class Node(value: Int) {
var data: Int = 0;
var left: Node? = null;
var right: Node? = null;
var height: Int = 1;
var size: Int = 0;
init {
data = value;
left = null;
right = null;
}
}
class AVLTree {
fun leftRotate(rootNode: Node?): Node? {
var newRoot: Node? = rootNode!!.right;
rootNode!!.right = rootNode.right!!.left;
newRoot!!.left = rootNode;
rootNode.height = setHeight(rootNode);
rootNode.size = setSize(rootNode);
newRoot.height = setHeight(newRoot);
newRoot.size = setSize(newRoot);
return newRoot;
}
fun rightRotate(rootNode: Node?): Node? {
var newRoot: Node? = rootNode!!.left;
rootNode!!.left = rootNode.left!!.right;
newRoot!!.right = rootNode;
rootNode.height = setHeight(rootNode);
rootNode.size = setSize(rootNode);
newRoot.height = setHeight(newRoot);
newRoot.size = setSize(newRoot);
return newRoot;
}
fun setSize(rootNode: Node?): Int {
if (rootNode == null) {
return 0;
}
return 1 + Math.max(
(if (rootNode.left != null) rootNode.left!!.size else 0),
(if (rootNode.right != null) rootNode.right!!.size else 0)
);
}
fun insert(rootNode: Node?, data: Int): Node? {
var rtNode: Node?;
if (rootNode == null) {
rtNode = Node(data);
return rtNode;
}
if (data < rootNode.data)
rootNode.left = insert(rootNode.left, data);
else if (data > rootNode.data)
rootNode.right = insert(rootNode.right, data);
var balanceFactor = balance(rootNode.left, rootNode.right);
if (balanceFactor > 1) {
if (height(rootNode.left!!.left) >= height(rootNode.left!!.right)) {
rtNode = rightRotate(rootNode);
} else {
rootNode.left = leftRotate(rootNode.left);
rtNode = rightRotate(rootNode);
}
} else if (balanceFactor < -1) {
if (height(rootNode.right!!.right) >= height(rootNode.right!!.left)) {
rtNode = leftRotate(rootNode);
} else {
rootNode.right = rightRotate(rootNode.right);
rtNode = leftRotate(rootNode);
}
} else {
rootNode.height = setHeight(rootNode);
rootNode.size = setSize(rootNode);
rtNode = rootNode;
}
return rtNode;
}
fun balance(rootNodeLeft: Node?, rootNodeRight: Node?): Int {
return height(rootNodeLeft) - height(rootNodeRight);
}
fun setHeight(rootNode: Node?): Int {
if (rootNode == null) {
return 0;
}
return 1 + Math.max(
(if (rootNode.left != null) rootNode.left!!.height else 0),
(if (rootNode.right != null) rootNode.right!!.height else 0)
);
}
fun height(rootNode: Node?): Int {
if (rootNode == null) {
return 0;
} else {
return rootNode.height;
}
}
}
class TreeTraversal {
var root: Node? = null;
fun inOrder(node: Node?) {
if (node != null) {
inOrder(node.left);
print("${node.data} ");
inOrder(node.right);
}
}
}
fun main(arr: Array<String>) {
var avlTree = AVLTree();
var root: Node? = null;
root = avlTree.insert(root, 16);
root = avlTree.insert(root, 10);
root = avlTree.insert(root, 25);
root = avlTree.insert(root, 2);
root = avlTree.insert(root, 13);
root = avlTree.insert(root, 18);
root = avlTree.insert(root, 30);
root = avlTree.insert(root, 7);
root = avlTree.insert(root, 8);
var tt = TreeTraversal();
println("Inorder Traversal : \n");
tt.inOrder(root);
}
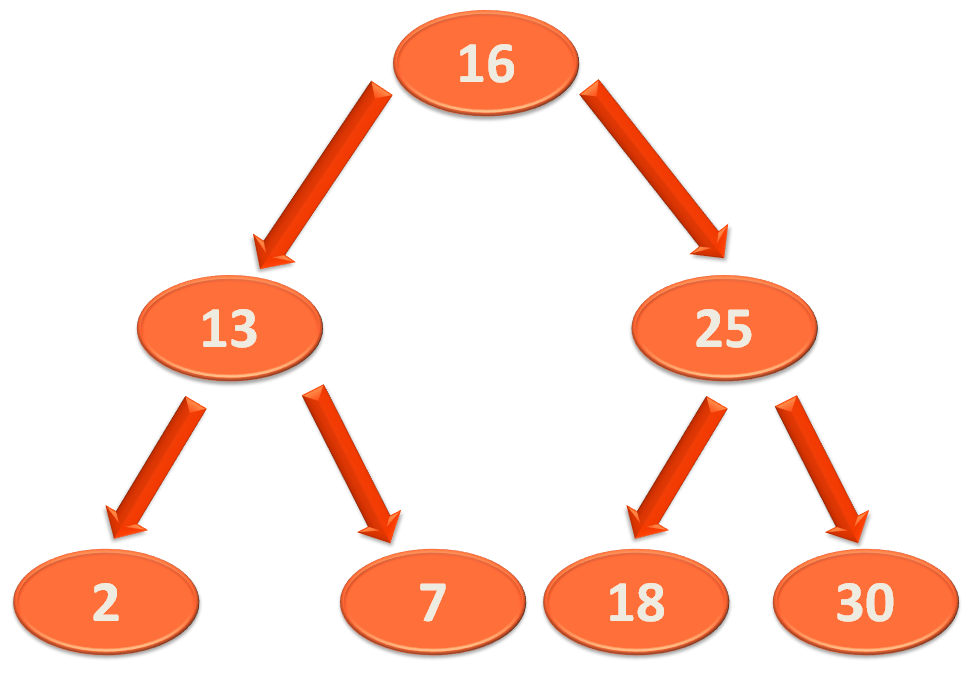
So, we will constructing the below Balanced Binary Search Tree, by inserting the elements one by one.
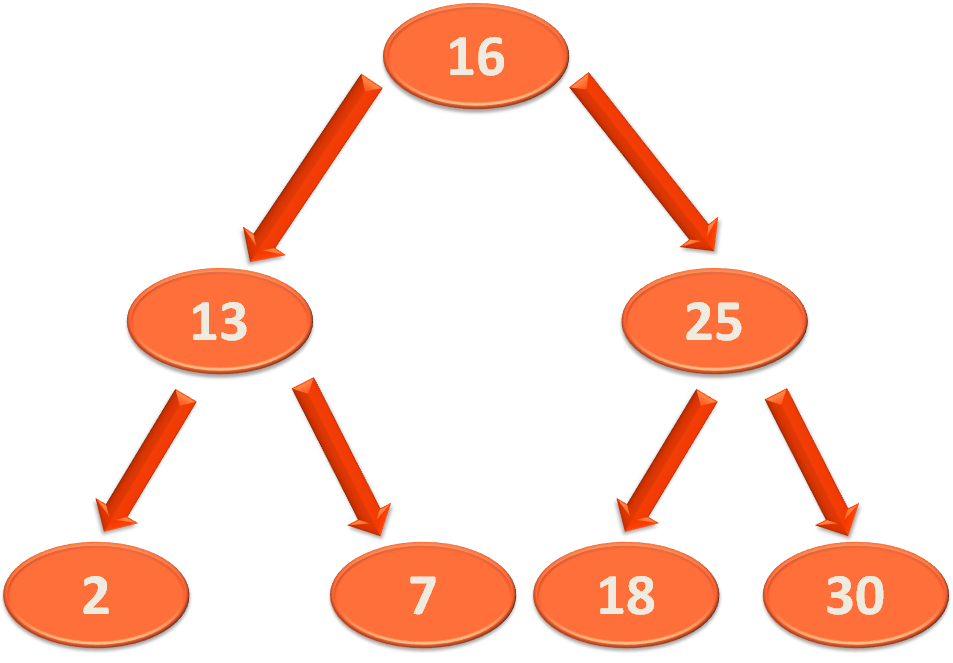
And we have the below methods :
Firstly, we would be constructing the above Binary Search Tree, with the help of insert method.
var root: Node? = null; root = avlTree.insert(root, 16);
Initially, the variable root is null. So, we take the element i.e. 16 in this case. And pass the root and the element 16 to the insert method.
fun insert(rootNode: Node?, data: Int): Node? {
var rtNode: Node?;
if (rootNode == null) {
rtNode = Node(data);
return rtNode;
}
if (data < rootNode.data)
rootNode.left = insert(rootNode.left, data);
else if (data > rootNode.data)
rootNode.right = insert(rootNode.right, data);
var balanceFactor = balance(rootNode.left, rootNode.right);
if (balanceFactor > 1) {
if (height(rootNode.left!!.left) >= height(rootNode.left!!.right)) {
rtNode = rightRotate(rootNode);
} else {
rootNode.left = leftRotate(rootNode.left);
rtNode = rightRotate(rootNode);
}
} else if (balanceFactor < -1) {
if (height(rootNode.right!!.right) >= height(rootNode.right!!.left)) {
rtNode = leftRotate(rootNode);
} else {
rootNode.right = rightRotate(rootNode.right);
rtNode = leftRotate(rootNode);
}
} else {
rootNode.height = setHeight(rootNode);
rootNode.size = setSize(rootNode);
rtNode = rootNode;
}
return rtNode;
}The first line of the insert(...) checks if the rootNode is null or not.
if (rootNode == null) {
rootNode = Node(data);
return rootNode;
}And in this case rootNode is null. So, we create a new Node object with the data i.e. 16. And the Node object is created with the below constructor.
class Node(value: Int)
init {
data = value;
left = null;
right = null;
}Then assign it to the Node object root.
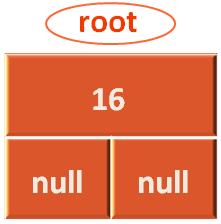
And return the Node root.
return root;
In the next line we try to insert the element 13 in the Binary Search Tree using the insert(...) method.
root = avlTree.insert(root, 10);
And the insert(...) method is called.
And in the similar way we check,
if (data < rootNode.data) rootNode.left = insert(rootNode.left, data); else if (data > rootNode.data) rootNode.right = insert(rootNode.right, data);
If the data i.e. 13 is less than the root element root.data. And the first condition matches.
if (data < rootNode.data) rootNode.left = insert(rootNode.left, data);
And a recursive call is made to insert(...) method.
rootNode.left = insert(rootNode.left, data);
So, the method executes and sets the value of rootNode.left with this Node that contains 13.
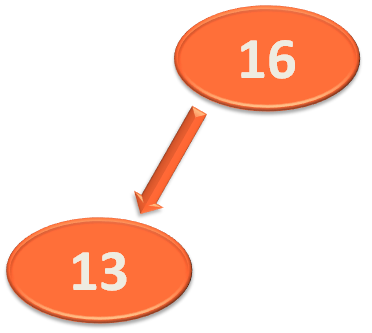
And since we are dealing with AVL tree, it is time to calculate the Balance Factor.
var balanceFactor = balance(rootNode.left, rootNode.right);
And the balance(...) method is called.
fun balance(rootNodeLeft: Node?, rootNodeRight: Node?): Int {
return height(rootNodeLeft) - height(rootNodeRight);
}And the balance(...) method is quite simple to understand. It calls the height(...) method for the Left Node and Right Node and calculates the difference between Left and Right Node.
And as we know, Balance Factor is the difference of Left and Right Node.
And now since we got the Balance Factor, we need to perform Left or Right rotation if the value of Balance Factor is other than -1, 0 or 1.
if (balanceFactor > 1) {
if (height(rootNode.left!!.left) >= height(rootNode.left!!.right)) {
rtNode = rightRotate(rootNode);
} else {
rootNode.left = leftRotate(rootNode.left);
rtNode = rightRotate(rootNode);
}
} else if (balanceFactor < -1) {
if (height(rootNode.right!!.right) >= height(rootNode.right!!.left)) {
rtNode = leftRotate(rootNode);
} else {
rootNode.right = rightRotate(rootNode.right);
rtNode = leftRotate(rootNode);
}
} else {
rootNode.height = setHeight(rootNode);
rootNode.size = setSize(rootNode);
rtNode = rootNode;
}So, if the Balance Factor is greater than 1.
if (balanceFactor > 1) {
if (height(rootNode.left!!.left) >= height(rootNode.left!!.right)) {
rtNode = rightRotate(rootNode);
} else {
rootNode.left = leftRotate(rootNode.left);
rtNode = rightRotate(rootNode);
}
}We go to the left child of the rootNode and try checking, if the height of the left child of the left node is greater than the height of the right child of the left node.
if (height(rootNode.left!!.left) >= height(rootNode.left!!.right)) {
rtNode = rightRotate(rootNode);
}If the above condition satisfies, then we can assume that we need to right rotate the tree.
And the rightRotate(...) method is called to balance the tree.
fun rightRotate(rootNode: Node?): Node? {
var newRoot: Node? = rootNode!!.left;
rootNode!!.left = rootNode.left!!.right;
newRoot!!.right = rootNode;
rootNode.height = setHeight(rootNode);
rootNode.size = setSize(rootNode);
newRoot.height = setHeight(newRoot);
newRoot.size = setSize(newRoot);
return newRoot;
}Let us take the below example to understand the rightRotate(...) method.
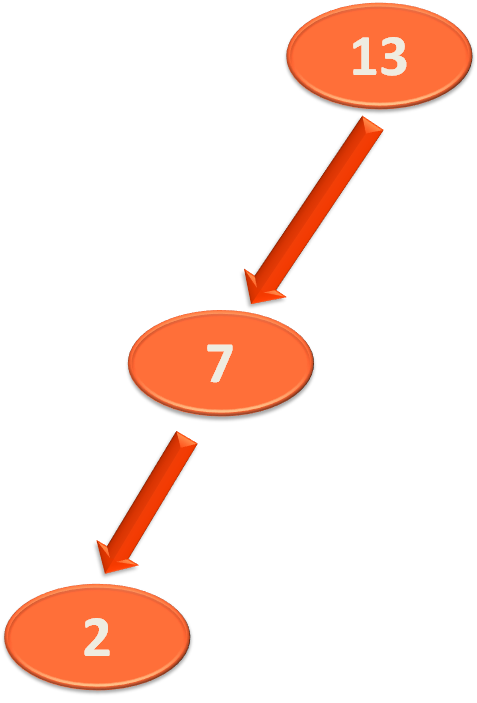
Say, rootNode has the element 13.
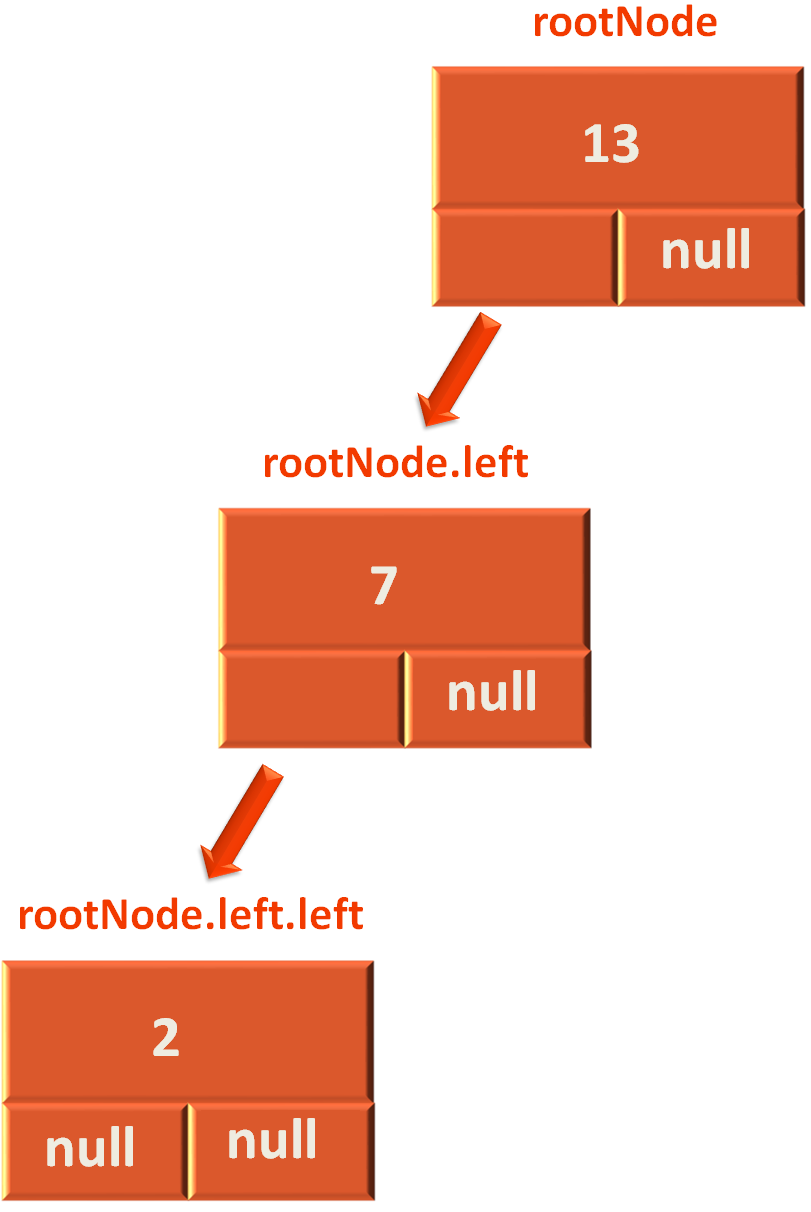
Now, we create a Node named newNode and assign the Node rootNode.left to it.
var newRoot: Node? = rootNode!!.left;
And as we can see in the above diagram rootNode.left has the element 7 in it.
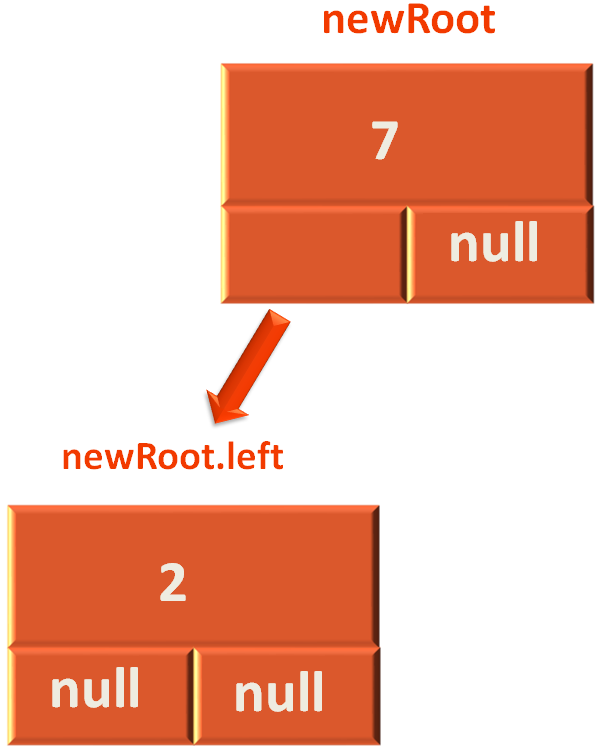
Then we take the rootNode.left.right (i.e. The right child of 7, which is null in the above case) and assign it to rootNode.left.
rootNode.left = rootNode.left.right;
And the below tree looks like,
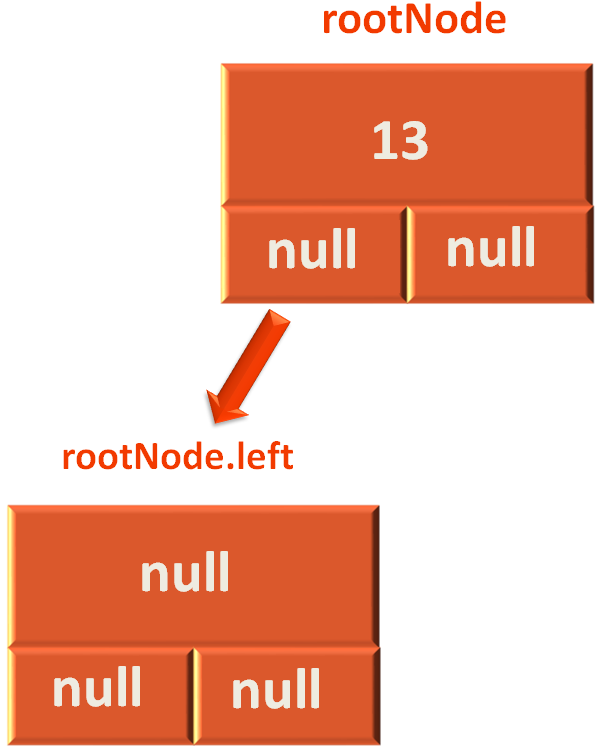
Next, we take the rootNode and assign it as the right child of the newly created Node newRoot.
newRoot.right = rootNode;
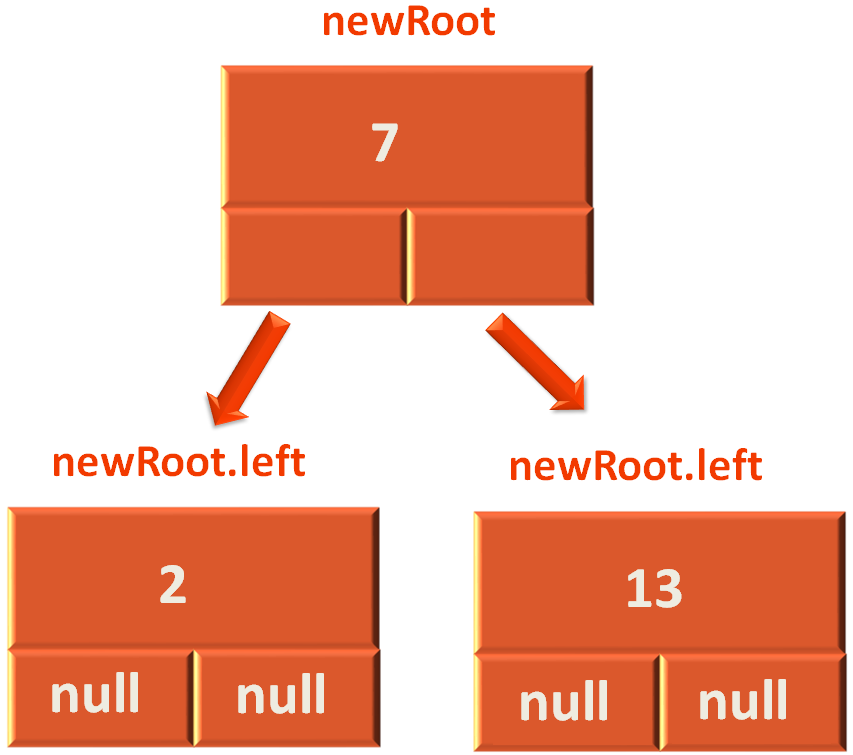
So, the right rotation is performed,
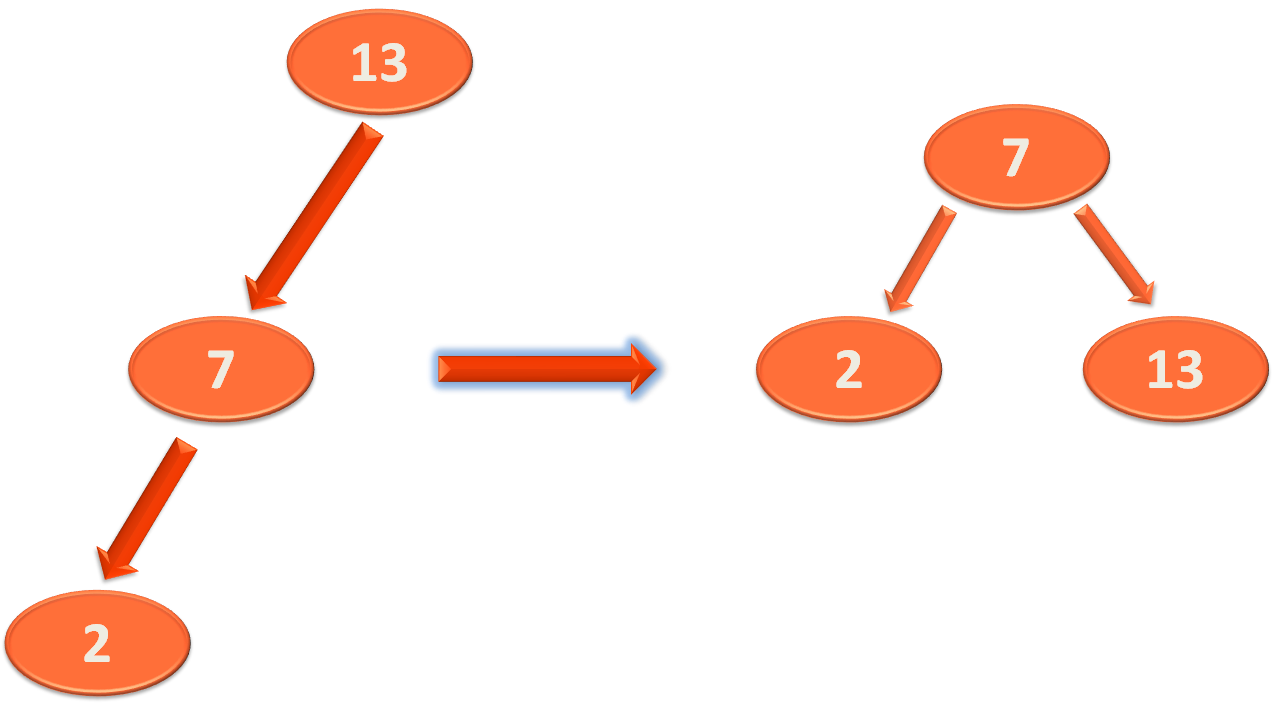
The rest few lines of the method is quite easy to understand.
The height is set by calling the setHeight(...) method.
rootNode.height = setHeight(rootNode);
And finally, the Node newRoot is returned.
return newRoot;
And continuing this way we get the below AVL tree.