#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
const int V = 5;;
class AdjacencyMatrixGraph {
public :
void insertEdge(bool adjacentMatrix[][V], int i, int j) {
adjacentMatrix[i][j] = true;
}
void removeEdge(bool adjacentMatrix[][V], int i, int j) {
adjacentMatrix[i][j] = false;
}
void printAdjacencyMatrix(bool adjacentMatrix[][V]) {
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < V; j++) {
int val = adjacentMatrix[i][j]?1:0;
cout << "| " << val << " |";
}
cout << endl;
}
}
};
int main() {
AdjacencyMatrixGraph adjacencyMatrixGraph;
bool adjacentMatrix[V][V];
//Insert Edges
adjacencyMatrixGraph.insertEdge(adjacentMatrix, 0, 1);
adjacencyMatrixGraph.insertEdge(adjacentMatrix, 0, 2);
adjacencyMatrixGraph.insertEdge(adjacentMatrix, 0, 3);
adjacencyMatrixGraph.insertEdge(adjacentMatrix, 1, 0);
adjacencyMatrixGraph.insertEdge(adjacentMatrix, 1 ,4);
adjacencyMatrixGraph.insertEdge(adjacentMatrix, 2, 0);
adjacencyMatrixGraph.insertEdge(adjacentMatrix, 2, 3);
adjacencyMatrixGraph.insertEdge(adjacentMatrix, 2, 4);
adjacencyMatrixGraph.insertEdge(adjacentMatrix, 3, 0);
adjacencyMatrixGraph.insertEdge(adjacentMatrix, 3 ,2);
adjacencyMatrixGraph.insertEdge(adjacentMatrix, 3, 4);
adjacencyMatrixGraph.insertEdge(adjacentMatrix, 4, 3);
adjacencyMatrixGraph.insertEdge(adjacentMatrix, 4, 2);
adjacencyMatrixGraph.insertEdge(adjacentMatrix, 4, 1);
cout << "+------------------------------------------------------------+" << endl;
adjacencyMatrixGraph.printAdjacencyMatrix(adjacentMatrix);
cout << "+------------------------------------------------------------+";
}
+----------------------------------------------------------+ | 0 || 1 || 1 || 1 || 0 | | 1 || 0 || 0 || 0 || 1 | | 1 || 0 || 0 || 1 || 1 | | 1 || 0 || 1 || 0 || 1 | | 0 || 1 || 1 || 1 || 0 | +----------------------------------------------------------+
The code for Adjacency Matrix is quite simple.
There are two important methods defined above :
As the name of the method suggests insertEdge(...), is used to add an Edge to the Adjacency Matrix.
void insertEdge(bool adjacentMatrix[][V], int i, int j) {
adjacentMatrix[i][j] = true;
}So, the actual adjacency matrix, we are going to create, looks like the below structure,
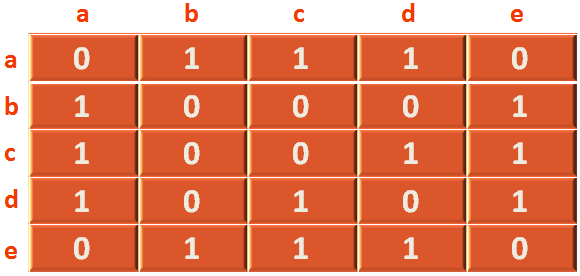
Now, if we look at the main(...) method. We create a 2D array, that holds either true or false.
bool adjacentMatrix[V][V];
Where, V is a constant,
const int V = 5;
So, the above line creates a 2D array with 5 rows and 5 columns that initially contains false.
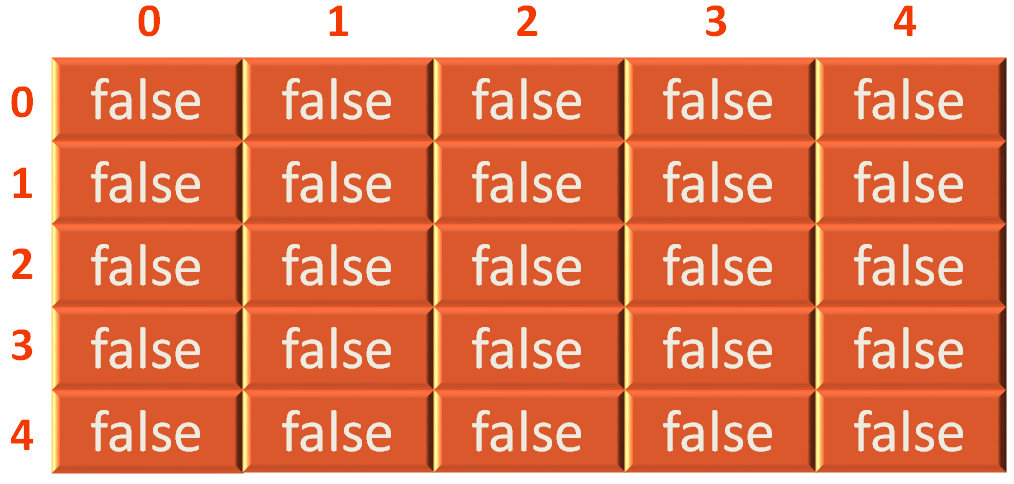
Now, all we need to do is, wherever we want to insert an edge. We will mark it with value true.
Say, for example :
There is an edge in [0][1] (As mentioned in the adjacency matrix above).
All we are doing is, calling the void insertEdge(...) method,
adjacencyMatrixGraph.insertEdge(adjacentMatrix, 0, 1);
and passing 0 and 1 as parameters.
And in the void insertEdge(...) method, we have the below line,
adjacentMatrix[i][j] = true;
Now, since value of i = 0 and j = 1,
adjacentMatrix[0][1] = true;
And adjacentMatrix[0][1] is marked to true.
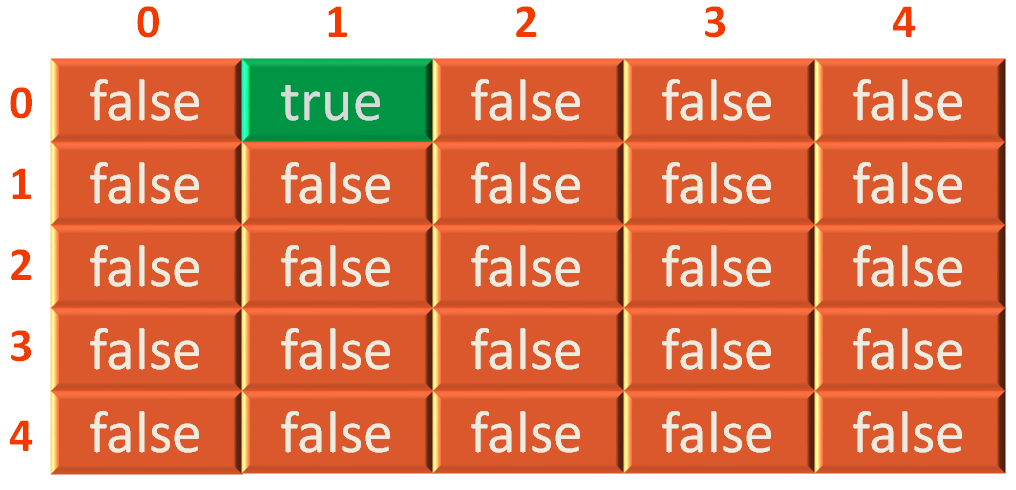
In other words, we have inserted an edge in adjacentMatrix[0][1] above.
Similarly, we insert the edges one by one, calling the void insertEdge(...) method.
adjacencyMatrixGraph.insertEdge(adjacentMatrix, 0, 2); adjacencyMatrixGraph.insertEdge(adjacentMatrix, 0, 3); ... ... ...
Even, to delete an Edge, we follow the same steps.
As we know, there is an Edge in [0][2]. To remove it, all we need to do is call,
adjacencyMatrixGraph.removeEdge(adjacentMatrix, 0, 2);
And mark that particular location to false.
void removeEdge(bool adjacentMatrix[][V], int i, int j) {
adjacentMatrix[i][j] = false;
}And the Edge is deleted.