.
Let us say, we want to store the String Hello World in a Variable(Say x).
And the process of storing a String is same as storing a number, but with a mild difference.
Below is the JavaScript Code :
<html> <body> <script language = "javascript" type = "text/javascript"> var x = "Hello World" document.write(x) </script> </body> </html>
So, in the above code, we have initialised the String Hello World to the variable x.
x = "Hello World"
The only thing to note here is, if you are initialising a String (i.e. Hello World), it should be either in Double Quotes ("") or Single Quotes (''). i.e. "Hello World" or Hello World.

The above line,
x = "Hello World"
Can also be written as,
x = 'Hello World'
JavaScript also gives us the flexibility to assign one value to multiple variables.
Below is the JavaScript Code :
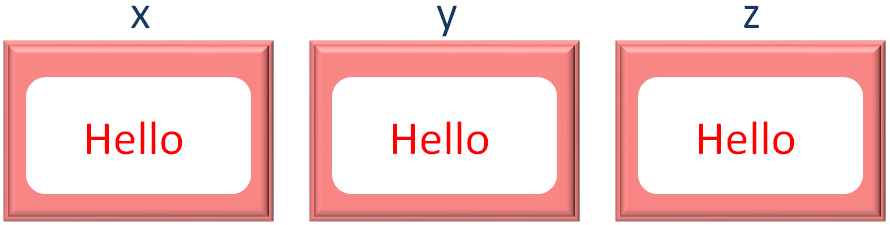
<html> <body> <script language = "javascript" type = "text/javascript"> var x = y = z = "Hello" document.write(x) document.write(y) document.write(z) </script> </body> </html>
So, in the above code, we have three variables x, y and z. And we have assigned the string Hello to all the three variables in a single line.
var x = y = z = "Hello"
And what happens is, three variables, x, y and z are created and assigned with the value Hello.
Just like any other language, there is a rule to declare the Variables.
Although, the Variables can be of any names with some restriction.
Below are the rules :
So, if you have two numbers and need to assign them to two Variables. You can either declare the variables as x and y starting with var keyword.
var x = 5
And
var y = 7
But the preferred way to name the Variables would be firstNumber and secondNumber.
var firstNumber = 5
And
var secondNumber = 7
But you can never use Variable names with spaces like first number or variables with a '-' (i.e. first-number).