Although Stack Data Structure is already defined in Ruby's Ruby.util package. But for the sake of learning, we will define our own Stack class and define all the methods there.
def push(i)
if (size() == $SIZE)
puts "Stack Overflow"
return false
else
$stackArray.push(i)
return true
end
end
def pop()
element = 0
if (isEmpty())
puts "Stack is Empty"
return -1
else
element = $stackArray.pop()
print("The element ",element," is popped out of the Stack \n")
return element
end
end
def top()
if (isEmpty())
puts "Stack is Empty"
return -1
else
print("The top element is ",$stackArray[$stackArray.length-1],"\n")
return $stackArray[$stackArray.length-1]
end
end
def size()
return $stackArray.length
end
def isEmpty()
return ($stackArray.length<0)
end
$SIZE = 10
$stackArray = []
push(10)
push(20)
push(30)
top()
pop()
pop()
pop()
As we know the most important operations/methods of Stack are Push and Pop. However, there are other methods that we will be using here.
So, we have the below methods :
So, at first, we define the array where we will be storing the elements of the Stack.
$stackArray = []
Also, we have defined a constant called SIZE where we have defined the size of the array.
$SIZE = 10
Now, let us go to the main program and see the Stack in action.
So, initially we have an empty Stack.
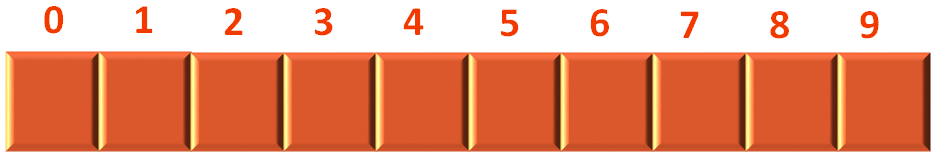

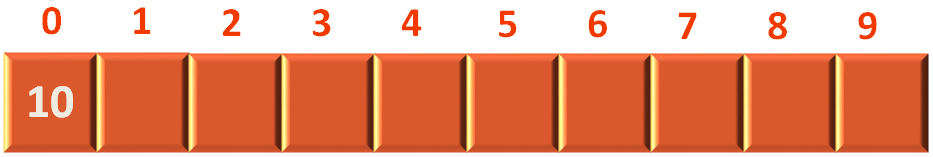
Then we try to push the element 10 into the Stack
push(10)
So, the push() method is called,
def push(i) if (size() == $SIZE) puts "Stack Overflow" return false else $stackArray.push(i) return true end end
Now, the push() method calls the size() method to check the size of the Array.
def size() return $stackArray.length end
The size() method returns $stackArray.length.
So, size() method returns size of the array i.e. 0.
So, we are back in the push() method with the value 0 returned from size() method.
Now, in the if statement, we find the condition,
if (size() == $SIZE)
But in this case size() returned 0 and SIZE is initialised with 10.
So, we come to the else part,
else $stackArray.push(i) return true end
Inserts the element 10(As i is 10) to the 0th location of the Array stackArray.

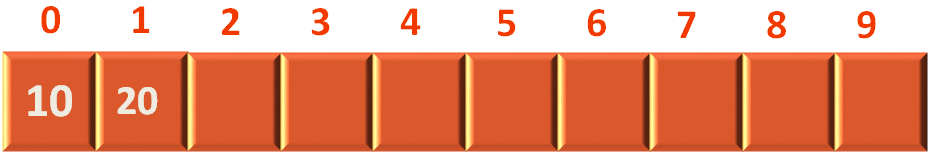
Then we try inserting the element 20 using the push(...) method again.
push(20)
Similarly, push(...) method is called,
def push(i) if (size() == $SIZE) puts "Stack Overflow" return false else $stackArray.push(i) return true end end
Now the value of i is 20.
Same way as above, the if condition checks, if the total number of elements in the array(Determined by the size() method) is equal to the size of the array.
In this case the total number of elements in the array is just one i.e. 10(And we are going to insert 20). And the size of the array is 10.
So, we come to the else part.
else $stackArray.push(i) return true end
And 20 gets inserted into the stack. And just remember 20 is the top element now.

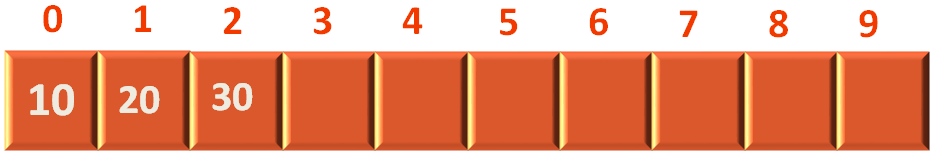
After that, we try inserting the element 30 using the push(...) method again.
push(30)
And, as usual, push(...) method is called and the element 30 is inserted into the Stack.


Next, we try getting the top element of the stack by calling the top(..) mkethod.
top()
And as we know the variable tp always points to the top element. So, if we could get the value of the variable tp, we could get the top element.
And exactly, the same thing is done in the top() method.
def top()
if (isEmpty())
puts "Stack is Empty"
return -1
else
print("The top element is ",$stackArray[$stackArray.length-1],"\n")
return $stackArray[$stackArray.length-1]
end
endIn the top() method, we check if the array is empty or not.
if (isEmpty()) puts "Stack is Empty" return -1
And if the array is not empty, we come to the else part. Where the value of the top position is returned.
return $stackArray[$stackArray.length-1]
So, return $stackArray[$stackArray.length-1] would return 30 as the top element.
Next, we try popping the elements from the Stack. One at a time.
So, when we run the first pop() method.
pop()
The pop() method is called.
def pop()
element = 0
if (isEmpty())
puts "Stack is Empty"
return -1
else
element = $stackArray.pop()
print("The element ",element," is popped out of the Stack \n")
return element
end
endSo, as usual we check if the array is empty or not.
if (isEmpty()) puts "Stack is Empty" return -1
Now, if the array is not empty, we come to the else part.
else
element = $stackArray.pop()
print("The element ",element," is popped out of the Stack \n")
return element
endThe operation is quite simple,
We take the current top element in the element variable.
element = $stackArray.pop()
i.e.
element = 30.
Then we replace the current top element with 0.

Similarly, after running pop() method twice,
pop() pop()
Both the elements 20 and 10 are popped out of the Stack.
