We have the Array with three values, 5, John and JavaScript. And we want to access the second element i.e. John.
<html>
<body>
<script language = "javascript" type = "text/javascript">
var x = [5, "John", "JavaScript"]
document.write(x[1])
</script>
</body>
</html>
So, in the above code we have created a Array and initialised to the variable x.
var x = [5, "John", "JavaScript"]
Now, let us see, how the values are positioned in the Array
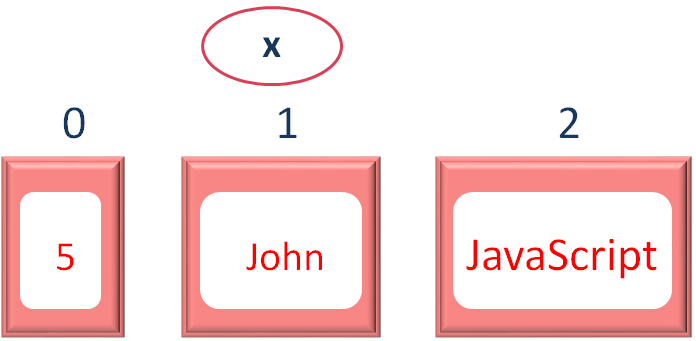
So, as we can see the elements are positioned as 0, 1 and 2. And if we want to access the second element, we can refer to the position 1 using the square brackets (i.e. x[1]).
And the document.write statement prints the value of the second element of the Array (i.e. John).
document.write(x[1])
We have the Array with five values, Mohan, John, Paul, Kriti and Salim. And we want to access the second, third and fourth element i.e. John, Paul and Kriti.
<html>
<body>
<script language = "javascript" type = "text/javascript">
var x = ["Mohan", "John", "Paul", "Kriti", "Salim"]
for (let i = 1; i < 4; i++) {
document.write(x[i], "</br>")
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
So, in the above code we have created a Array and initialised to the variable x.
var x = ["Mohan", "John", "Paul", "Kriti", "Salim"]
Now, let us see, how the values are positioned in the Array
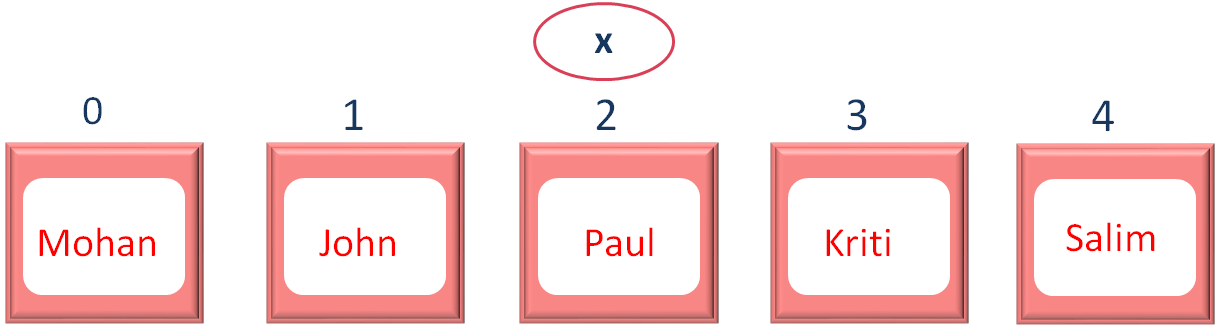
So, as we can see the elements are positioned as 0, 1, 2, 3 and 4.
Now, if we want to access the second, third and fourth element (i.e. John, Paul and Kriti). We can specify the range in a for loop.
for (let i = 1; i < 4; i++) {
document.write(x[i], "</br>")
}The for loop actually tells, to pick the elements from index/position 1 to the index/position 4-1 i.e. 3.
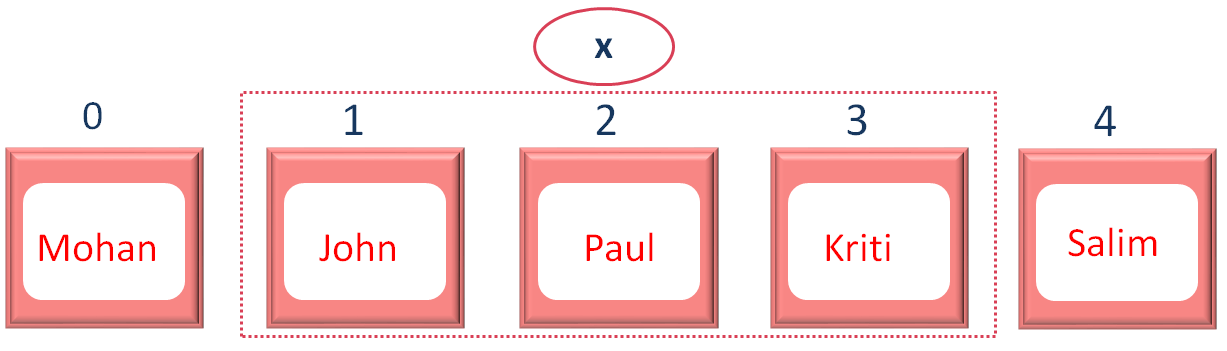
And the document.write statement prints the second, third and fourth element (i.e. John, Paul and Kriti).
document.write(x[i], "</br>")