import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class AdjacencyListGraph {
void insertVertex(LinkedList<String> vertices, String vertex) {
vertices.add(vertex);
}
void constructAdjacencyList(LinkedList<LinkedList<String>> adjcList, int u, String val) {
adjcList.add(new LinkedList<String>());
adjcList.get(u).add(val);
}
void printAdjacencyList(LinkedList<LinkedList<String>> adjcList, LinkedList<String> vertices) {
int i = 0;
for (String vtx : vertices) {
System.out.println("The Adjacency List for vertex "+vtx+" at index "+i+" :");
for (Iterator iter = adjcList.get(i).iterator() ; iter.hasNext(); ) {
System.out.print(iter.next()+" --> ");
}
System.out.println("\b\b\b\b");
i++;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
AdjacencyListGraph adjacencyListGraph = new AdjacencyListGraph();
LinkedList<String> vertices = new LinkedList<>();
LinkedList<LinkedList<String>> adjacencyList = new LinkedList<>();
// Insert Vertices
adjacencyListGraph.insertVertex(vertices, "a");
adjacencyListGraph.insertVertex(vertices, "b");
adjacencyListGraph.insertVertex(vertices, "c");
adjacencyListGraph.insertVertex(vertices, "d");
adjacencyListGraph.insertVertex(vertices, "e");
// Create Adjacency List
adjacencyListGraph.constructAdjacencyList(adjacencyList, 0, "b");
adjacencyListGraph.constructAdjacencyList(adjacencyList, 0, "c");
adjacencyListGraph.constructAdjacencyList(adjacencyList, 0, "d");
adjacencyListGraph.constructAdjacencyList(adjacencyList, 1, "a");
adjacencyListGraph.constructAdjacencyList(adjacencyList, 1 ,"e");
adjacencyListGraph.constructAdjacencyList(adjacencyList, 2, "a");
adjacencyListGraph.constructAdjacencyList(adjacencyList, 2, "d");
adjacencyListGraph.constructAdjacencyList(adjacencyList, 2, "e");
adjacencyListGraph.constructAdjacencyList(adjacencyList, 3, "a");
adjacencyListGraph.constructAdjacencyList(adjacencyList, 3 ,"c");
adjacencyListGraph.constructAdjacencyList(adjacencyList, 3, "e");
adjacencyListGraph.constructAdjacencyList(adjacencyList, 4, "b");
adjacencyListGraph.constructAdjacencyList(adjacencyList, 4, "c");
adjacencyListGraph.constructAdjacencyList(adjacencyList, 4, "d");
adjacencyListGraph.printAdjacencyList(adjacencyList, vertices);
}
}
There are two methods in the above code :
While the first method is quite simple.
void insertVertex(LinkedList<String> vertices, String vertex) {
vertices.add(vertex);
}
As the name of the method 'void insertVertex(...)' suggests. The method is used to add vertices to the Linked List.
Let us take the example to add the vertex 'a' to the Linked List.
So, in the 'main(...)' method, we have created a Linked List to hold the vertices.
LinkedList<String> vertices = new LinkedList<>();
Then we call the 'void insertVertex(...)' method and pass the Linked List 'vertices' and the vertex 'a' to the method.
adjacencyListGraph.insertVertex(vertices, "a");
Now, if we go to the definition of the 'void insertVertex(...)' method. We can see, there is just one line in it,
vertices.add(vertex);
That takes the vertex ('a' in this case) and adds it to the 'vertices' Linked List.
Next, let us come to the next method that creates the Adjacency List.
void constructAdjacencyList(LinkedList<LinkedList<String>> adjcList, int u, String val) {
adjcList.add(new LinkedList<String>());
adjcList.get(u).add(val);
}
Let's start with at the 'main(...)' method. Where we have defined a 2D Linked List to hold the Adjacency List.
LinkedList<LinkedList<String>> adjacencyList = new LinkedList<>();
But why do we need a 2D Linked List?
Let us look at the below diagram to get it clarified.
Vertex 'a' is at index '0'. Similarly, vertex 'b' is at index 1 and so on.

Now, we can consider the above as a 2D Linked List.
But How?
Let us take vertex 'a' at index '0'. Then take its Adjacent Vertices and pass it to 'void constructAdjacencyList(...)' method.
adjacencyListGraph.constructAdjacencyList(adjacencyList, 0, "b");
The first adjacent vertex of 'a' at index '0' is 'b'. So, we pass the index i.e. 0 and its adjacent vertex i.e. b.
Now let's go to the 'void constructAdjacencyList(...)' method definition.
And we come across the first line :
adjcList.add(new LinkedList<String>());
Now, since 'adjcList' is a 2D Linked List, we need to initialise the first row(As mentioned in the diagram) with a Linked List (i.e. new LinkedList<String>())
And this row will hold the Adjacent vertices of vertex 'a' at index '0' (i.e. b, c & d)
And then comes the line that will be adding elements to the above created Linked List.
adjcList.get(u).add(val);
So, in the above line, the first thing we do is, get the Linked List at index '0'
adjcList.get(0) [Since the value of 'u' is '0']
Then, add 'b' to the Lined List.
adjcList.get(0).add("b"); [Since, the value of 'val' is 'b'].
And the below Linked List is formed.

Then, we come to the next line in the 'main(...)' method.
adjacencyListGraph.constructAdjacencyList(adjacencyList, 0, "c");
The second adjacent vertex of 'a' at index '0' is 'c'. So, we pass the index i.e. 0 and its adjacent vertex i.e. c.
Now let's come to the 'void constructAdjacencyList(...)' method definition.
And we come across the first line :
adjcList.add(new LinkedList<String>());
And then comes the line that will be adding elements to the above created Linked List.
adjcList.get(u).add(val);
So, in the above line, the first thing we do is, get the Linked List at index '0'
adjcList.get(0) [Since the value of 'u' is '0']
Then, add 'c' to the Lined List.
adjcList.get(0).add("c"); [Since, the value of 'val' is 'c']
And the below Linked List is formed.

Similarly, we come to the next line in the 'main(...)' method.
adjacencyListGraph.constructAdjacencyList(adjacencyList, 0, "d");
The second adjacent vertex of 'a' at index '0' is 'd' . So , we pass the index i.e. 0 and its adjacent vertex i.e. d.
And the below Linked List is formed.
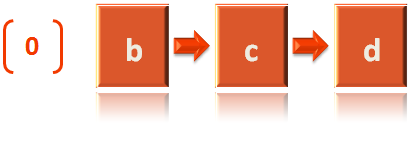
Now, us take vertex 'b' at index '1'. Then take its Adjacent Vertices and pass it to 'void constructAdjacencyList(...)' method.
adjacencyListGraph.constructAdjacencyList(adjacencyList, 1, "a");
The first adjacent vertex of 'b' at index '1' is 'a'. So, we pass the index i.e. 1 and its adjacent vertex i.e. a.
Now let's go to the 'void constructAdjacencyList(...)' method definition.
And we come across the first line :
adjcList.add(new LinkedList<String>());
Now, since 'adjcList' is a 2D Linked List, we need to initialise the 2nd row(As mentioned in the diagram) with a Linked List ( i.e. new LinkedList<String>())
And this row will hold the Adjacent vertices of vertex 'b' at index '1' ( i.e. a & e).
And then comes the line that will be adding elements to the above created Linked List.
adjcList.get(u).add(val);
So, in the above line, the first thing we do is, get the Linked List at index '1'
adjcList.get(1) [Since, the value of 'val' is 'c']
Then, add '1' to the Lined List.
adjcList.get(1).add("a"); [Since, the value of 'val' is 'a'].
And the below Linked List is formed.

And continuing this way we get the Adjacency List.