package main
import "fmt"
var adjacentMatrix [][]bool
func insertEdge(i int, j int) {
adjacentMatrix[i][j] = true
}
func removeEdge(i int, j int) {
adjacentMatrix[i][j] = false
}
func printAdjacencyMatrix() {
for i := 0; i < len(adjacentMatrix); i++ {
for j := 0; j < len(adjacentMatrix[i]); j++ {
var val int
if (adjacentMatrix[i][j]) {
val = 1
} else {
val = 0
}
fmt.Print("| ",val," |")
}
fmt.Println()
}
}
func main() {
V := 5
adjacentMatrix = make([][]bool, V)
for i := range adjacentMatrix {
adjacentMatrix[i] = make([]bool, V)
}
//Insert Edges
insertEdge(0, 1)
insertEdge(0, 2)
insertEdge(0, 3)
insertEdge(1, 0)
insertEdge(1 ,4)
insertEdge(2, 0)
insertEdge(2, 3)
insertEdge(2, 4)
insertEdge(3, 0)
insertEdge(3 ,2)
insertEdge(3, 4)
insertEdge(4, 3)
insertEdge(4, 2)
insertEdge(4, 1)
fmt.Println("+----------------------------------------------------------+")
printAdjacencyMatrix()
fmt.Println("+----------------------------------------------------------+")
}
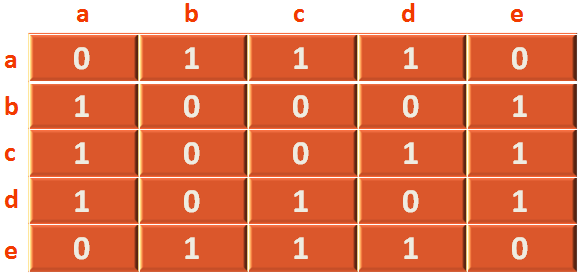
+----------------------------------------------------------+ | 0 || 1 || 1 || 1 || 0 | | 1 || 0 || 0 || 0 || 1 | | 1 || 0 || 0 || 1 || 1 | | 1 || 0 || 1 || 0 || 1 | | 0 || 1 || 1 || 1 || 0 | +----------------------------------------------------------+
The code for Adjacency Matrix is quite simple.
There are two important methods defined above :
As the name of the method suggests insertEdge(...), is used to add an Edge to the Adjacency Matrix.
func insertEdge(i int, j int) {
adjacentMatrix[i][j] = true
}So, the actual adjacency matrix, we are going to create, looks like the below structure,
Now, if we look at the main(...) method. We create a 2D array, that holds either true or false.
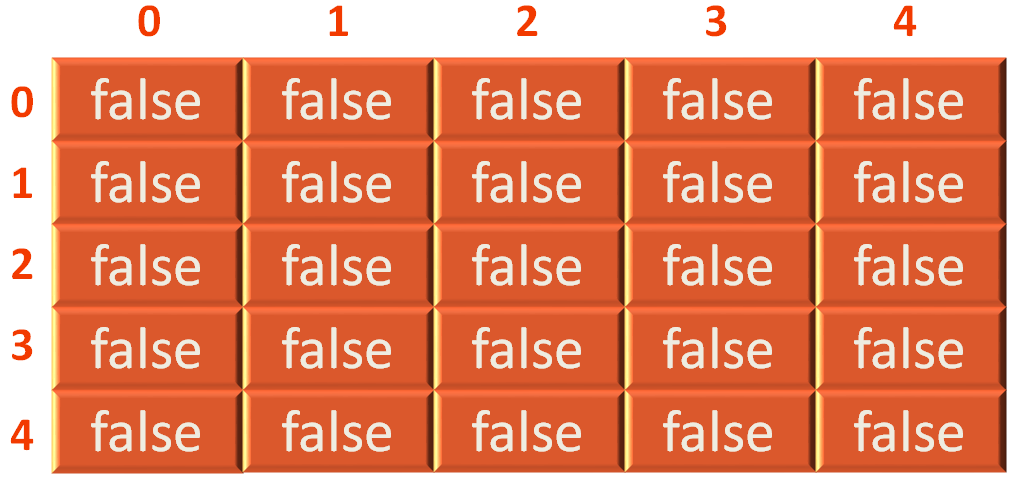
And initially we initialise the 2D array with false value by default.
V := 5
adjacentMatrix = make([][]bool, V)
for i := range adjacentMatrix {
adjacentMatrix[i] = make([]bool, V)
}So, the above line creates a 2D array with 5 rows and 5 columns that initially contains false.
Now, all we need to do is, wherever we want to insert an edge. We will mark it with value true.
Say, for example :
There is an edge in [0][1] (As mentioned in the adjacency matrix above).
All we are doing is, calling the func insertEdge(i int, j int) method,
insertEdge(0, 1)
and passing 0 and 1 as parameters.
And in the func insertEdge(i int, j int) method, we have the below line,
adjacentMatrix[i][j] = true
Now, since value of i = 0 and j = 1,
adjacentMatrix[0][1] = true
And adjacentMatrix[0][1] is marked to true.
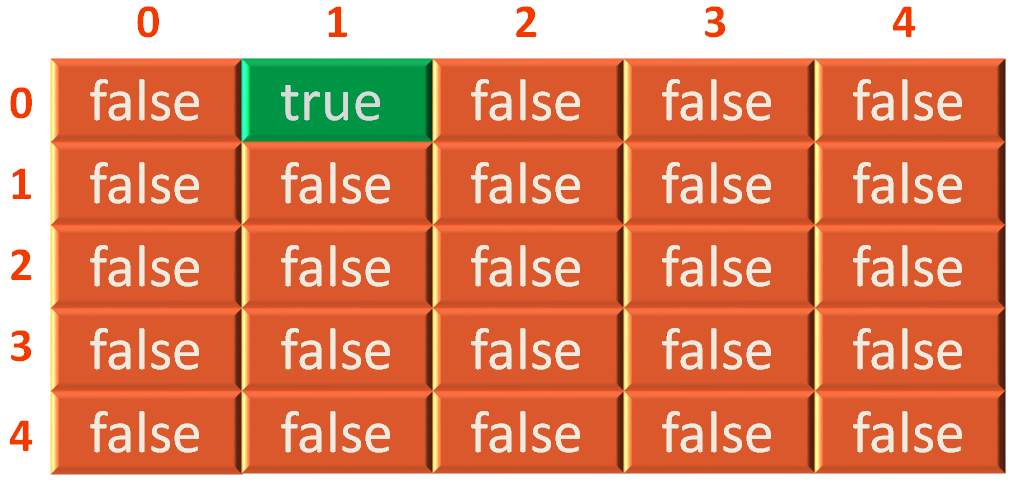
In other words, we have inserted an edge in adjacentMatrix[0][1] above.
Similarly, we insert the edges one by one, calling the void insertEdge(...) method.
insertEdge(0, 2) insertEdge(0, 3) ... ... ...
Even, to delete an Edge, we follow the same steps.
As we know, there is an Edge in [0][2]. To remove it, all we need to do is call,
removeEdge(0, 2)
And mark that particular location to false.
func removeEdge(i int, j int) {
adjacentMatrix[i][j] = false
}And the Edge is deleted.