So far we have learnt, while loops and for loops.
Well! They can be combined together, one inside the other. And this is called Nested Loops.A loop inside a loop.
Let us understand with the below example.
Say, we want to write a program that prints the below output:
1 John 1 Sam 2 John 2 Sam
Let us write the code for the same using a for loop inside while loop i.e. Nested Loops.
<html>
<body>
<script language = "javascript" type = "text/javascript">
var x = 1
var names = ["John", "Sam"]
while (x <= 2) {
for (y of names) {
document.write(x, " ", y, " :: ")
}
x++
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
So, in the above code we have two loops.
Let us see in detail, how the loops work.
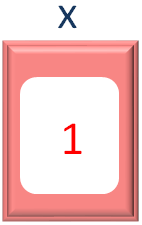
So, we have declared a variable names x to maintain the while loop.
var x = 1
That stores the initial value as 1.
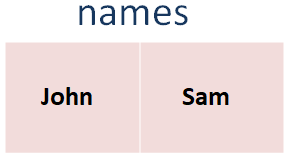
Then we have declared a Array named names for the for loop.
var names = ["John", "Sam"]
Which has the names, John and Sam.
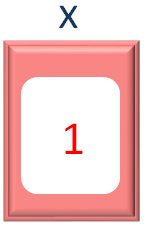
Then we have the while loop,
while (x <= 2)
And the control checks, if the value of x is less than or equal to 2. In this case the value of x is 1.
So, the control enters the while loop.
During the first iteration of while loop, we find the for loop inside the while loop.
for (y of names)
And we start the iteration of for loop inside the 1st Iteration of while loop.
And in the 1st Iteration of for loop, we find the document.write statement.
document.write(x, " ", y, " :: ")
If we check the current value of x, it is 1.
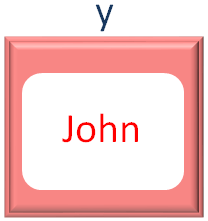
And in the first iteration of for loop, the first value from the names Array is taken and placed into the variable y.
So, we got the value of x and y. And the output is,
And we are done with the first iteration of for loop. And begin the second iteration of for loop.
Now, in the 2nd Iteration of for loop, we find the document.write statement.
document.write(x, " ", y, " :: ")
Similarly, we get the current value of x, which is still 1.
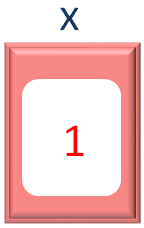
And in the second iteration of for loop, the second value from the names Array is taken and placed into the variable y. Which is Sam.
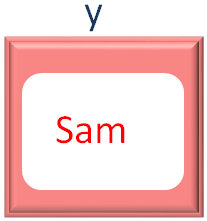
So, we got the value of x and y. And the output is,
So, we are done with the execution of the inner for loop. And we get out of the for loop.
And we encounter the line,
x++
Where we have incremented the value of x by 1.
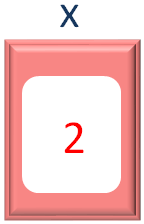
Then we come back to the while loop.
while (x <= 2)
And the condition of while loop satisfies as the value of x is 2. So, we start the second iteration of while loop.
Similarly, during the second iteration of while loop, we find the for loop inside the while loop.
for (y of names)
And we start the iteration of for loop inside the 2nd Iteration of while loop.
And in the 1st Iteration of for loop, we find the document.write statement.
document.write(x, " ", y, " :: ")
If we check the current value of x, it is 2.
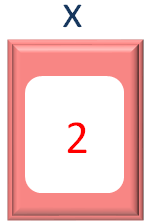
And in the first iteration of for loop, the first value from the names Array is taken and placed into the variable y.
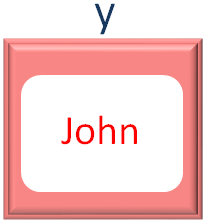
So, we got the value of x and y. And the output is,
And we are done with the first iteration of for loop. And begin the second iteration of for loop.
Now, in the 2nd Iteration of for loop, we find the document.write statement.
document.write(x, " ", y, " :: ")
Similarly, we get the current value of x, which is still 2.
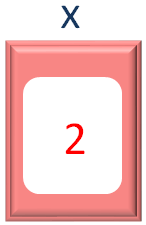
And in the second iteration of for loop, the second value from the names Array is taken and placed into the variable y. Which is Sam.
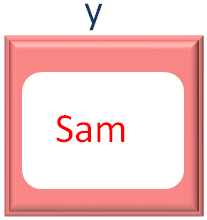
So, we got the value of x and y. And the output is,
So, we are done with the execution of the inner for loop. And we get out of the for loop.
And we encounter the line,
x++
Where we have incremented the value of x by 1.
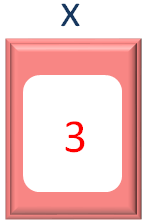
Then we come back to the while loop.
while (x <= 2)
And the condition of while loop fails, as the value of x is 3. And the execution ends.
So, we have learnt, how the execution of a for loop inside a while loop works.
Now, let us look at a little complex example, of a Nested for loop. i.e. A for loop inside a for loop.
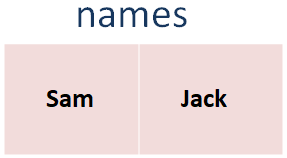
Say, we have a Array that has two names, Sam and Jack.
Now, we need to document.write each letter of the name, as stated below :
S, a, m, --> J, a, c, k, -->
Let us explain with the below example.
<html>
<body>
<script language = "javascript" type = "text/javascript">
var names = ["Sam", "Jack"]
for (x of names) {
for (y of x) {
document.write(y , ", ")
}
document.write(" --> ")
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
So, if we look at the above code, we have created a Array named names,
var names = ["Sam", "Jack"]
And stored the names, Sam and Jack in it.
Now, our main motto is, to document.write each letters of the names. And for that we have used two for loops.
So, we come to the next line where the execution of Outer for loop begins.
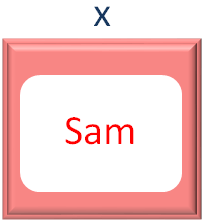
for (x of names)
So, in the 1st Iteration of the Outer for loop, we get the first element(i.e. Sam) from the Array names and store it in the variable x.
Then we come to the inner for loop.
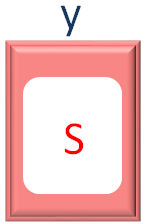
for (y of x)
Now, in the 1st Iteration of the Inner for loop, we collect the value from x, one by one and store in the variable y.
Since, there is Sam stored in x. The first element of x (i.e. S) is taken and stored in y.
Then we encounter the document.write statement.
document.write(y , ", ")
Where we print the value of y.
Then we start the second Iteration of the Inner for loop.
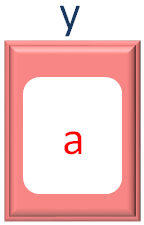
Similarly, in the 2nd Iteration of the Inner for loop, we collect second value from x, and store it in the variable y.
Since, there is Sam stored in x. The second element of x (i.e. a) is taken and stored in y.
Then we encounter the document.write statement.
document.write(y)
Where we document.write the value of y.
Then we start the third Iteration of the Inner for loop.
Similarly, in the 3rd Iteration, we collect third value from x, and store it in the variable y.
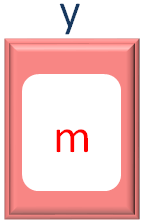
And document.write the value of y.
And we come to an end of the Inner for loop and print -->
document.write(" --> ")Then JavaScript control goes back to the outer for loop.
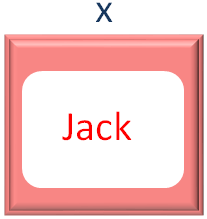
Again, in the 2nd Iteration of the Outer for loop, we get the second element(i.e. Sam) from the Array names.
And store it in the variable x.
Then we come to the inner for loop.
for (y of x)
Now, in the 1st Iteration of the Inner for loop, we collect the value from x, one by one and store in the variable y.
Since, there is Jack stored in x. The first element of x (i.e. J) is taken and stored in y.
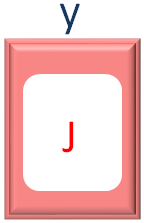
Then we encounter the document.write statement.
document.write(y , ", ")
Where we document.write the value of y.
And continuing in the same way, we get the below output.