import java.util.LinkedList
class Edge {
var startVertex = "";
var endVertex = "";
var value = "";
};
class EdgeListGraph {
fun insertVertex(vertices: LinkedList<String>, vertex: String) {
vertices.add(vertex);
}
fun insertEdge(edgeList: LinkedList<Edge>, vertex1: String, vertex2: String, edgeVal: String) {
var edge = Edge();
edge.startVertex = vertex1;
edge.endVertex = vertex2;
edge.value = edgeVal;
edgeList.add(edge);
}
fun printEdgeList(edgeList: LinkedList<Edge>) {
for (edge in edgeList) {
println("The Edge between ${edge.startVertex} and ${edge.endVertex} is ${edge.value}");
}
}
}
fun main(arr: Array<String>) {
var edgeListGraph = EdgeListGraph();
var vertices = LinkedList<String>();
var edgeList = LinkedList<Edge>();
// Adding vertices one by one
edgeListGraph.insertVertex(vertices, "a");
edgeListGraph.insertVertex(vertices, "b");
edgeListGraph.insertVertex(vertices, "c");
edgeListGraph.insertVertex(vertices, "d");
edgeListGraph.insertVertex(vertices, "e");
//Adding edges with values.
edgeListGraph.insertEdge(edgeList, "a", "b", "13A");
edgeListGraph.insertEdge(edgeList, "b", "a", "45C");
edgeListGraph.insertEdge(edgeList, "a", "d", "20F");
edgeListGraph.insertEdge(edgeList, "d", "e", "23E");
edgeListGraph.insertEdge(edgeList, "e", "b", "12B");
edgeListGraph.insertEdge(edgeList, "e", "c", "30F");
edgeListGraph.insertEdge(edgeList, "c", "d", "42V");
edgeListGraph.insertEdge(edgeList, "a", "c", "18C");
edgeListGraph.printEdgeList(edgeList);
}
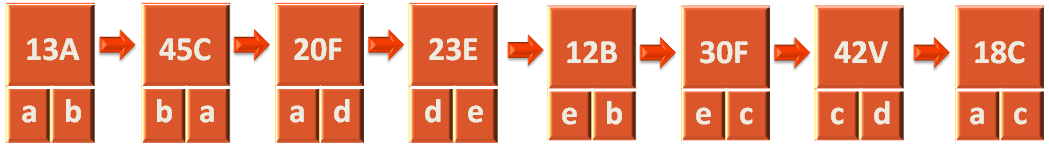
In the Edge List Data Structure, we are trying to create a Linked List of Edges.
Where each Edge will contain the start vertex, end vertex and value of the Edge.
Say for Example, the first element of the Edge Linked List i.e. Bus number 13A, travels from city/Vertex a to city/Vertex b.
So, we will be having two pointers in the first element of Edge Linked List,

And thus, we have constructed an Edge class that contains, start vertex, end vertex and value of the Edge.
class Edge {
var startVertex = "";
var endVertex = "";
var value = "";
};We have 2 methods in the Code :
The first method is quite easy to understand.
fun insertVertex(vertices: LinkedList<String>, vertex: String) {
vertices.add(vertex);
}Let us take the vertex a to understand the above method.
In the main(...) method, we have created a Linked List that would contain all the vertices :
var vertices = LinkedList<String>();
Then we have taken the vertex a and passed it to the fun insertVertex(...) method.
edgeListGraph.insertVertex(vertices, "a");
And if we see the fun insertVertex(...) method, we would see it accepts two parameters,
vertices: LinkedList<String>
and
vertex: String
It is quite self explanatory, vertices: LinkedList<String> contains the actual Linked List that contains the vertices and vertex: String contains the vertex a.
And we just have one statement in the fun insertVertex(...) method.
vertices.add(vertex);
That takes each vertex a and adds to the Linked List.
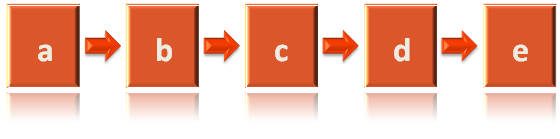
After adding all the vertices to the LinkedList, we get the below LinkedList.
Then comes the second method, that adds the edges to the Linked List(with values). Justifying the name Edge List Data Structure.
fun insertEdge(edgeList: LinkedList<Edge>, vertex1: String, vertex2: String, edgeVal: String) {
var edge = Edge();
edge.startVertex = vertex1;
edge.endVertex = vertex2;
edge.value = edgeVal;
edgeList.add(edge);
}We will take a small chunk to explain the above method.

Where the bus/edge 13A is traveling from city a to city b.
Now, let us take a look at the main(...) method.
We have created a Linked List that would store all the edges in that Linked List.
var edgeList = LinkedList<Edge>();
Next, we will pass the edgeList, the start vertex(i.e. a), end vertex(i.e. b) and the value(i.e. 13A) to the fun insertEdge(...) method.
edgeListGraph.insertEdge(edgeList, "a", "b", "13A");
Now, let us come to the contents of fun insertEdge(...) method.
In the first line, we have created the Edge object,
var edge = Edge();
Then, initialised the attributes of the Edge object with the actual values,
edge.setStartVertex(vertex1); edge.setEndVertex(vertex2); edge.setValue(edgeVal);
And the Edge object looks somewhat like this,

And add the above edge object to the Linked List,
edgeList.add(edge);
After adding all the edges to the Linked List, we get the below Linked List.