So, we will start the coding by comparing the above nine step process. The coding for Merge sort is based on a technique called Recursion. If you are not aware of Recursion you can read it. However, in this tutorial, we will try to explain Recursion as much as possible.
package main
import "fmt"
func divideSort(arr []int, left int, right int) {
if(left < right) {
mid := (left + right) / 2 // Calculates the mid point of the array.
divideSort(arr, left, mid) // Sorts the left half of the array recursively.
divideSort(arr, mid+1, right) // Sorts the second part of the array recursively.
merge(arr, left, mid, right) // Merge or combine the both parts of array.
}
}
func merge(arr []int, start int, mid int, end int) {
// Let us take the starting point of left and right array.
leftStart := start
rightStart := mid+1
n := len(arr)
//Create temporary Array of same length as the initial array.
var arrTemp = make([]int, n)
//Copy the contents of the actual array to the temporary array.
for i := start ;i <= end ;i++ {
arrTemp[i] = arr[i]
}
for i := start ;i <= end ;i++ {
if (rightStart > end) {
arr[i] = arrTemp[leftStart]
leftStart++
} else if (leftStart > mid) {
arr[i] = arrTemp[rightStart]
rightStart++
} else if(arrTemp[leftStart] < arrTemp[rightStart]) {
arr[i] = arrTemp[leftStart]
leftStart++
} else {
arr[i] = arrTemp[rightStart]
rightStart++
}
}
}
func main() {
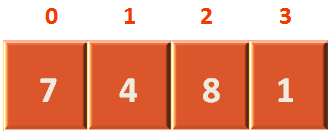
arr := []int{7, 4, 8, 1}
fmt.Println("Array before Sorting")
for _, val := range arr {
fmt.Println(val)
}
fmt.Println()
divideSort(arr, 0, len(arr)-1)
fmt.Println("Array after Sorting");
for _, val := range arr {
fmt.Println(val)
}
}
In the above code we have two methods:
func divideSort(arr []int, left int, right int)
and
func merge(arr []int, start int, mid int, end int)
The first method func divideSort(...) divides the Array into two parts and then sorts them individually.
And the next method func merge(...) merges the splited lists after sorting them.
func divideSort(arr []int, left int, right int) {
if(left < right) {
mid := (left + right) / 2 // Calculates the mid point of the array.
divideSort(arr, left, mid) // Sorts the left half of the array recursively.
divideSort(arr, mid+1, right) // Sorts the second part of the array recursively.
merge(arr, left, mid, right) // Merge or combine the both parts of array.
}
}So, we are passing the array arr, its starting point i.e. 0(mentioned left) and the end point i.e. arr.length-1 (mentioned right).
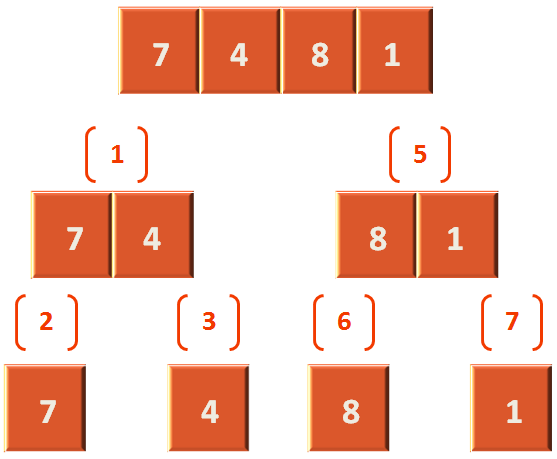
The array contains (1, 4, 7, 8). And the left is 0. The length of the array is 4. Which means (4-1), i.e. 3. So, the right is 3.
In the next step we check
if(left < right)
Which means the array length should be more than 1.
Then we calculate the mid point of the array, so that we can divide the array into two parts.
Now, comes the fun part.
divideSort(arr, left, mid);
We call the divideSort(...) method from the divideSort(...) method. And this is called recursion. Where a method keeps on calling itself until it comes to an end. And it maintains an internal stack which is hidden from the programmer.
Let us see it in brief,

if(left < right)
mid := (left + right) / 2

if(left < right)
divideSort(arr, left, mid);
divideSort(arr, mid+1, right);
merge(arr, left, mid, right);

if(left < right)

The merge(...) method has the following lines of code:
func merge(arr []int, start int, mid int, end int) {
// Let us take the starting point of left and right array.
leftStart := start
rightStart := mid+1
n := len(arr)
//Create temporary Array of same length as the initial array.
var arrTemp = make([]int, n)
//Copy the contents of the actual array to the temporary array.
for i := start ;i <= end ;i++ {
arrTemp[i] = arr[i]
}
for i := start ;i <= end ;i++ {
if (rightStart > end) {
arr[i] = arrTemp[leftStart]
leftStart++
} else if (leftStart > mid) {
arr[i] = arrTemp[rightStart]
rightStart++
} else if(arrTemp[leftStart] < arrTemp[rightStart]) {
arr[i] = arrTemp[leftStart]
leftStart++
} else {
arr[i] = arrTemp[rightStart]
rightStart++
}
}
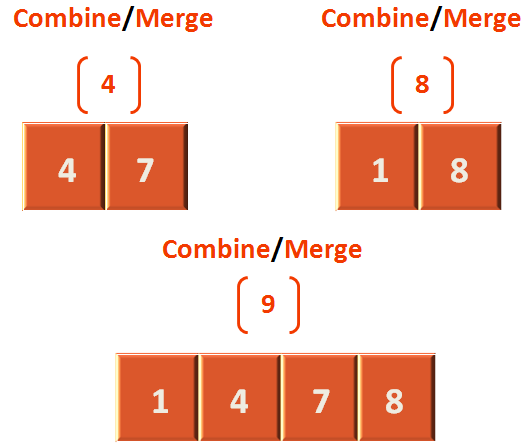
}As we know merging is a process where we combine two sorted arrays/lists after sorting them.
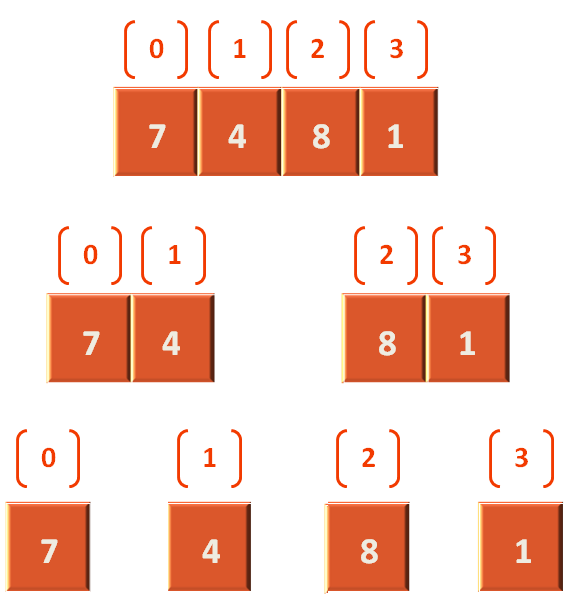
Let us take the lists from step 4 and step 8 and see how they are merged after sorting.
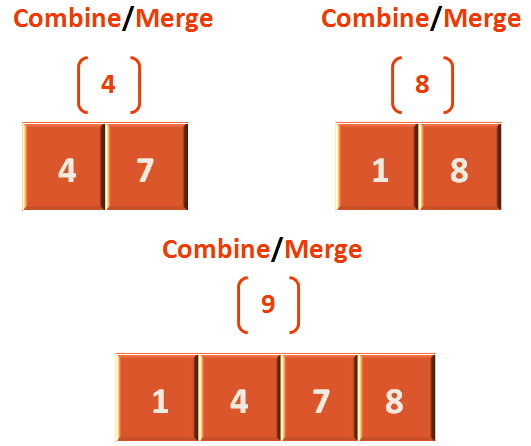
Seeing the above diagram, in void merge(int arr[], int start, int mid, int end) method, we pass the array, arr that contains the values (4,7,1,8). Where start is 0, mid is 1 and end is 3. We have assumed that (4,7) is the left half and (1,8) is the right half.
Now, we have to combine them using the above method.
Initially, we have taken the starting point of the left and right arrays.
leftStart := start rightStart := mid+1;
Which means, leftStart = 0 and rightStart = mid + 1, which is, rightStart = 2.
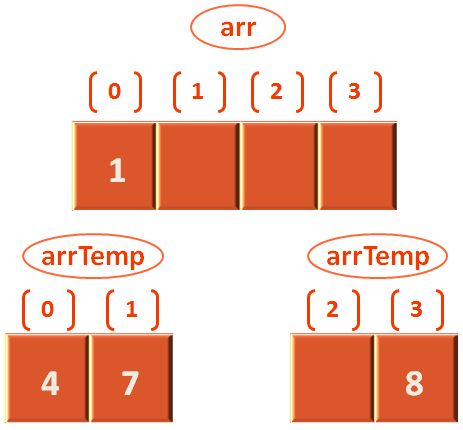
Next, we create a temporary array,
var arrTemp = make([]int, n)
And copy the contents of the actual array arr[] to the temporary array arrTemp[].
for i := start ;i <= end ;i++ {
arrTemp[i] = arr[i]
}Then we run a loop, inside which the actual merge happens after sorting.
for i := start ;i <= end ;i++
We will explain the usage of the condition,
if (rightStart > end)
And
else if (leftStart > mid)
But, at first let us jump to the condition,
else if(arrTemp[leftStart] < arrTemp[rightStart]) {
arr[i] = arrTemp[leftStart]
leftStart++
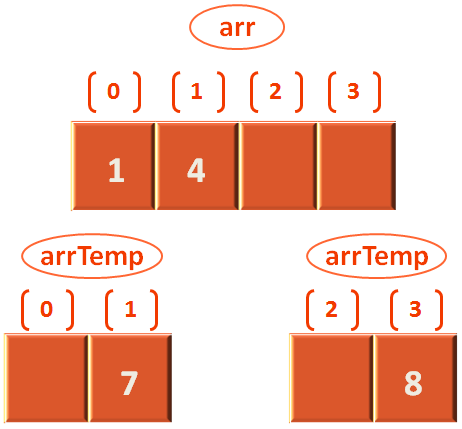
}As we have seen, leftStart = 0 and rightStart = 2.
So, the above condition doesn't match as arrTemp[leftStart] i.e. 4 is greater than arrTemp[rightStart] i.e. 1.
And we jump to the else condition,
else {
arr[i] = arrTemp[rightStart]
rightStart++
}And arr[0] is initialized with the value from arrTemp[2] i.e. 1. Also we increment rightStart by 1. So, rightStart is 3 now.
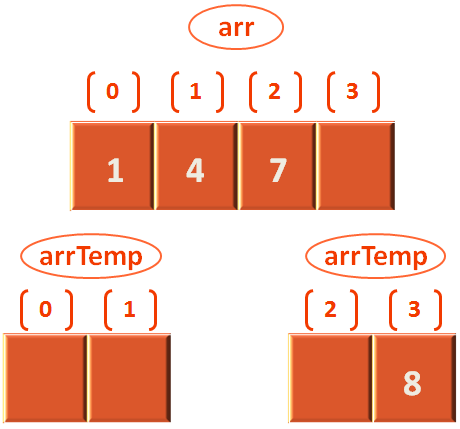
Again, we check with the if conditions and finally reach the condition,
else if(arrTemp[leftStart] < arrTemp[rightStart]) {
arr[i] = arrTemp[leftStart];
leftStart++;
}And, arrTemp[leftStart] is arrTemp[0] and arrTemp[rightStart] is arrTemp[3] as rightStart is 3.
Which means 4 is less than 8. So, we initialise arr[1] with arrTemp[leftStart] i.e. 4. And leftStart is incremented by 1. i.e. leftStart is 1 now.
Once again, after all the if conditions, we come to the condition
else if(arrTemp[leftStart] < arrTemp[rightStart]) {
arr[i] = arrTemp[leftStart]
leftStart++
}And, arrTemp[leftStart] is arrTemp[1] as leftStart is 1 and arrTemp[rightStart] is arrTemp[3] as rightStart is 3.
Which means 7 is less than 8. So, we initialise arr[2] with arrTemp[leftStart] i.e. 7. And leftStart is incremented by 1. i.e. leftStart is 2 now.
So, the condition,
else if (leftStart > mid) {
arr[i] = arrTemp[rightStart]
rightStart++
}matches and arr[3] is assigned with the value 3 from arrTemp[rightStart] i.e. arrTemp[3].
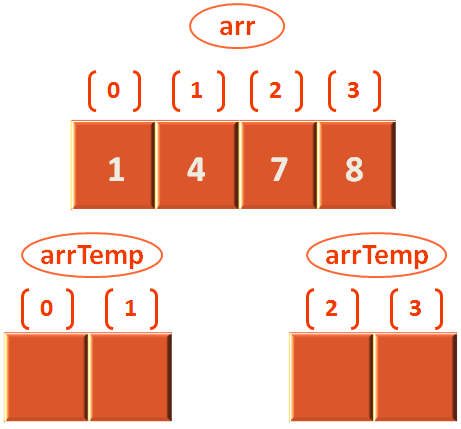
And we come to the end of the for loop and find the elements are sorted.
There are complicated processes to understand the efficiency/running for Merge Sort. But we will keep it simple, so that it becomes simple to understand and we can calculate the running time for any algorithm this way.
Let us look at the entire process to calculate the Running time:
At first we keep on dividing the Array by calculating the mid point.
And the above step only takes constant time or O(1) because we are just dividing the array by calculating the mid point.
Then we will sort each divided arrays and then merge them after sorting. Let us see the below diagram and understand it,
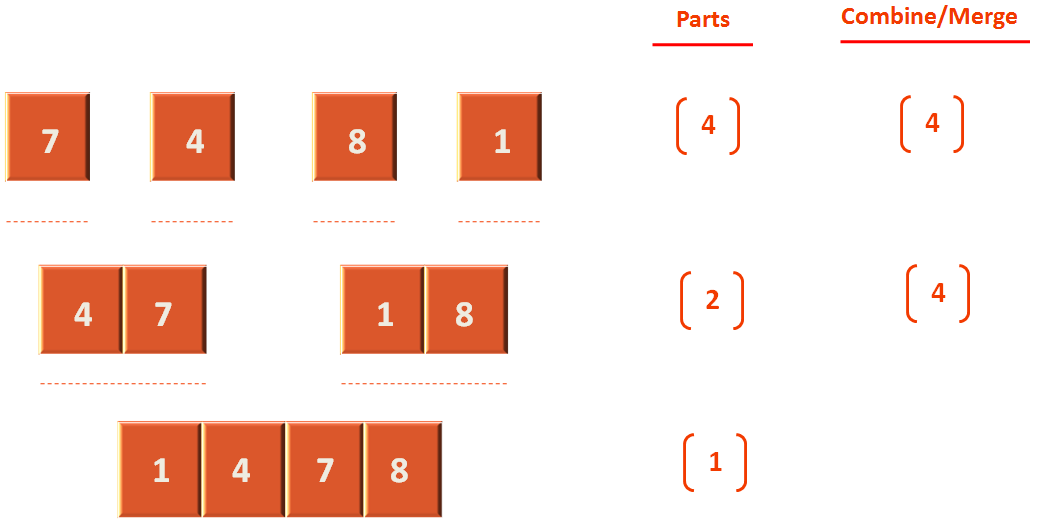
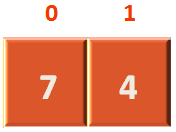
At the top level we have divided the Array into 4 parts. Although, they contain single elements. Still we can assume that we will sort each element. Then in the merge/combine step, we group them as two elements and sort them. So, combine/merge step will run 4 times
Next, the lists are divided into two parts. So, we can assume we have to sort 2 lists individually. And the combine/merge step will run 4 times because it will compare each element in both arrays.
And finally we have the main array which is one.
To understand it better, let us take an array of size 8.

So, at first we divide the array that will take constant time.
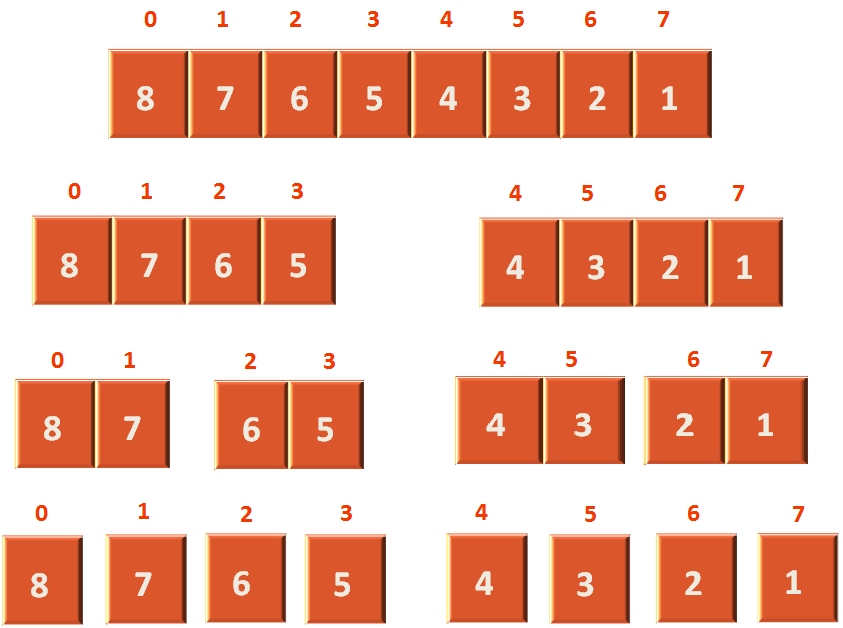
Then we will sort each divided arrays and then merge them after sorting. Let us see the below diagram and understand it,
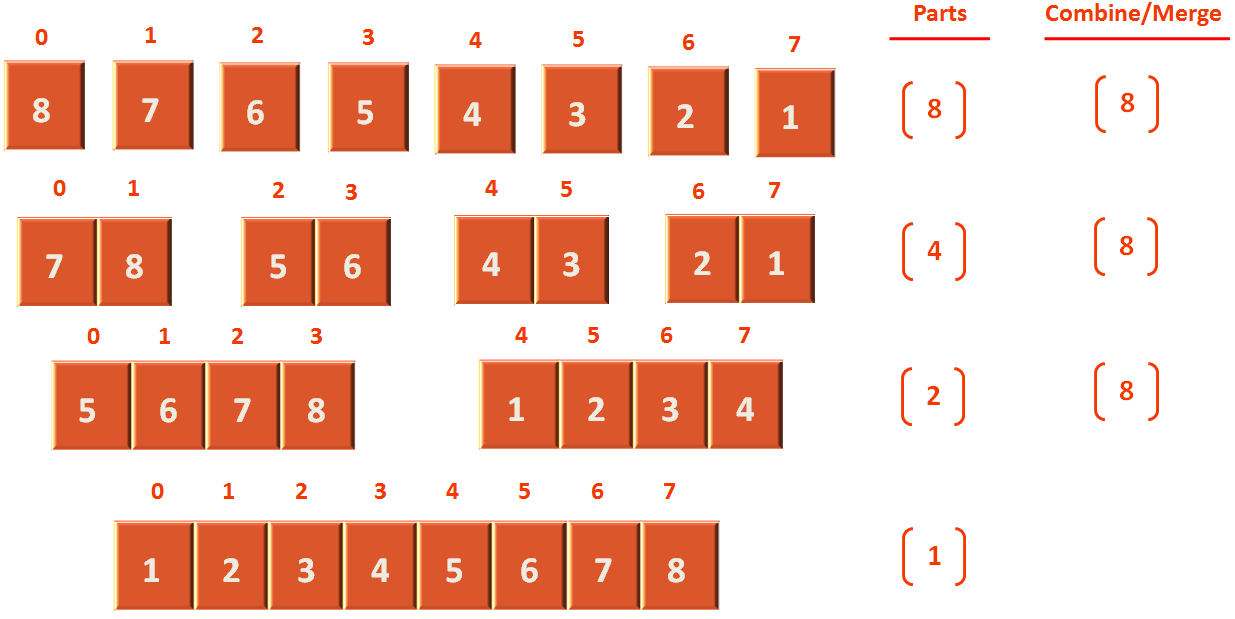
Now, if we consider the above diagram. Although, the merge/combining happens 8 times in each level. But the parts on which it does the merge/combining comes down in the order 8, 4, 2, 1. Which has 4 levels. And the other way to represent this order is log 8.
We know that the size of the Array is 8 or n. So, the time taken by merge/combine step is n. And the time taken to combine each part is log n.
So, if we consider the total running time. It becomes O(nlog n).
And since, it compares by dividing the Array. The running time in,
Best Case : O(nlogn)
Average Case : O(nlogn)
Worst Case : O(nlogn)