A String is a collection of letters/alphabets. It can be a word or a sentence.
The Data Type for String is str.
When JavaScript finds data inside Double Quotes ("") of Single Quotes (''). It creates a String type variable for that value.
var x = "Hello World"
Or
var x = 'Hello World'
And that's all! You have a String in place.
<html>
<body>
<script language = "javascript" type = "text/javascript">
var x = "Hello World"
document.write(x)
</script>
</body>
</html>
Next, let us see, how can we find the length of a String.
<html>
<body>
<script language = "javascript" type = "text/javascript">
var x = "Hello"
var y = x.length
document.write("The length of the String Hello is : ",y)
</script>
</body>
</html>
So, in the above code, we have used the length with the variable x.
var y = x.length
To find the length of the String Hello.
Now, if you want to access a particular character of a String, how can you do that?
Say, you have a String "Hello". And you want the letter e to be assigned to a variable.
Let us see below.
<html>
<body>
<script language = "javascript" type = "text/javascript">
var x = "Hello"
var y = x[1]
document.write(y)
</script>
</body>
</html>
So, we have a string Hello,
x = "Hello"
And we have assigned Hello to a variable x.

Let us elaborate more, on how the String Hello is stored in the variable x.
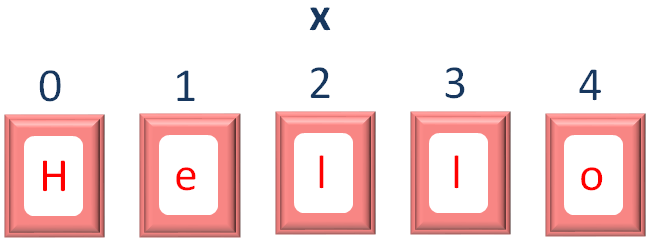
You can assume the variable x is divided into 5 parts to store Hello.
Now, if you check from the front, the count starts from 0 and ends with 4.
So, if we look at the next line in the code,
var y = x[1]
We are trying to access the 2nd location,
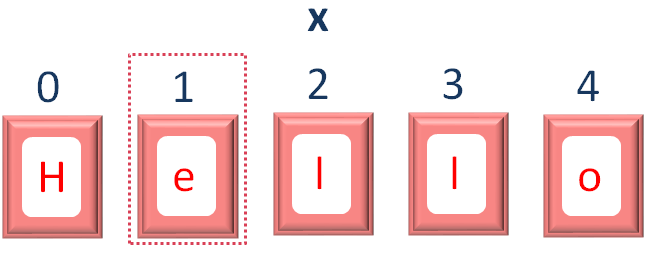
So, x[1] is referring to the 2nd location where e is stored.
y = x[1]
And we have assigned e to the variable y.
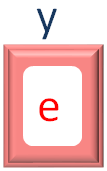
Now, if you look at the document.write statement,
document.write(y)
The value of y is printed as output.
Also, remember that x[1] and x[-4] is referring to the same location that has e. You can use the negative positions or positive. That is completely upto you.
x = "Hello" y = x[-4] document.write(y)
Next, let us see, how can we access a portion of a String. i.e. Say you want to take ell from the String Hello and store it in a different variable.
In the above example, we have seen the + sign. And as we know, + is used for addition of two numbers.
Well! In JavaScript, + can be used to join two Strings as well.
Say, we have two Strings, Hello and World. And we want to join/concatenate them into one String, HelloWorld.
Let us solve it with the below example.
<html>
<body>
<script language = "javascript" type = "text/javascript">
var x = "Hello"
var y = "World"
var z = x + y
document.write(z)
</script>
</body>
</html>
So, we have stored the String Hello in x.
var x = "Hello"
And, stored the String World in y.
var y = "World"
And used the + operator to join/concatenate Hello and World.
z = x + y
And store the concatenated value in z.
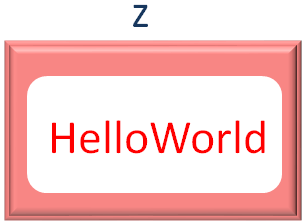
So, + is not just used to add two numbers but + is also used to join/concatenate two Strings.
We can also use the + operator to join/concatenate a number and a String.
<html>
<body>
<script language = "javascript" type = "text/javascript">
var x = 5
var y = "World"
var z = x + y
document.write(z)
</script>
</body>
</html>
Next, let us see how to Iterate through the values of a String.
<html>
<body>
<script language = "javascript" type = "text/javascript">
var x = "Hello"
for (y of x) {
document.write(y, ", ")
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
So, each Iteration of for loop,
for (y of x)
The values are taken from the variable x, one by one and put in the variable y.
And values are printed at each Iteration.
document.write(y, ", ")
Now, let us look at a scenario, where you need to find out, if a particular letter or a chunk of letters is present in the string or not.
Let us check, if the substring el is present in the String Hello or not.
<html>
<body>
<script language = "javascript" type = "text/javascript">
var x = "Hello"
if (x.includes("el")) {
document.write("The sub-string, el is present in the String, Hello")
}
else {
document.write("The sub-string, el is not present in the String, Hello")
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
So, to check if the substring el is present in the String Hello, we have used the if statement.
if (x.includes("el"))And the if statement is combined with includes() method to check if the substring el is present in the String Hello or not.
Similarly, the ! keyword is used to check if the substring is not present.
<html>
<body>
<script language = "javascript" type = "text/javascript">
var x = "Hello"
if (!x.includes("el")) {
document.write("The sub-string, el is present in the String, Hello")
}
else {
document.write("The sub-string, el is not present in the String, Hello")
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
Now, if you look at the output, although the substring el is present in Hello, the output is printed from the else block.
The sub-string, el is not present in the String, Hello
So far we have declared a String using,
var x = "John"
A String can also be declared using new String().
var x = new String("John")And the variable x is treated as an Object.
Next, let us look at the Methods provided by JavaScript to handle Strings more effectively.
You can check the individual methods by clicking on it.