class Node
attr_accessor :data, :next
def initialize(data)
@data = data
@next = nil
end
end
def insertFirst(value)
node = Node.new(value)
node.next = $headNode
$headNode = node
end
def insertNode(value)
newNode = Node.new(value)
if ($headNode == nil)
$headNode = newNode
else
nextNode = $headNode
while (nextNode.next != nil)
nextNode = nextNode.next
end
nextNode.next = newNode
end
end
def insertNext(previousNode, value)
node = Node.new(value)
node.next = previousNode.next
previousNode.next = node
end
def deleteFirst()
if ($headNode == nil)
return
else
$headNode = $headNode.next
end
end
def deleteNode(position)
if ($headNode == nil)
return
end
if (position == 0)
$headNode = $headNode.next
return
end
node = $headNode
i = 1
while (node != nil and i < position)
node = node.next
i+=1
end
if (node == nil or node.next == nil)
return
end
nextTemp = node.next.next
node.next = nextTemp
end
def displayLinkedList()
node = $headNode
while (node != nil)
print(node.data,"\n")
node = node.next
end
end
$headNode = nil
insertNode("John")
insertNode("Pradeep")
insertNode("Andrew")
insertNode("Beck")
displayLinkedList()
deleteNode(1)
print("--------\n")
displayLinkedList()
We have seen that a List that is Linked to each other is a Linked List.

Now, we will learn a new term. i.e. Each item in a Linked List is called a Node.
And we can see there are four records in the above Linked List.
Say, for example, the below record is a Node.
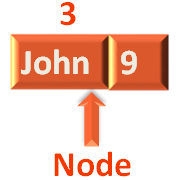
So, far we have seen, there were two records in a Node. First record is the actual data or name (In the above example i.e. John). And the second record contains the pointer to the next Node (The second record of John i.e. 9 in the above case was referring to the location of Pradeep).
Even in our Code, we have created a class called Node.
class Node attr_accessor :data, :next def initialize(data) @data = data @next = nil end end
The above class Node has two attributes :
The first attribute data is fine. It can hold the name "John" or "Pradeep". But what about the second attribute of Node type i.e. next?
Don't you think, the second attribute should have an Integer type variable?So that it can store the pointer to the next Node(i.e. 9 in the above case was referring to the location of Pradeep).
Well ! In this case we are trying something different. i.e. We will let Ruby decide the next Node.
Sounds Complex ?
Stay with me. Things will become easy with each line.
Let us go to the Node class. And as we can see, there is a constructor in the Node class.
def initialize(data) @data = data @next = nil end
So, when we create a Node object, we simply, pass the data or name(Say "John").
node1 = Node.new("John")And the constructor creates a Node object for us, with John as the actual data and next as nil. Because it is not referring to any Node object yet.

Then the next time, when we create the Node object with Pradeep,
node2 = Node.new("Pradeep")
We will make node1 object point to node2 by replacing nil with node1.

Fair enough !
Now, let us see the Code explanation for Linked List.
So, there are five methods that we have used in the Linked List :
Now, let us see the Linked List in action.
So, in the first line we insert the value John,
insertNode("John")By using the insertNode(value) method.
def insertNode(value) newNode = Node.new(value) if ($headNode == nil) $headNode = newNode else nextNode = $headNode while (nextNode.next != nil) nextNode = nextNode.next end nextNode.next = newNode end end
So, what we are doing in the insertNode(value) method is, we are creating a new Node object.
newNode = Node.new(value)
And as we have seen there is a constructor in the Node class that helps in initialising the values to the Node object.
And the below Node object is created.

Now, just remember, we have a variable Node headNode, that always points to the first element in the Linked List. And since, this is the first time we are creating the Linked List. The headNode would be initialised.
if ($headNode == nil) $headNode = newNode

And we don't go to the else part.
Similarly, we try inserting Pradeep.
insertNode("Pradeep")And the insertNode(value) method is called.
And the same way, we are creating a new Node object.
newNode = Node.new(value)
And as we have seen there is a constructor in the Node class that helps in initialising the values to the Node object.
And the below Node object is created.

Now since, headNode is not nil
if (headNode == nil)
And we come to the else part.
else nextNode = $headNode while (nextNode.next != nil) nextNode = nextNode.next end nextNode.next = newNode end
In the else part, we create a Node called newNode and initialise it with headNode.
nextNode = headNode
And Since the headNode is the Node where John resides.

Then we run a while loop to reach the end of the Linked List.
while (nextNode.next != nil) nextNode = nextNode.next end
In this case nextNode.next is equal the nil. So, we do not get into the while loop.
And we know newNode contains Pradeep.

And make the nextNode (i.e. The Node containing John) point to newNode.

So, the Linked List is formed with two elements.
Similar way, all the other elements are added to the Linked List.

The next is put as next as the linking will be decided by Ruby internally.
Now, let us see how do we delete an element from a specific location.
deleteNode(1)
So, we will be deleting the second element as the count starts from 0.

And the deleteNode(position) method is called,
def deleteNode(position) if ($headNode == nil) return end if (position == 0) $headNode = $headNode.next return end node = $headNode i = 1 while (node != nil and i < position) node = node.next i+=1 end if (node == nil or node.next == nil) return end nextTemp = node.next.next node.next = nextTemp end
The first if statement checks, if the headNode is nil or not. i.e. If the headNode is nil, then there are no elements in the Linked List. And we stop the execution.
if ($headNode == nil) return end
The next if statement checks, if we are asking to remove the first element.
$headNode = $headNode.next return end
We initialise the headNode with headNode.next i.e. nil. And the Linked List becomes empty.
If the above two if statement are not satisfied then we come to the n ext line.
node = headNode
Where we declare a Node named node and initialise with the headNode Node.
Now since, headNode contains the details of John. node is initialised with John.

Then we run a for loop until we reach a position just before the node that is asked to be deleted.
In this case the second element is asked to be deleted(i.e. 1).
i = 1 while (node != nil and i < position) node = node.next i+=1 end
So, we exit the for loop, when we are at the second node.
Then we do a check to see if the first node is nil or is it not pointing to any element?
if (node == nil or node.next == nil) return end
If so we stop the execution.
Then we create a Node called next. And initialise the Node with it that contains Andrew.
nextTemp = node.next.next

And finally, we make the Node of John point to the Node that contains Andrew.
node.next = nextTemp
And we get the Linked List that doesn't have the the second Node. i.e. The node that contained Pradeep.
