class Node(value: String) {
var data: String = "";
var left: Node?;
var right: Node?;
init {
data = value;
left = null;
right = null;
}
}
class TreeTraversal {
var root: Node? = null;
init {
root = null;
}
fun preorder(node: Node?) {
if (node != null) {
print(node.data + " ");
preorder(node.left);
preorder(node.right);
}
}
fun postorder(node: Node?) {
if (node != null) {
postorder(node.left);
postorder(node.right);
print(node.data + " ");
}
}
fun inorder(node: Node?) {
if (node != null) {
inorder(node.left);
print(node.data + " ");
inorder(node.right);
}
}
}
fun main(arr: Array<String>) {
var treeTraversal = TreeTraversal();
treeTraversal.root = Node("A");
treeTraversal.root!!.left = Node("B");
treeTraversal.root!!.right = Node("C");
treeTraversal.root!!.left?.right = Node("D");
treeTraversal.root!!.right?.left = Node("E");
println("Preorder traversal : ");
treeTraversal.preorder(treeTraversal.root);
println("\n");
println("Postorder traversal : ");
treeTraversal.postorder(treeTraversal.root);
println("\n");
println("Inorder traversal : ");
treeTraversal.inorder(treeTraversal.root);
}
So, in this case we have taken the below Tree and and calculated the Preorder, Postorder and Inorder Traversal for the below Tree.
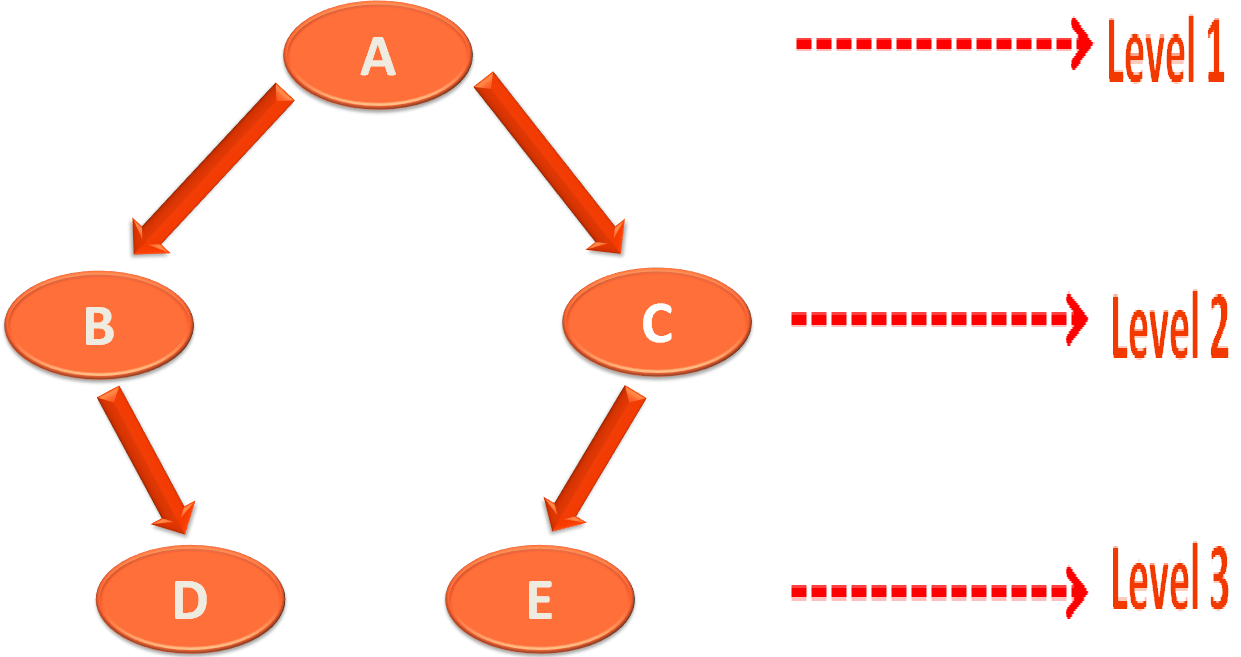
Just remember, we have used a process called Recursion. Where Kotlin maintains an internal Stack to remember the visited Nodes. So, that the Nodes are not visited twice.
So, we have a Node class,
class Node(value: String) {
var data: String = "";
var left: Node?;
var right: Node?;
init {
data = value;
left = null;
right = null;
}
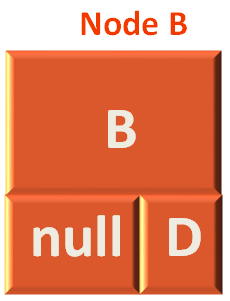
}To understand the Node class, let us take any Node and understand it in detail.
Let us take the Node A as example.
So, the Node A has a name i.e A. A Left part that should hold the Left Node i.e. B and a Right part to hold the Right Node i.e. C.
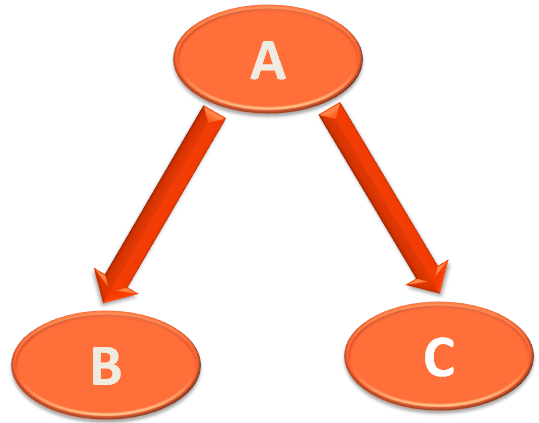
Now, if you look at the Node class. It has String type attribute String data to hold name of the Node i.e. A.
There is also a Node type attribue Node left that holds the left Node of A, i.e. B and there is a Node type attribue Node right that holds the right Node of A, i.e. C.
So, Node A looks somewhat like,

Now, let us see the Tree Traversal in action.
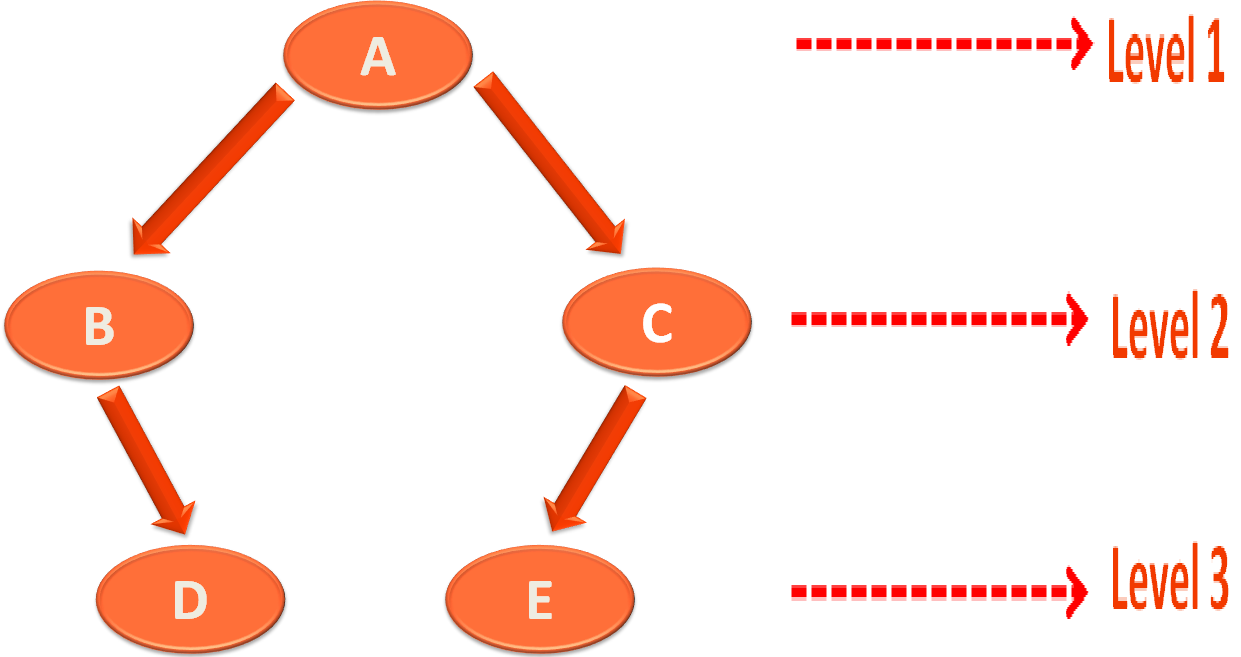
So, at first we construct the Tree,
treeTraversal.root = Node("A");
treeTraversal.root!!.left = Node("B");
treeTraversal.root!!.right = Node("C");
treeTraversal.root!!.left?.right = Node("D");
treeTraversal.root!!.right?.left = Node("E");And there is the constructor in the Node class that helps us create the Nodes.
class Node(value: String)
init {
data = value;
left = null;
right = null;
}And the tree is constructed,
Next, we start the Preorder Traversal,
treeTraversal.preorder(treeTraversal.root);
And the preorder(Node node) method is called, and just remember that we are passing the root Node to the method.
fun preorder(node: Node?) {
if (node != null) {
print(node.data + " ");
preorder(node.left);
preorder(node.right);
}
}Although, the lines of code looks very less. It is because, the recursion process is doing a lot for us. And it all happens internally, hidden from us.
Let us understand the process in detail.
So, the root Node is A and the node variable has the details of Node A in it.

In the first line we perform a null check
if (node != null)
And then begin the Preorder Traversal. And the rule is Root --> Left --> Right.
i.e. We visit the root element first, then visit all the elements of the Left Sub-Tree and finally, visit all the elements of the Right Sub-Tree.
So, as per the rule we will visit the root Node A and print it first.
print(node.data + " ");
So, the result is :
A
Then we are suppose to visit all the elements of the Left Sub-Tree. And thus we call the preorder(...) method from itself, by passing the Left Node i.e. B (As node.left contains B).
preorder(node.left);
Now, the preorder(...) method is called again. And this time Node B becomes the new root element.
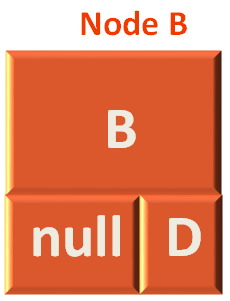
And once again the same method is executed with Node B.
fun preorder(node: Node?) {
if (node != null) {
print(node.data + " ");
preorder(node.left);
preorder(node.right);
}
}Even in this case, as per the Preorder traversal process Root --> Left --> Right. We print the new root element B.
print(node.data + " ");
So, the result is :
A B
And once again we call the preorder(...) method.
preorder(node.left);
And this time node.left is null. Because B has no left element.
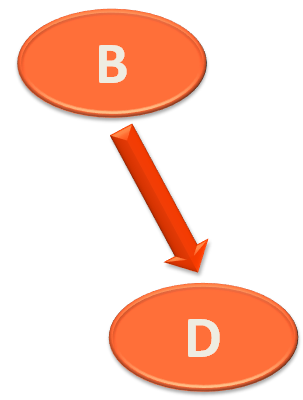
So, preorder(...) method is called with the new root element as null.
fun preorder(node: Node?) {
if (node != null) {
print(node.data + " ");
preorder(node.left);
preorder(node.right);
}
}And this time node variable is null. So, the method execution ends here.
if (node != null)
But ! Just Hold on !
The program execution has not yet ended. This is the time when kotlin starts backtracking.
Don't get scared by the word backtracking. We will understand it eventually.
Now, just think! The method execution in the above case was not completed. i.e. The line preorder(node.right) never got executed. Well! Kotlin also remembers it.
And Kotlin does a time travel and goes back to the time when the method executed with Node B.
fun preorder(node: Node?) {
if (node != null) {
print(node.data + " ");
preorder(node.left);
preorder(node.right);
}
}
And executes the unfinished line,
preorder(node.right);
And this time preOrder(...) method is called with Node D.
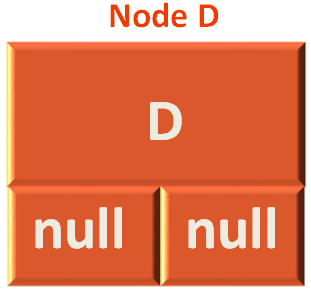
And same way, Node D would be printed.
print(node.data + " ");
So, the result is :
A B D
And since, there are no children of Node D. It is time to complete the unfinished execution, i.e. When Node A was the root element.

fun preorder(node: Node?) {
if (node != null) {
print(node.data + " ");
preorder(node.left);
preorder(node.right);
}
}And we come to the unfinished line of preorder(...) method.
i.e.
preorder(node.right);
And think logically, we are done with the root element A. Also we are done traversing all the elements of the Left Sub-Tree B. And now, it's time for us to traverse the Right Sub-Tree C.
So, this time the method preorder(...) is called with the root Node C.
fun preorder(node: Node?) {
if (node != null) {
print(node.data + " ");
preorder(node.left);
preorder(node.right);
}
}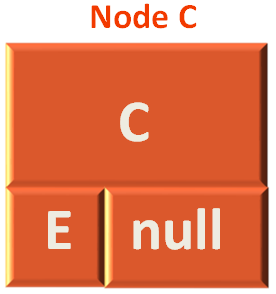
Since the root Node is C. So, we print C.
print(node.data + " ");
So, the result is :
A B D C
Then the preOrder(...) method is called with E as root(Since, E is the left child of C).
preorder(node.left);
And the method is called again printing C.
A B D C E
And finally, all the elements are visited and with this we complete the Preorder traversal.
And exactly the same execution pattern follows for the methods :