package main
import "fmt"
func search(arr []int, n int) int {
len := len(arr)
for i := 0; i < len; i++ {
if(arr[i] == n) {
return i
}
}
return -1
}
func main() {
arr := []int{5, 3, 6, 2, 1, 4}
n := 2 // Element to be searched.
fmt.Println("The Array elements are : ")
for _, val := range arr {
fmt.Println(val)
}
index := search(arr, n)
if(index == -1) {
fmt.Println("Element is not present in the array")
} else {
fmt.Println("The element", n, "is present at index",index)
}
}
Element is not present in the array
The above code is quite simple,
We will be searching the element 2,
n := 2 // Element to be searched.
From the array,
arr := []int{5, 3, 6, 2, 1, 4}Next, we pass the array and the element 2, to the search(...) method.
index := search(arr, n)
func search(arr []int, n int) int {
len := len(arr)
for i := 0; i < len; i++ {
if(arr[i] == n) {
return i
}
}
return -1
}We need to search the element 2 from the below array.
So, we run a for loop. Starting from the 1st location to the end of the array.
for i := 0; i < len; i++ {
if(arr[i] == n) {
return i
}
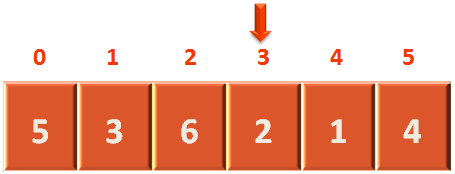
}And at every step, we keep on checking if the element is present in the array or not.
if(arr[i] == n) {
return i
}If we find the element, we return that particular location.
return i
But, what if we are searching for an element that is not present in the array?
Say, we are searching for number 8. Which is not present in the array.
In that case, we return -1.
return -1
Which states the number is not found.
Finally, the returned value is stored in the index variable.
index := search(arr, n)
And we print it using :
fmt.Println("The element", n, "is present at index",index)