import java.util.*;
var vertices = LinkedList<String?>();
var adjcList = LinkedList<LinkedList<Edge>>() ;
var vertexVal = HashMap<String?,Int>();
// Stores the Minimum spanning Tree
var result = ArrayList<Edge>();
class Edge {
var startVertex: String? = "";
var endVertex: String? = "";
var value = 0;
}
class MinHeap(vertexValue: HashMap<String?, Int>) {
var vertexVal = HashMap<String?, Int>();
var verticesKeyArray: Array<String?> = emptyArray()
init {
vertexVal = vertexValue;
}
fun heapify(verticesArray: Array<String?>, root: Int, length: Int) {
var left = (2*root)+1;
var right = (2*root)+2;
var smallest = root;
if ((left < length) && (right <= length) && (vertexVal[verticesArray[right]]!! < vertexVal[verticesArray[left]]!!)) {
smallest = right;
}
else if (left <= length){
smallest = left;
}
if (vertexVal.get(verticesArray[root])!! > vertexVal.get(verticesArray[smallest])!!) {
var temp = verticesArray[root];
verticesArray[root] = verticesArray[smallest];
verticesArray[smallest] = temp;
heapify(verticesArray, smallest, length);
}
}
fun buildHeap() {
var verticesSet = vertexVal.keys;
// Now convert the above keys to an Array.
var verticesArray: Array<String?> = verticesSet.toTypedArray();
var len = verticesArray.size-1;
for (parent in (len-1)/ 2 downTo 0) {
heapify(verticesArray, parent, len);
}
verticesKeyArray = verticesArray;
}
fun updateHeap(vertex: String?, length: Int) {
vertexVal.put(vertex, length);
// Get all the keys (i.e. Vertices ) for the Map.
var verticesSet = vertexVal.keys;
// Now convert the above keys to an Array.
var verticesArray: Array<String?> = verticesSet.toTypedArray();
var len = verticesArray.size-1;
for (parent in (len-1)/ 2 downTo 0)
heapify(verticesArray, parent, len);
verticesKeyArray = verticesArray;
}
fun containsVertex(vertex: String?): Boolean{
if (vertexVal.containsKey(vertex))
return true;
else
return false;
}
fun deleteMin(): String? {
var temp = verticesKeyArray[0];
var len = verticesKeyArray.size-1;
verticesKeyArray[0] = verticesKeyArray[len];
vertexVal.remove(temp);
verticesKeyArray = Arrays.copyOf(verticesKeyArray, len);
if (len>0)
heapify(verticesKeyArray, 0, len-1);
return temp;
}
fun getWeight(vertex: String? ): Int? {
return vertexVal[vertex];
}
fun empty(): Boolean {
if (verticesKeyArray.size>0)
return false;
else
return true;
}
}
class PrimMST {
init {
adjcList = LinkedList<LinkedList<Edge>>();
vertices = LinkedList<String?>();
vertexVal = LinkedHashMap<String?,Int>();
// Stores the Minimum spanning Tree
result = ArrayList<Edge>();
}
fun primMST(){
vertexVal = LinkedHashMap<String?,Int>();
// Vertex to Edge Map
var vertexToEdge = HashMap<String?, Edge>();
// Assign all the initial values as infinity for all the Vertices.
for(v in vertices) {
vertexVal.put(v,Int.MAX_VALUE);
}
var minHeap = MinHeap(vertexVal);
// Call buildHeap() to create the MinHeap
minHeap.buildHeap();
// Replace the value of start vertex to 0.
minHeap.updateHeap("a",0);
// Continue until the Min-Heap is not empty.
while(!minHeap.empty()){
// Extract minimum value vertex from Map in Heap
var currentVertex = minHeap.deleteMin();
// Need to get the edge for the vertex and add it to the Minimum Spanning Tree..
// Just note, the edge for the source vertex will not be added.
var spanningTreeEdge = vertexToEdge.get(currentVertex);
if(spanningTreeEdge != null) {
result.add(spanningTreeEdge);
}
// Get all the adjacent vertices and iterate through them.
for(edge in getEdges(currentVertex)){
var adjacentVertex = edge.endVertex;
// We check if adjacent vertex exist in 'Map in Heap' and length of the edge is with this vertex
// is greater than this edge length.
if(minHeap.containsVertex(adjacentVertex) && minHeap.getWeight(adjacentVertex)!! > edge.value){
// Replace the edge length with this edge weight.
minHeap.updateHeap(adjacentVertex, edge.value);
vertexToEdge.put(adjacentVertex, edge);
}
}
}
}
fun getEdges(vertex: String?): List<Edge>{
var edgeList = LinkedList<Edge>();
var i = vertices.indexOf(vertex);
var iter = adjcList.get(i).iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
edgeList.add( iter.next());
}
return edgeList;
}
fun constructAdjacencyList(vertex1: String, vertex2: String , edgeVal: Int) {
var edge = Edge();
edge.startVertex = vertex1;
edge.endVertex = vertex2;
edge.value = edgeVal;
adjcList.add(LinkedList<Edge>());
adjcList.get(vertices.indexOf(vertex1)).add(edge);
}
fun insertVertex(vertex: String) {
vertices.add(vertex);
}
fun printEdgeList() {
for (edge in result) {
println("The Edge between ${edge.startVertex} and ${edge.endVertex} is ${edge.value}" );
}
}
}
fun main(arr: Array<String>) {
var primMST = PrimMST();
// Insert Vertices
primMST.insertVertex("a");
primMST.insertVertex("b");
primMST.insertVertex("c");
primMST.insertVertex("d");
primMST.insertVertex("e");
// Create Adjacency List with Edges.
primMST.constructAdjacencyList("a", "b",1);
primMST.constructAdjacencyList("a", "c",5);
primMST.constructAdjacencyList("a", "d",4);
primMST.constructAdjacencyList("b", "a",1);
primMST.constructAdjacencyList("b" ,"e",8);
primMST.constructAdjacencyList("c", "a",5);
primMST.constructAdjacencyList("c", "d",12);
primMST.constructAdjacencyList("c", "e",9);
primMST.constructAdjacencyList("d", "a", 4);
primMST.constructAdjacencyList("d", "c", 12);
primMST.constructAdjacencyList("d", "e", 3);
primMST.constructAdjacencyList("e", "b", 8);
primMST.constructAdjacencyList("e", "c", 9);
primMST.constructAdjacencyList("e", "d", 3);
primMST.primMST();
primMST.printEdgeList();
}
Let us recapitulate the 3 step process for Prim's Algorithm :
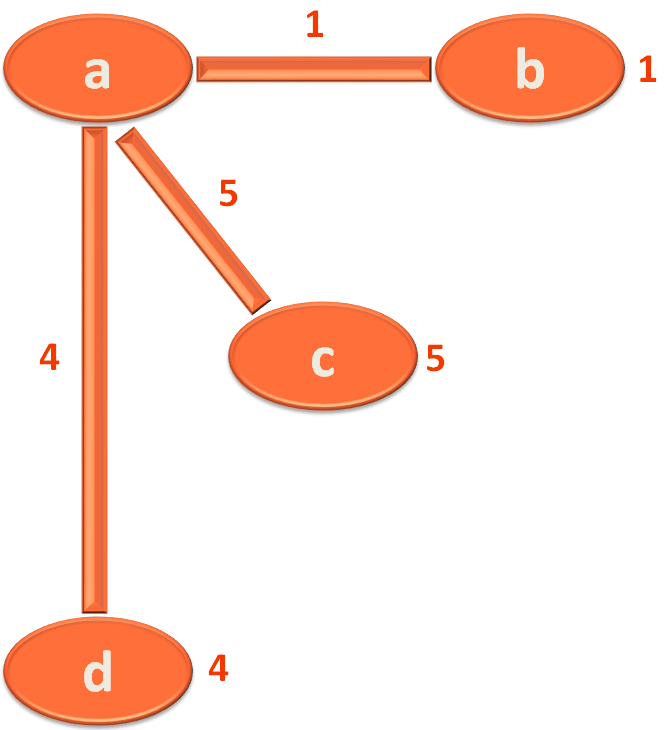
Let us take the below graph, to understand the above code.
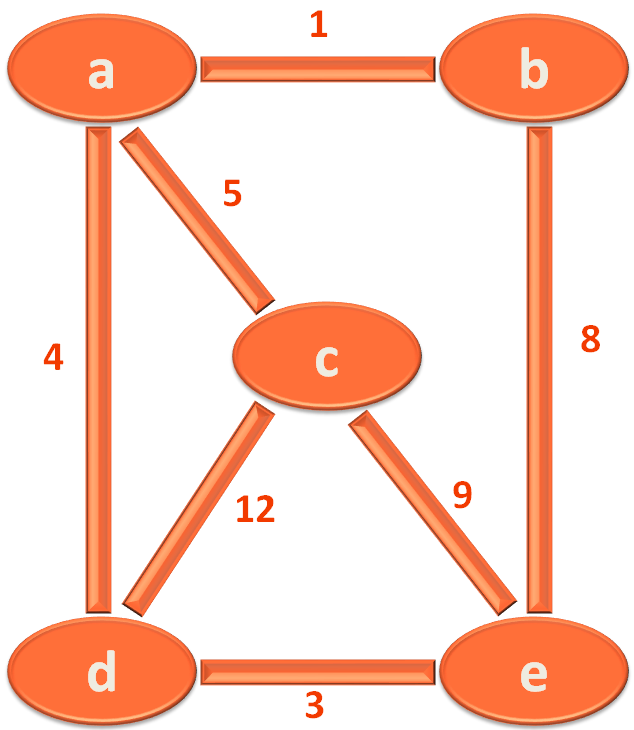
The first task is to construct the Graph. So, we need to store the Vertices first.
var vertices = LinkedList<String?>();
And also we know, we have to represent the edges as Adjacency List.
var adjcList = LinkedList<LinkedList<Edge>>();
Eventually, in the main(...) method. We have initialised the vertices,
primMST.insertVertex("a");
primMST.insertVertex("b");
primMST.insertVertex("c");
primMST.insertVertex("d");
primMST.insertVertex("e");And, created the Adjacency List with Edges.
// Create Adjacency List with Edges.
primMST.constructAdjacencyList("a", "b", 1);
primMST.constructAdjacencyList("a", "c", 5);
primMST.constructAdjacencyList("a", "d", 4);
primMST.constructAdjacencyList("b", "a", 1);
primMST.constructAdjacencyList("b" ,"e", 8);
primMST.constructAdjacencyList("c", "a", 5);
primMST.constructAdjacencyList("c", "d", 12);
primMST.constructAdjacencyList("c", "e", 9);
primMST.constructAdjacencyList("d", "a", 4);
primMST.constructAdjacencyList("d", "c", 12);
primMST.constructAdjacencyList("d", "e", 3);
primMST.constructAdjacencyList("e", "b", 8);
primMST.constructAdjacencyList("e", "c", 9);
primMST.constructAdjacencyList("e", "d", 3);Let us understand creation process of Adjacency List. If you already know it, you can skip.
Click Here - For the creation process of Adjacency List.
fun constructAdjacencyList(vertex1: String, vertex2: String , edgeVal: Int) {
var edge = Edge();
edge.startVertex = vertex1;
edge.endVertex = vertex2;
edge.value = edgeVal;
adjcList.add(LinkedList<Edge>());
adjcList.get(vertices.indexOf(vertex1)).add(edge);
}Let us take the example of the Edge (a,b) with length 1 and understand the above code.
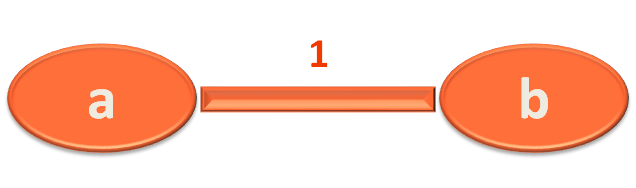
primMST.constructAdjacencyList("a", "b", 1);Now, if we look at the method definition,
fun constructAdjacencyList(vertex1: String, vertex2: String , edgeVal: Int)
vertex1: String is initialised with a.
vertex2: String is initialised with b.
edgeVal: Int is initialised with 1.
The next thing we do is, create an Edge object.
var edge = Edge();
And initialise the var edge object with the start vertex, end vertex and the length of the Edge.
edge.startVertex = vertex1; edge.endVertex = vertex2; edge.value = edgeVal;
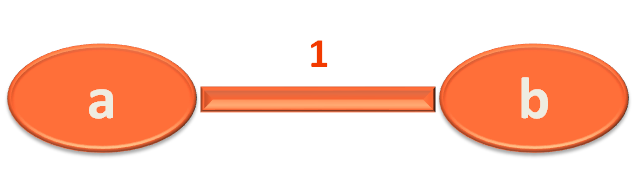
And the Edge object looks somewhat like,

Now, since we have the Edge (a,b) initialised. The next task would be, to add this Edge to the AdjacencyList.
And as we have seen, there is a 2D LinkedList to store the Adjacency List.
var adjcList = LinkedList<LinkedList<Edge>>();
Now, we will be creating the first row of LinkedList,
adjcList.add(LinkedList<Edge>());
And then we will try finding out, for which vertex we are going to insert the Edge.
adjcList.get(vertices.indexOf(vertex1)).add(edge);
In simple words, vertices.indexOf(vertex1) will tell us about the position of the start vertex.
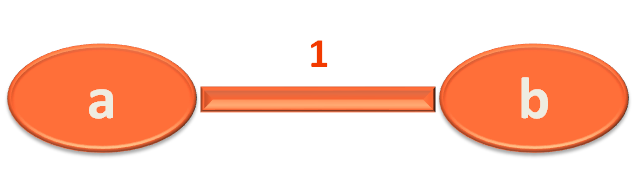
In this case, the start vertex is a. And vertices.indexOf(vertex1) will tell us about its position, i.e. 0.
So, if we substitute the line,
adjcList.get(vertices.indexOf(vertex1)).add(edge);
With the value of vertices.indexOf(vertex1),
adjcList.get(0).add(edge);
The edge would be added to the 0th location of the 2d LinkedList.
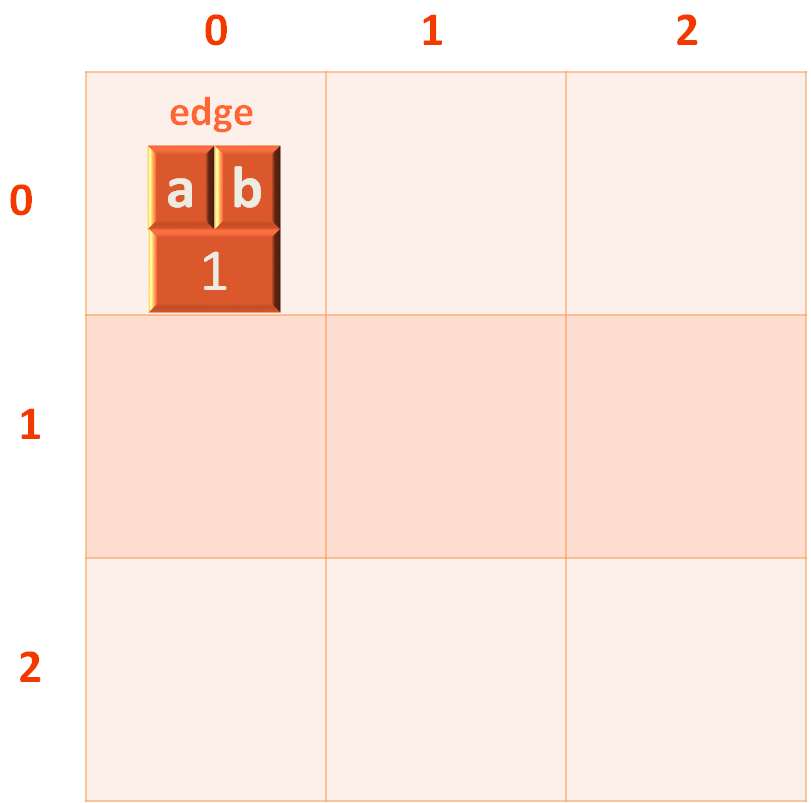
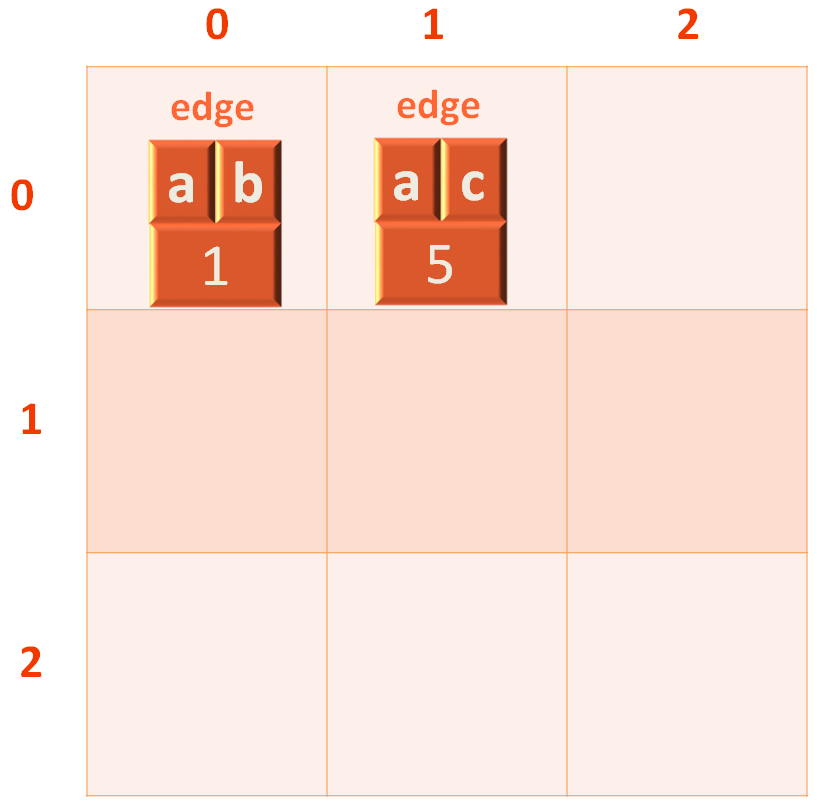
This is how a 2D LinkedList looks like. Just remember, the empty blocks are not yet created, but will be created eventually.
For now, only the first row is created with the first column where the edge
is inserted.
Next, when we try to insert the second adjacent edge of a i.e. a,c.
primMST.constructAdjacencyList("a", "c", 5);An edge object will be created
edge.startVertex = vertex1; edge.endVertex = vertex2; edge.value = edgeVal;
And the Edge object looks somewhat like,

Once again the start vertex is a. And vertices.indexOf(vertex1) will tell us about its position, i.e. 0.
So, if we substitute the line,
adjcList.get(vertices.indexOf(vertex1)).add(edge);
With the value of vertices.indexOf(vertex1),
adjcList.get(0).add(edge);
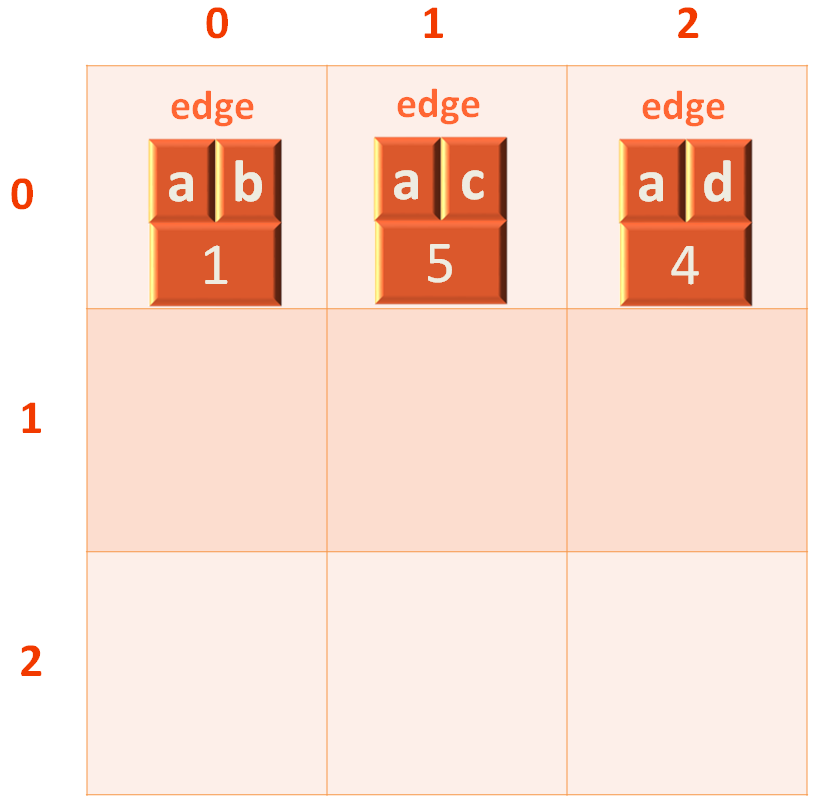
The edge would be added to the 1st row of the 2d LinkedList, just next to the first edge.
Similarly, we insert the third adjacent edge of a i.e. a,d.
primMST.constructAdjacencyList("a", "d", 4);An edge object will be created
edge.startVertex = vertex1; edge.endVertex = vertex2; edge.value = edgeVal;
And the Edge object looks somewhat like,

Once again the start vertex is a. And vertices.indexOf(vertex1) will tell us about its position, i.e. 0.
So, if we substitute the line,
adjcList.get(vertices.indexOf(vertex1)).add(edge);
With the value of vertices.indexOf(vertex1),
adjcList.get(0).add(edge);
The edge would be added to the 1st row of the 2d LinkedList, just next to the first edge.
Similarly, we insert the adjacent edge of b i.e. b,a.
primMST.constructAdjacencyList("b", "a", 1);An edge object will be created
edge.startVertex = vertex1; edge.endVertex = vertex2; edge.value = edgeVal;
And the Edge object looks somewhat like,

Now, the start vertex is b. And vertices.indexOf(vertex1) will tell us about its position, i.e. 1.
So, if we substitute the line,
adjcList.get(vertices.indexOf(vertex1)).add(edge);
With the value of vertices.indexOf(vertex1),
adjcList.get(1).add(edge);
And this time, the edge would be added to the 2nd row of the 2d LinkedList.
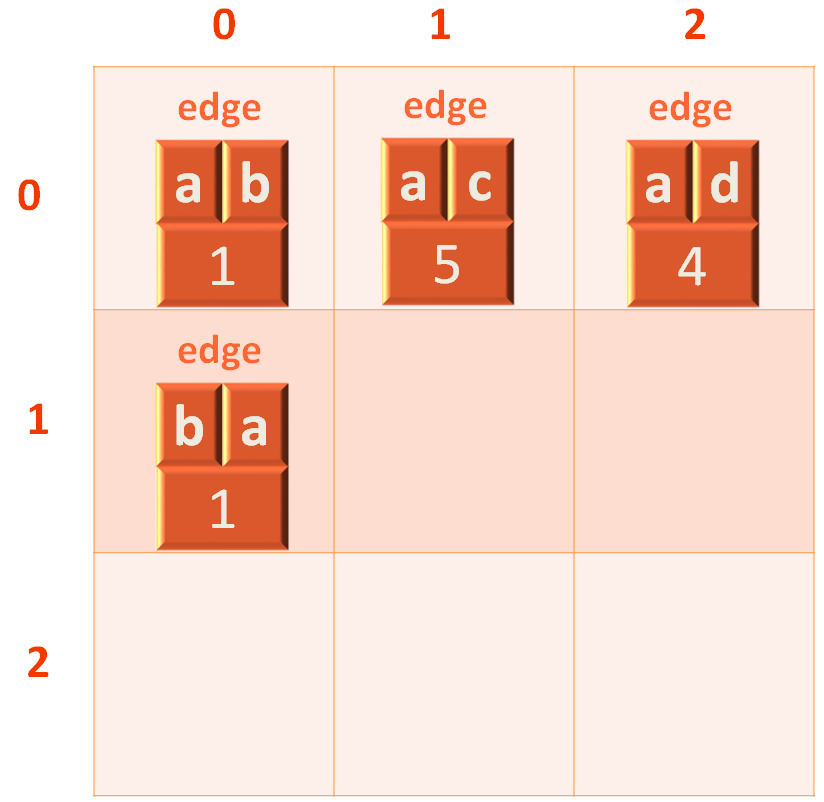
And eventually the AdjacencyList with Edges would be created with the 2D LinkedList.
Once we are done creating the AdjacencyList with Edges. The next task would be to call the actual method for Prim's Algorithm,
primMST.primMST();
Before we understand primMST() method in detail. Let us understand the Min-Heap Data Structure.
If you already know Min-Heap Data Structure, you can skip the below part.
Click Here - For Min-Heap Data Structure Recap.
There are four important method in the MinHeap class that are quite important.
They are :
Now, if we look at the primMST() method, we could see that initially the MinHeap object is created using a parameterised constructor.
var minHeap = MinHeap(vertexVal);
And if we look at the Constructor definition,
class MinHeap(vertexValue: HashMap<String?, Int>)
And init block for the constructor,
init{
vertexVal = vertexValue;
}The Map vertexValue: HashMap<String?, Int> is getting initialised here.
vertexVal = vertexValue;
Where, vertexVal is the class attribute,
var vertexVal = HashMap<String?, Int>();
Next, we initialise the Map with the vertices as key and assign the value as Int.MAX_VALUE. This Int.MAX_VALUE is so large that it could be compared with infinity.
// Assign all the initial values as infinity for all the Vertices.
for(v in vertices) {
vertexVal.put(v,Int.MAX_VALUE);
}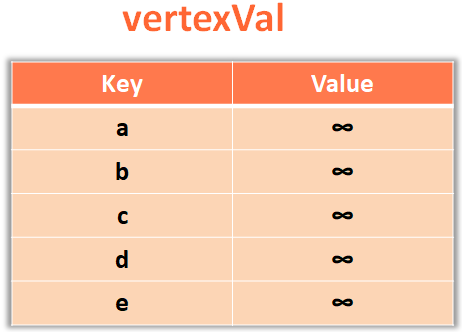
So, the Map vertexVal is loaded with values.
Next, we call the buildHeap() method to create the MinHeap, with the values of the Map vertexVal.
minHeap.buildHeap();
fun buildHeap() {
var verticesSet = vertexVal.keys;
// Now convert the above keys to an Array.
var verticesArray: Array<String?> = verticesSet.toTypedArray();
var len = verticesArray.size-1;
for (parent in (len-1)/ 2 downTo 0) {
heapify(verticesArray, parent, len);
}
verticesKeyArray = verticesArray;
}Just remember, Map is not a good Data Structure for Heap. Whereas array is an excellent Data Structure for Heap.
So, we take the keys from the Map and create an Array out of it.
To do this, there is a two step process involved.
First, we extract the key from the Map and put it into a Set.
var verticesSet = vertexVal.keys;
Second, we create an Array and convert the Set to the Array.
var verticesArray: Array<String?> = verticesSet.toTypedArray();
Then, we take the length of the Array.
var len = verticesArray.size-1;
Then, we divide the Array into two parts and run a for loop. Then call the Heapify method.
for (parent in (len-1)/ 2 downTo 0) {
heapify(verticesArray, parent, len);
}So, what does the heapify(..) method do?
Let us see .
fun heapify(verticesArray: Array<String?>, root: Int, length: Int) {
var left = (2*root)+1;
var right = (2*root)+2;
var smallest = root;
if ((left < length) && (right <= length) && (vertexVal[verticesArray[right]]!! < vertexVal[verticesArray[left]]!!)) {
smallest = right;
}
else if (left <= length){
smallest = left;
}
if (vertexVal.get(verticesArray[root])!! > vertexVal.get(verticesArray[smallest])!!) {
var temp = verticesArray[root];
verticesArray[root] = verticesArray[smallest];
verticesArray[smallest] = temp;
heapify(verticesArray, smallest, length);
}
}Since, all the values of the Map vertexVal are infinity now. So, it doesn't matter how the values will be inserted in the Min-Heap.
For the sake of understanding, let us understand the functionality of heapify(...) method.
So, we have passed the verticesArray, root element and the length of the Array to heapify(...) method.
Then, we have calculated the left, right and root element of the Heap.
var left = (2*root)+1; var right = (2*root)+2; var smallest = root;
Since, this is a Min-Heap. The smallest element would be at the root of the Heap.
So, we try initialising the smallest element with its right value.
And the below if condition checks, if the left and right element is less than the length of the Array.
if ((left < length) && (right <= length) && (vertexVal[verticesArray[right]]!! < vertexVal[verticesArray[left]]!!)) {
smallest = right;
}
else if (left <= length){
smallest = left;
}And, if the element on the right side of the Map vertexVal is less than the element on the right side.
vertexVal[verticesArray[right]]!! < vertexVal[verticesArray[left]]!!)
Then element on the right side of the Map is the smallest element.
smallest = right;
And in the else part, we can assume that the element on the left side of the Map has the smallest element.
smallest = left;
Now, since we got the smallest element. We need to check if the actual root element is greater than the smallest element or not.
if (vertexVal.get(verticesArray[root])!! > vertexVal.get(verticesArray[smallest])!!) {
var temp = verticesArray[root];
verticesArray[root] = verticesArray[smallest];
verticesArray[smallest] = temp;
heapify(verticesArray, smallest, length);
}And this is where, we swap the contents of the root element and the smallest element. Assuming the element in the root is greater than the smallest element.
Which shouldn't be. As the root element should always be the smallest element.
Then a recursive call is made to heapify(...) method.
heapify(verticesArray, smallest, length);
And the recursion continues until all the elements are arranged in MinHeap.
In the next line, we would update the value of source element a to 0.
// Replace the value of start vertex to 0.
minHeap.updateHeap("a",0);Now, if we see the updateHeap(...) method,
fun updateHeap(vertex: String?, length: Int) {
vertexVal.put(vertex, length);
// Get all the keys (i.e. Vertices ) for the Map.
var verticesSet = vertexVal.keys;
// Now convert the above keys to an Array.
var verticesArray: Array<String?> = verticesSet.toTypedArray();
var len = verticesArray.size-1;
for (parent in (len-1)/ 2 downTo 0)
heapify(verticesArray, parent, len);
verticesKeyArray = verticesArray;
}The first thing we do is, replace the value in the Map vertexVal.
vertexVal.put(vertex, length);
Then we follow the same process we followed above. i.e. Extract the keys from the Map. Make it a Set and then convert the Set into an Array.
var verticesSet = vertexVal.keys; var verticesArray: Array<String?> = verticesSet.toTypedArray();
Then we call the heapify(...) method. Because we have updated a new value and in that case the Heap has to be rearranged to form a Min-Heap.
Now, that we have understood Min-Heap. Let us understand the details about the actual method that calculates the Minimum Spanning Tree using Prim's Algorithm.
fun primMST(){
vertexVal = LinkedHashMap<String?,Int>();
// Vertex to Edge Map
var vertexToEdge = HashMap<String?, Edge>();
// Assign all the initial values as infinity for all the Vertices.
for(v in vertices) {
vertexVal.put(v,Int.MAX_VALUE);
}
var minHeap = MinHeap(vertexVal);
// Call buildHeap() to create the MinHeap
minHeap.buildHeap();
// Replace the value of start vertex to 0.
minHeap.updateHeap("a",0);
// Continue until the Min-Heap is not empty.
while(!minHeap.empty()){
// Extract minimum value vertex from Map in Heap
var currentVertex = minHeap.deleteMin();
// Need to get the edge for the vertex and add it to the Minimum Spanning Tree..
// Just note, the edge for the source vertex will not be added.
var spanningTreeEdge = vertexToEdge.get(currentVertex);
if(spanningTreeEdge != null) {
result.add(spanningTreeEdge);
}
// Get all the adjacent vertices and iterate through them.
for(edge in getEdges(currentVertex)){
var adjacentVertex = edge.endVertex;
// We check if adjacent vertex exist in 'Map in Heap' and length of the edge is with this vertex
// is greater than this edge length.
if(minHeap.containsVertex(adjacentVertex) && minHeap.getWeight(adjacentVertex)!! > edge.value){
// Replace the edge length with this edge weight.
minHeap.updateHeap(adjacentVertex, edge.value);
vertexToEdge.put(adjacentVertex, edge);
}
}
}
}Three things to remember :
Now, let us look at the steps involved :
vertexVal = LinkedHashMap<String?,Int>();
var vertexToEdge = HashMap<String?, Edge>();
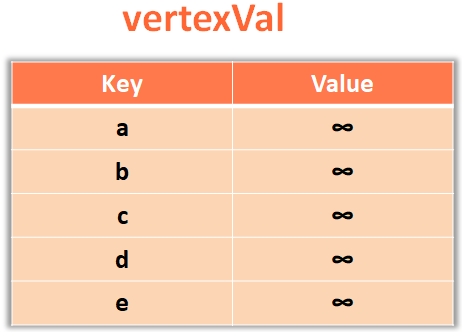
for(v in vertices) {
vertexVal.put(v,Int.MAX_VALUE);
}
var minHeap = MinHeap(vertexVal);
minHeap.buildHeap();
minHeap.updateHeap("a",0);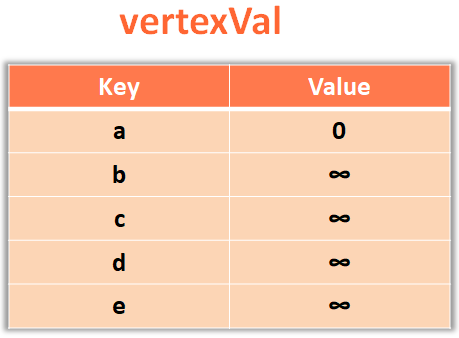
while(!minHeap.empty()){
// Extract minimum value vertex from Map in Heap
var currentVertex = minHeap.deleteMin();
// Need to get the edge for the vertex and add it to the Minimum Spanning Tree..
// Just note, the edge for the source vertex will not be added.
var spanningTreeEdge = vertexToEdge.get(currentVertex);
if(spanningTreeEdge != null) {
result.add(spanningTreeEdge);
}
// Get all the adjacent vertices and iterate through them.
for(edge in getEdges(currentVertex)){
var adjacentVertex = edge.endVertex;
// We check if adjacent vertex exist in Map in Heap and length of the edge is with this vertex
// is greater than this edge length.
if(minHeap.containsVertex(adjacentVertex) && minHeap.getWeight(adjacentVertex)!! > edge.value){
// Replace the edge length with this edge weight.
minHeap.updateHeap(adjacentVertex, edge.value);
vertexToEdge.put(adjacentVertex, edge);
}
}
}var currentVertex = minHeap.deleteMin();
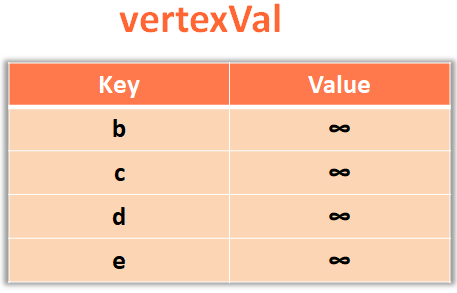
var spanningTreeEdge = vertexToEdge.get(currentVertex);
if(spanningTreeEdge != null) {
result.add(spanningTreeEdge);
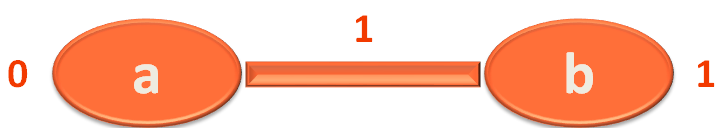
}
for(edge in getEdges(currentVertex)){
var adjacentVertex = edge.endVertex;
// We check if adjacent vertex exist in Map in Heap and length of the edge is with this vertex
// is greater than this edge length.
if(minHeap.containsVertex(adjacentVertex) && minHeap.getWeight(adjacentVertex)!! > edge.value){
// Replace the edge length with this edge weight.
minHeap.updateHeap(adjacentVertex, edge.value);
vertexToEdge.put(adjacentVertex, edge);
}
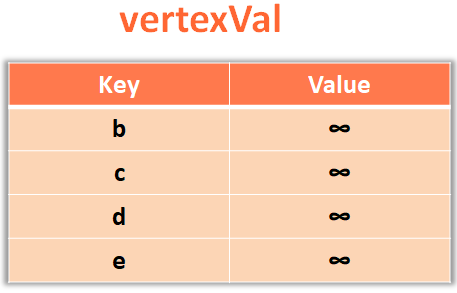
}
var adjacentVertex = edge.endVertex;
if(minHeap.containsVertex(adjacentVertex) && minHeap.getWeight(adjacentVertex)!! > edge.value){
// Replace the edge length with this edge weight.
minHeap.updateHeap(adjacentVertex, edge.value);
vertexToEdge.put(adjacentVertex, edge);
}minHeap.updateHeap(adjacentVertex, edge.value);
vertexToEdge.put(adjacentVertex, edge);
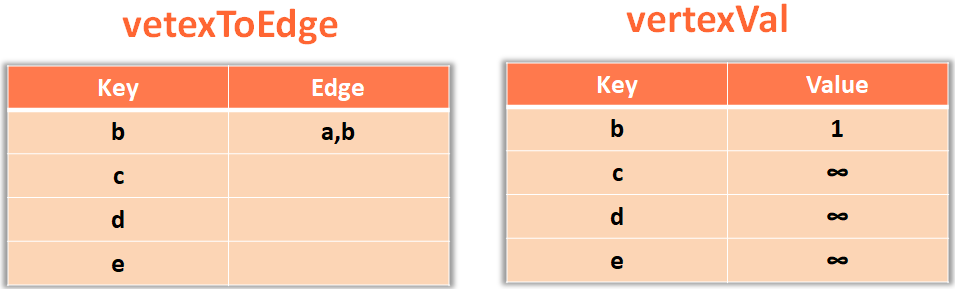
The similar process gets repeated and we get the Minimum Spanning Tree using Prim's Algorithm.
The time complexity of Prim's Algorithm for Minimum Spanning Tree is : O(E logV)
Where E is the Edge
And V is the Vertex
The time complexity O(E logV) is only when we will be using the above combination of MIn-Heap and Adjacency List.