The super() Function is used in the child class and is used to call a method of its Parent class.
We have seen the above example. Let us say the Parent class, LivingBeing has a constructor constructor() and we want to initialise its source attribute there.
Sounds Complex ?
Let's simplify with the below example.
<html>
<body>
<script>
class LivingBeing {
constructor(source) {
this.source = source
}
breathe() {
document.write("Breathes oxygen from ",this.source)
}
}
class Human extends LivingBeing {
constructor(name, food, language, source) {
super(source)
this.name = name
this.food = food
this.language = language
}
eat() {
document.write(this.name," eats ",this.food, "</br>")
}
speak() {
document.write(this.name," speaks ",this.language, "</br>")
}
}
human1 = new Human("John", "Burger", "English", "Air")
human1.eat()
human1.speak()
human1.breathe()
</script>
</body>
</html>
So in the above example, we have an attribute named source and a method breathe() in the Parent class, LivingBeing.
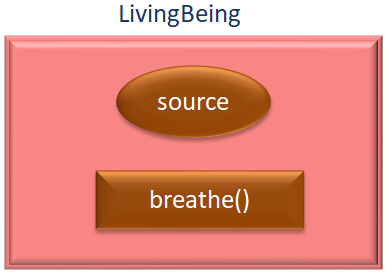
class LivingBeing {
constructor(source) {
this.source = source
}
breathe() {
document.write("Breathes oxygen from ",this.source)
}
}And we wanted to initialise the source attribute in the constructor() constructor of LivingBeing.
But as we know, the constructor() constructor is only called at the time of Object creation. And we won't be creating any objects of LivingBeing.
And this is where super() function comes to picture.
Let us see, how can we use the super() function to call the constructor().
Then we have declared the Human class inheriting all the contents of the LivingBeing class.
class Human extends LivingBeing {
constructor(name, food, language, source) {
super(source)
this.name = name
this.food = food
this.language = language
}
eat() {
document.write(this.name," eats ",this.food, "</br>")
}
speak() {
document.write(this.name," speaks ",this.language, "</br>")
}
}Now, in the constructor() constructor of the Human class,
constructor(name, food, language, source) {
super(source)
this.name = name
this.food = food
this.language = language
}We have called the constructor() constructor of the HumanBeing class using the super() Function.
super(source)
And the value of the attribute source gets set in the constructor() constructor of the Parent class HumanBeing.
constructor(source) {
this.source = source
}So, just the way super() Function is used to call the constructor() of the Parent,HumanBeing class from the child, Human class.
Similarly, the super() Function can be used to call any method of the parent class.