def bubble_sort(arr):
n = len(arr)
temp = 0
for i in range(n-1):
# (n-i-1) is to ignore the comparisons that is already done.
for j in range(n-i-1):
if(arr[j] > arr[j+1] ):
temp = arr[j]
arr[j] = arr[j+1]
arr[j+1] = temp
arr = [7, 4, 8, 1, 6]
bubble_sort(arr)
for i in range(len(arr)):
print(arr[i])
We are just concerned about the def bubble_sort(arr) method, where the sorting logic is defined.
We have the array
arr = [7, 4, 8, 1, 6]
Which we have passed to the bubble_sort(..) method.
In the bubble_sort(..) method, we have taken the count of the elements of the array.
n = len(arr)
Now, let us corelate this code with the explanation of Bubble Sort.
Let us take the same diagram.
And take the chunk of code and explain it.
for i in range(n-1): # (n-i-1) is to ignore the comparisons that is already done. for j in range(n-i-1): if(arr[j] > arr[j+1] ): temp = arr[j] arr[j] = arr[j+1] arr[j+1] = temp
So, the outer loop, i.e.
for i in range(n-1)
Determines the Passes. If you see the above explanation you can find the first pass,
Then comes the the inner loop, i.e.
for j in range(n-i-1)
Which determines the iterations.
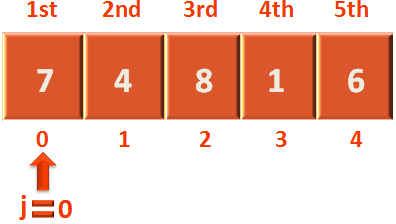
Next, comes the comparison where we compare 1st and 2nd element. And if the 1st element is greater than 2nd element we swap it.
if(arr[j] > arr[j+1] ): temp = arr[j] arr[j] = arr[j+1] arr[j+1] = temp
Where arr[j] refers to the first element i.e. 7 and arr[j+1] refers to the second element i.e. 4.
And continue in the same pattern.
If we consider the Bubble Sort Algorithm, there are two loops. Firstly, there is the for loop. And inside the for loop there is also a for loop.
The for loop executes n times(Assuming the array contains n elements).
Now, for each iteration of for loop, the nested for loop also executes approximately n times.
Which means for 1st iteration of for loop,
the nested for loop also runs n time.Similarly, for 2nd iteration of for loop,
inner for loop runs (n-1) times.Similarly, for nth iteration of for loop,
inner for loop runs 1 time.So, the running time is close to n*n or n^2.
So, in worst case the running time is O(n^2).