#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Sort {
public:
void insertionSort(int *arr, int size) {
for (int i=1; i < size; i++) {
int key = arr[i];
int j = i-1;
/* Insert arr[i] or key into the sorted sequence arr[0...i-1] */
while(j>=0 && arr[j] > key) {
arr[j+1] = arr[j];
j--;
}
arr[j+1] = key;
}
}
};
int main() {
int arr[] = {5, 3, 6, 2, 1, 4};
int size = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
Sort sort;
sort.insertionSort(arr, size);
for(int i=0; i < size; i++) {
cout << arr[i] << ", ";
}
}
We are just bothered about the void insertionSort(int *arr, int size) method, where the sorting logic is defined.
In the main() method, we have the array,
int arr[] = {5, 3, 6, 2, 1, 4};Then, we have calculated the size of the array,
int size = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
Then we have passed the array and the size of the array to the insertionSort(..) method.
Next, we are running a for loop which will iterate the array starting from the second element till the last element.
for (int i=1; i < n=size; i++)
And we are setting the 2nd element of the array as the key.
int key = arr[i];
i.e. Content of arr[1] is the key initially. So, the value of key is 3.
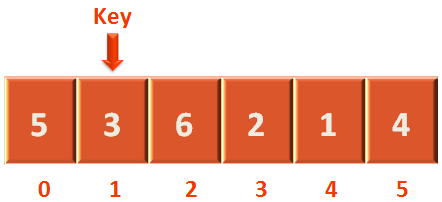
Then we make the value of j as i-1.
int j = i-1;
That's because we need to compare the key (i.e. arr[1]) with the left hand side elements (i.e. arr[0], where the value of j is 0) of the key.
And that is where the while loop comes into picture. Which takes care of the comparison of the key with the left hand side of the array.
while(j>=0 && arr[j] > key) {
arr[j+1] = arr[j];
j--;
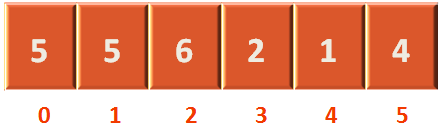
}The above while loop is quite self explanatory. Where, we are getting into the while loop if the key(i.e. value of arr[1] that is 3) is less than arr[j] (i.e. value of arr[0] that is 5).
And we are replacing the value of arr[j+1](i.e. arr[1]) with arr[j] (i.e. arr[0]).
arr[j+1] = arr[j];
Now, arr[1] contains 5. Also arr[0] contains 5, but arr[0] should be 3.
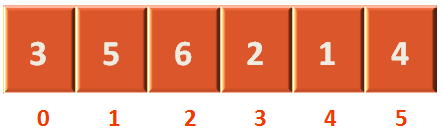
So, how the value of arr[0] is replaced by 3.
That happens when we get out of the loop, when the condition j>=0 is met by while loop.
And set the value of arr[0] with the key (i.e. 3).
arr[j+1] = key;
Since, -1+1 is 0. So the above is arr[0] = key.
And finally, arr[0] is set to 3.
Similar, process follows for the entire loop.
If we consider the Insertion Sort Algorithm, there are two loops. First is the for loop. And inside the for loop there is a while loop.
The for loop executes n times(Assuming the array contains n elements).
Now, for each iteration of for loop, the while loop also executes n times in worst case.
Which means for 1st iteration of for loop,
while loop runs 1 time.Similarly, for 2nd iteration of for loop,
while loop runs 2 times.Similarly, for nth iteration of for loop,
while loop runs n times.So, the running time is close to n*n or n^2.
So, in worst case the running time is O(n^2).
And in best case the running time is O(n).